Determine the next phase in a lunar cycle
Help Questions
Earth Science › Determine the next phase in a lunar cycle
If the moon were more than twice as far away from Earth as it is now, how would the moon cycle change?
It would occur in the same order but more slowly
It would occur in a different order.
It would occur in the same order more quickly.
It would occur in a different order and more slowly.
Explanation
The answer is "It would occur in the same order but more slowly." The moon generates no light of its own. It can be seen because it reflects the light from the sun. Though it does not always appear so from Earth, half of the moon is always illuminated, and the other half is always in darkness. However, as the moon orbits the Earth, its position in relation to the Earth and the sun changes, and more or less of the illuminated side may be seen from Earth. These different views are called “phases of the moon.”
- New moon: When the moon is directly between the sun and the Earth, the side of the moon facing the Earth is in darkness; hence, it is not visible in the sky. The light from the sun reflects off the moon back toward the sun; not toward Earth. This phase is called the new moon.
- Waxing crescent: As the moon continues to move in its orbit around the Earth, a sliver of the illuminated side of the moon becomes visible. This phase is called the waxing crescent. (To wax is to increase.)
- First quarter: When the moon has completed one quarter of its orbit around the Earth, it makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. One half of the moon is still illuminated by the sun, and the other half is still in darkness. However, from the Earth, the moon now appears to be a half circle. This phase is called the first quarter.
- Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues in its orbit, the portion of the illuminated side of the moon visible from the Earth continues to increase. When the moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon, it is called a gibbous moon. At this point in its orbit, the moon appears to be growing, so this phase is called a waxing gibbous.
- Full moon: When the moon has completed one half of its orbit around the Earth, it is almost in a straight line with the Earth and the sun. The entire side of the moon that faces Earth is illuminated. This phase is called a full moon.
- Waning gibbous: The darkened side of the moon begins to reappear to observers after the full moon. This phase is called a waning gibbous. The moon is described as waning when it appears to grow smaller. (To wane is to decrease.)
- Third quarter: When the moon has completed three‐quarters of its orbit around the Earth, it again makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. This phase is called the third quarter or last quarter.
- Waning crescent: As the moon’s orbit continues, the moon appears as a crescent shape once again. Since it appears to grow smaller, this phase is called a waning crescent.
- New Moon again: The darkened area continues to grow larger until no portion of the illuminated moon can be seen. The moon has returned to the new moon phase.

What best describes the phase of the moon in the blank designated by the #1?
Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues in its orbit, the portion of the illuminated side of the moon visible from the Earth continues to increase. When the moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon, it is called a gibbous moon. At this point in its orbit, the moon appears to be growing, so this phase is called a waxing gibbous.
Waxing gibbous: The darkened side of the moon begins to reappear to observers after the full moon. This phase is called a waxing gibbous. The moon is described as waxing when it appears to grow smaller. (To wax is to decrease.)
Waxing gibbous: As the moon’s orbit continues, the moon appears as a crescent shape once again. Since it appears to grow smaller, this phase is called a waxing gibbous.
Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues to move in its orbit around the Earth, a sliver of the illuminated side of the moon becomes visible. This phase is called the waxing gibbous. (To wax is to increase.)
Explanation
The answer is: "Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues in its orbit, the portion of the illuminated side of the moon visible from the Earth continues to increase. When the moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon, it is called a gibbous moon. At this point in its orbit, the moon appears to be growing, so this phase is called a waxing gibbous."
The moon generates no light of its own. It can be seen because it reflects the light from the sun. Though it does not always appear so from Earth, half of the moon is always illuminated, and the other half is always in darkness. However, as the moon orbits the Earth, its position in relation to the Earth and the sun changes, and more or less of the illuminated side may be seen from Earth. These different views are called “phases of the moon.”
- New moon: When the moon is directly between the sun and the Earth, the side of the moon facing the Earth is in darkness; hence, it is not visible in the sky. The light from the sun reflects off the moon back toward the sun; not toward Earth. This phase is called the new moon.
- Waxing crescent: As the moon continues to move in its orbit around the Earth, a sliver of the illuminated side of the moon becomes visible. This phase is called the waxing crescent. (To wax is to increase.)
- First quarter: When the moon has completed one quarter of its orbit around the Earth, it makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. One half of the moon is still illuminated by the sun, and the other half is still in darkness. However, from the Earth, the moon now appears to be a half circle. This phase is called the first quarter.
- Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues in its orbit, the portion of the illuminated side of the moon visible from the Earth continues to increase. When the moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon, it is called a gibbous moon. At this point in its orbit, the moon appears to be growing, so this phase is called a waxing gibbous.
