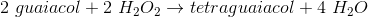Create an account to track your scores
and create your own practice tests:
Test: ACT Science
Chemical reactions involve two main components, reactants and products. The reactants, often referred to as substrates, interact with each other and rearrange in order to be converted into products. The speeds of these reactions are often defined by substrate concentration and the presence of enzymes. Enzymes are referred to as catalysts. Peroxidase is traditionally derived from turnips; however, it is commonly found in many plant and animal cells. This enzyme helps plant cells by removing hydrogen peroxide from cells in the form of tetraguaiacol.
Study 1
A scientist wants to observe the production of tetraguaiacol by observing a reaction between hydrogen peroxide and guaiacol. The product of this reaction is orange-brown in color. The scientist measures the intensity of color in each sample using a spectrophotometer. In the control experiment, the scientist mixed the substrates together and measured the reaction rate. In the test experiment, a peroxidase enzyme was added to a new set of substrates and rate of reaction was measured. The results of these reactions are plotted in Figure 1.

Figure 1
Study 2
A research team decides to study the effects of the peroxidase facilitated reaction in the presence of heat. Reaction rates are known to speed up when heat is applied; however, at a certain point enzymes, such as peroxidase, denature and the reaction slows. The scientists perform a control trial at room temperature 




Figure 2
| 1. | According to the passage, guiacol rids cells of hydrogen peroxide by producing what two products? |
Tetraguaicol and hydrogen gas
Four guaiacols, water, and hydrogen gas
Tetraguaiacol and water
Hydrogen peroxide and water
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor