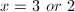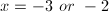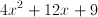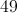All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Quadratic Equations And Inequalities
FOIL 
Remember that FOIL stands for First Outer Inner Last.
For this problem that would give us:
Simplify.
Example Question #2 : Quadratic Equations And Inequalities
FOIL 
Remember that FOIL stands for First Outer Inner Last.
For this problem that would give us:
Simplify:
Example Question #1 : Quadratic Equations And Inequalities
Solve the equation for 
Cross multiply.
Set the equation equal to zero.
Factor to find the roots of the polynomial.

Example Question #1 : Foil
Evaluate
In order to evaluate 
Multiply terms by way of FOIL method.
Now multiply and simplify.
Example Question #41 : Intermediate Single Variable Algebra
Expand 
To solve our given equation, we need to use FOIL (First, Outer, Inner, Last).
Combine like terms.
Example Question #42 : Intermediate Single Variable Algebra
FOIL 
Remember FOIL stands for First Outer Inner Last.
Combine like terms to get 
Example Question #1 : Understanding The Discriminant
Use the discriminant to determine the nature of the roots:






The formula for the discriminant is:
Since the discriminant is positive and not a perfect square, there are 
Example Question #2 : Understanding The Discriminant
Use the discriminant to determine the nature of the roots:






The formula for the discriminant is:
Since the discriminant is negative, there are 
Example Question #1 : Understanding The Discriminant
Use the discriminant to determine the nature of the roots:
Cannot be determined





The formula for the discriminant is:

Since the discriminant is negative, there are 
Example Question #1 : Discriminants
Given 
In general, the discriminant is 
In this particual case 
Plug in these three values and simplify:
Certified Tutor
All High School Math Resources