- Full moon: When the moon has completed one half of its orbit around the Earth, it is almost in a straight line with the Earth and the sun. The entire side of the moon that faces Earth is illuminated. This phase is called a full moon.
- Waning gibbous: The darkened side of the moon begins to reappear to observers after the full moon. This phase is called a waning gibbous. The moon is described as waning when it appears to grow smaller. (To wane is to decrease.)
- Third quarter: When the moon has completed three‐quarters of its orbit around the Earth, it again makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. This phase is called the third quarter or last quarter.
- Waning crescent: As the moon’s orbit continues, the moon appears as a crescent shape once again. Since it appears to grow smaller, this phase is called a waning crescent.
New Moon again: The darkened area continues to grow larger until no portion of the illuminated moon can be seen. The moon has returned to the new moon phase.
What is the name of the moon phase when it is directly between the sun and the Earth and the side of the moon facing the Earth is in darkness? (In this phase, the light from the sun reflects off the moon back toward the sun; not toward Earth. Hence, it is not visible in the sky.)
new moon
full moon
waxing crescent
waning gibbous
Explanation
The answer is "new moon."
The moon generates no light of its own. It can be seen because it reflects the light from the sun. Though it does not always appear so from Earth, half of the moon is always illuminated, and the other half is always in darkness. However, as the moon orbits the Earth, its position in relation to the Earth and the sun changes, and more or less of the illuminated side may be seen from Earth. These different views are called “phases of the moon.”
- New moon: When the moon is directly between the sun and the Earth, the side of the moon facing the Earth is in darkness; hence, it is not visible in the sky. The light from the sun reflects off the moon back toward the sun; not toward Earth. This phase is called the new moon.
- Waxing crescent: As the moon continues to move in its orbit around the Earth, a sliver of the illuminated side of the moon becomes visible. This phase is called the waxing crescent. (To wax is to increase.)
- First quarter: When the moon has completed one quarter of its orbit around the Earth, it makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. One half of the moon is still illuminated by the sun, and the other half is still in darkness. However, from the Earth, the moon now appears to be a half circle. This phase is called the first quarter.
- Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues in its orbit, the portion of the illuminated side of the moon visible from the Earth continues to increase. When the moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon, it is called a gibbous moon. At this point in its orbit, the moon appears to be growing, so this phase is called a waxing gibbous.
- Full moon: When the moon has completed one half of its orbit around the Earth, it is almost in a straight line with the Earth and the sun. The entire side of the moon that faces Earth is illuminated. This phase is called a full moon.
- Waning gibbous: The darkened side of the moon begins to reappear to observers after the full moon. This phase is called a waning gibbous. The moon is described as waning when it appears to grow smaller. (To wane is to decrease.)
- Third quarter: When the moon has completed three‐quarters of its orbit around the Earth, it again makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. This phase is called the third quarter or last quarter.
- Waning crescent: As the moon’s orbit continues, the moon appears as a crescent shape once again. Since it appears to grow smaller, this phase is called a waning crescent.
New Moon again: The darkened area continues to grow larger until no portion of the illuminated moon can be seen. The moon has returned to the new moon phase.
If a full moon occurs on the date March 23rd, which of the following dates would be closest to the next full moon?
April 23rd
March 30th
April 9th
June 23rd
Explanation
The answer is "April 23rd" because a lunar cycle is one month long.
The moon generates no light of its own. It can be seen because it reflects the light from the sun. Though it does not always appear so from Earth, half of the moon is always illuminated, and the other half is always in darkness. However, as the moon orbits the Earth, its position in relation to the Earth and the sun changes, and more or less of the illuminated side may be seen from Earth. These different views are called “phases of the moon.”
- New moon: When the moon is directly between the sun and the Earth, the side of the moon facing the Earth is in darkness; hence, it is not visible in the sky. The light from the sun reflects off the moon back toward the sun; not toward Earth. This phase is called the new moon.
- Waxing crescent: As the moon continues to move in its orbit around the Earth, a sliver of the illuminated side of the moon becomes visible. This phase is called the waxing crescent. (To wax is to increase.)
- First quarter: When the moon has completed one quarter of its orbit around the Earth, it makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. One half of the moon is still illuminated by the sun, and the other half is still in darkness. However, from the Earth, the moon now appears to be a half circle. This phase is called the first quarter.
- Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues in its orbit, the portion of the illuminated side of the moon visible from the Earth continues to increase. When the moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon, it is called a gibbous moon. At this point in its orbit, the moon appears to be growing, so this phase is called a waxing gibbous.
- Full moon: When the moon has completed one half of its orbit around the Earth, it is almost in a straight line with the Earth and the sun. The entire side of the moon that faces Earth is illuminated. This phase is called a full moon.
- Waning gibbous: The darkened side of the moon begins to reappear to observers after the full moon. This phase is called a waning gibbous. The moon is described as waning when it appears to grow smaller. (To wane is to decrease.)
- Third quarter: When the moon has completed three‐quarters of its orbit around the Earth, it again makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. This phase is called the third quarter or last quarter.
- Waning crescent: As the moon’s orbit continues, the moon appears as a crescent shape once again. Since it appears to grow smaller, this phase is called a waning crescent.
- New Moon again: The darkened area continues to grow larger until no portion of the illuminated moon can be seen. The moon has returned to the new moon phase.
Which of the following images represents the phase of the moon that follows a full moon?


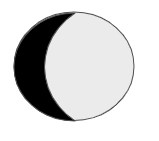

Explanation
The moon generates no light of its own. It can be seen because it reflects the light from the sun. Though it does not always appear so from Earth, half of the moon is always illuminated, and the other half is always in darkness. However, as the moon orbits the Earth, its position in relation to the Earth and the sun changes, and more or less of the illuminated side may be seen from Earth. These different views are called “phases of the moon.”
- New moon: When the moon is directly between the sun and the Earth, the side of the moon facing the Earth is in darkness; hence, it is not visible in the sky. The light from the sun reflects off the moon back toward the sun; not toward Earth. This phase is called the new moon.
- Waxing crescent: As the moon continues to move in its orbit around the Earth, a sliver of the illuminated side of the moon becomes visible. This phase is called the waxing crescent. (To wax is to increase.)
- First quarter: When the moon has completed one quarter of its orbit around the Earth, it makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. One half of the moon is still illuminated by the sun, and the other half is still in darkness. However, from the Earth, the moon now appears to be a half circle. This phase is called the first quarter.
- Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues in its orbit, the portion of the illuminated side of the moon visible from the Earth continues to increase. When the moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon, it is called a gibbous moon. At this point in its orbit, the moon appears to be growing, so this phase is called a waxing gibbous.
- Full moon: When the moon has completed one half of its orbit around the Earth, it is almost in a straight line with the Earth and the sun. The entire side of the moon that faces Earth is illuminated. This phase is called a full moon.
- Waning gibbous: The darkened side of the moon begins to reappear to observers after the full moon. This phase is called a waning gibbous. The moon is described as waning when it appears to grow smaller. (To wane is to decrease.)
- Third quarter: When the moon has completed three‐quarters of its orbit around the Earth, it again makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. This phase is called the third quarter or last quarter.
- Waning crescent: As the moon’s orbit continues, the moon appears as a crescent shape once again. Since it appears to grow smaller, this phase is called a waning crescent.
- New Moon again: The darkened area continues to grow larger until no portion of the illuminated moon can be seen. The moon has returned to the new moon phase.
Which of the following images best represents a waxing gibbous?




Explanation
The moon generates no light of its own. It can be seen because it reflects the light from the sun. Though it does not always appear so from Earth, half of the moon is always illuminated, and the other half is always in darkness. However, as the moon orbits the Earth, its position in relation to the Earth and the sun changes, and more or less of the illuminated side may be seen from Earth. These different views are called “phases of the moon.”
- New moon: When the moon is directly between the sun and the Earth, the side of the moon facing the Earth is in darkness; hence, it is not visible in the sky. The light from the sun reflects off the moon back toward the sun; not toward Earth. This phase is called the new moon.
- Waxing crescent: As the moon continues to move in its orbit around the Earth, a sliver of the illuminated side of the moon becomes visible. This phase is called the waxing crescent. (To wax is to increase.)
- First quarter: When the moon has completed one quarter of its orbit around the Earth, it makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. One half of the moon is still illuminated by the sun, and the other half is still in darkness. However, from the Earth, the moon now appears to be a half circle. This phase is called the first quarter.
- Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues in its orbit, the portion of the illuminated side of the moon visible from the Earth continues to increase. When the moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon, it is called a gibbous moon. At this point in its orbit, the moon appears to be growing, so this phase is called a waxing gibbous.
- Full moon: When the moon has completed one half of its orbit around the Earth, it is almost in a straight line with the Earth and the sun. The entire side of the moon that faces Earth is illuminated. This phase is called a full moon.
- Waning gibbous: The darkened side of the moon begins to reappear to observers after the full moon. This phase is called a waning gibbous. The moon is described as waning when it appears to grow smaller. (To wane is to decrease.)
- Third quarter: When the moon has completed three‐quarters of its orbit around the Earth, it again makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. This phase is called the third quarter or last quarter.
- Waning crescent: As the moon’s orbit continues, the moon appears as a crescent shape once again. Since it appears to grow smaller, this phase is called a waning crescent.
- New Moon again: The darkened area continues to grow larger until no portion of the illuminated moon can be seen. The moon has returned to the new moon phase.
Why are we able to see the moon at night?
it reflects the sun's light
it reflect's the Earth's light
it produces his own light
it reflect's light from distant stars
Explanation
The moon generates no light of its own. It can be seen because it reflects the light from the sun. Though it does not always appear so from Earth, half of the moon is always illuminated, and the other half is always in darkness. However, as the moon orbits the Earth, its position in relation to the Earth and the sun changes, and more or less of the illuminated side may be seen from Earth. These different views are called “phases of the moon.”
-
New moon: When the moon is directly between the sun and the Earth, the side of the moon facing the Earth is in darkness; hence, it is not visible in the sky. The light from the sun reflects off the moon back toward the sun; not toward Earth. This phase is called the new moon.
-
Waxing crescent: As the moon continues to move in its orbit around the Earth, a sliver of the illuminated side of the moon becomes visible. This phase is called the waxing crescent. (To wax is to increase.)
-
First quarter: When the moon has completed one quarter of its orbit around the Earth, it makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. One half of the moon is still illuminated by the sun, and the other half is still in darkness. However, from the Earth, the moon now appears to be a half circle. This phase is called the first quarter.
-
Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues in its orbit, the portion of the illuminated side of the moon visible from the Earth continues to increase. When the moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon, it is called a gibbous moon. At this point in its orbit, the moon appears to be growing, so this phase is called a waxing gibbous.
-
Full moon: When the moon has completed one half of its orbit around the Earth, it is almost in a straight line with the Earth and the sun. The entire side of the moon that faces Earth is illuminated. This phase is called a full moon.
-
Waning gibbous: The darkened side of the moon begins to reappear to observers after the full moon. This phase is called a waning gibbous. The moon is described as waning when it appears to grow smaller. (To wane is to decrease.)
-
Third quarter: When the moon has completed three‐quarters of its orbit around the Earth, it again makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. This phase is called the third quarter or last quarter.
-
Waning crescent: As the moon’s orbit continues, the moon appears as a crescent shape once again. Since it appears to grow smaller, this phase is called a waning crescent.
-
New Moon again: The darkened area continues to grow larger until no portion of the illuminated moon can be seen. The moon has returned to the new moon phase.
Which of the following images best represents a waning gibbous?




Explanation
The moon generates no light of its own. It can be seen because it reflects the light from the sun. Though it does not always appear so from Earth, half of the moon is always illuminated, and the other half is always in darkness. However, as the moon orbits the Earth, its position in relation to the Earth and the sun changes, and more or less of the illuminated side may be seen from Earth. These different views are called “phases of the moon.”
- New moon: When the moon is directly between the sun and the Earth, the side of the moon facing the Earth is in darkness; hence, it is not visible in the sky. The light from the sun reflects off the moon back toward the sun; not toward Earth. This phase is called the new moon.
- Waxing crescent: As the moon continues to move in its orbit around the Earth, a sliver of the illuminated side of the moon becomes visible. This phase is called the waxing crescent. (To wax is to increase.)
- First quarter: When the moon has completed one quarter of its orbit around the Earth, it makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. One half of the moon is still illuminated by the sun, and the other half is still in darkness. However, from the Earth, the moon now appears to be a half circle. This phase is called the first quarter.
- Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues in its orbit, the portion of the illuminated side of the moon visible from the Earth continues to increase. When the moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon, it is called a gibbous moon. At this point in its orbit, the moon appears to be growing, so this phase is called a waxing gibbous.
- Full moon: When the moon has completed one half of its orbit around the Earth, it is almost in a straight line with the Earth and the sun. The entire side of the moon that faces Earth is illuminated. This phase is called a full moon.
- Waning gibbous: The darkened side of the moon begins to reappear to observers after the full moon. This phase is called a waning gibbous. The moon is described as waning when it appears to grow smaller. (To wane is to decrease.)
- Third quarter: When the moon has completed three‐quarters of its orbit around the Earth, it again makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. This phase is called the third quarter or last quarter.
- Waning crescent: As the moon’s orbit continues, the moon appears as a crescent shape once again. Since it appears to grow smaller, this phase is called a waning crescent.
- New Moon again: The darkened area continues to grow larger until no portion of the illuminated moon can be seen. The moon has returned to the new moon phase.
How long is the lunar cycle?
1 month
1 year
1 day
1/4 of a year
Explanation
The moon generates no light of its own. It can be seen because it reflects the light from the sun. Though it does not always appear so from Earth, half of the moon is always illuminated, and the other half is always in darkness. However, as the moon orbits the Earth, its position in relation to the Earth and the sun changes, and more or less of the illuminated side may be seen from Earth. These different views are called “phases of the moon.”
- New moon: When the moon is directly between the sun and the Earth, the side of the moon facing the Earth is in darkness; hence, it is not visible in the sky. The light from the sun reflects off the moon back toward the sun; not toward Earth. This phase is called the new moon.
- Waxing crescent: As the moon continues to move in its orbit around the Earth, a sliver of the illuminated side of the moon becomes visible. This phase is called the waxing crescent. (To wax is to increase.)
- First quarter: When the moon has completed one quarter of its orbit around the Earth, it makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. One half of the moon is still illuminated by the sun, and the other half is still in darkness. However, from the Earth, the moon now appears to be a half circle. This phase is called the first quarter.
- Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues in its orbit, the portion of the illuminated side of the moon visible from the Earth continues to increase. When the moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon, it is called a gibbous moon. At this point in its orbit, the moon appears to be growing, so this phase is called a waxing gibbous.
- Full moon: When the moon has completed one half of its orbit around the Earth, it is almost in a straight line with the Earth and the sun. The entire side of the moon that faces Earth is illuminated. This phase is called a full moon.
- Waning gibbous: The darkened side of the moon begins to reappear to observers after the full moon. This phase is called a waning gibbous. The moon is described as waning when it appears to grow smaller. (To wane is to decrease.)
- Third quarter: When the moon has completed three‐quarters of its orbit around the Earth, it again makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. This phase is called the third quarter or last quarter.
- Waning crescent: As the moon’s orbit continues, the moon appears as a crescent shape once again. Since it appears to grow smaller, this phase is called a waning crescent.
New Moon again: The darkened area continues to grow larger until no portion of the illuminated moon can be seen. The moon has returned to the new moon phase.

Which of the following best describes what is happening in the blank section of the lunar cycle above?
all of these
It is the waning gibbous phase of the lunar cycle.
The moon is waning because the lighted part is growing smaller.
The moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon so it is a gibbous.
Explanation
The answer is all of these.
The moon generates no light of its own. It can be seen because it reflects the light from the sun. Though it does not always appear so from Earth, half of the moon is always illuminated, and the other half is always in darkness. However, as the moon orbits the Earth, its position in relation to the Earth and the sun changes, and more or less of the illuminated side may be seen from Earth. These different views are called “phases of the moon.”
- New moon: When the moon is directly between the sun and the Earth, the side of the moon facing the Earth is in darkness; hence, it is not visible in the sky. The light from the sun reflects off the moon back toward the sun; not toward Earth. This phase is called the new moon.
- Waxing crescent: As the moon continues to move in its orbit around the Earth, a sliver of the illuminated side of the moon becomes visible. This phase is called the waxing crescent. (To wax is to increase.)
- First quarter: When the moon has completed one quarter of its orbit around the Earth, it makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. One half of the moon is still illuminated by the sun, and the other half is still in darkness. However, from the Earth, the moon now appears to be a half circle. This phase is called the first quarter.
- Waxing gibbous: As the moon continues in its orbit, the portion of the illuminated side of the moon visible from the Earth continues to increase. When the moon appears to be more than a half moon but less than a full moon, it is called a gibbous moon. At this point in its orbit, the moon appears to be growing, so this phase is called a waxing gibbous.
- Full moon: When the moon has completed one half of its orbit around the Earth, it is almost in a straight line with the Earth and the sun. The entire side of the moon that faces Earth is illuminated. This phase is called a full moon.
- Waning gibbous: The darkened side of the moon begins to reappear to observers after the full moon. This phase is called a waning gibbous. The moon is described as waning when it appears to grow smaller. (To wane is to decrease.)
- Third quarter: When the moon has completed three‐quarters of its orbit around the Earth, it again makes a right angle with the Earth and the sun. This phase is called the third quarter or last quarter.
- Waning crescent: As the moon’s orbit continues, the moon appears as a crescent shape once again. Since it appears to grow smaller, this phase is called a waning crescent.
New Moon again: The darkened area continues to grow larger until no portion of the illuminated moon can be seen. The moon has returned to the new moon phase.