Create an account to track your scores
and create your own practice tests:
Test: ACT Science
The Ideal Gas Law is as follows:






A class of students began studying the Ideal Gas Law and how the Pressure and the Volume relate to one another. They took 20 moles of a sample gas and kept the room at a temperature of 300 Kelvin. They then used different sized containers of the gas to limit and expand the volume. At each different volume, they measure the pressure of the gas on its container. The table they made from their results is seen in table 1.
|
Temperature in Kelvin |
Pressure Measured in Pascals |
|
|
|
|
200 Kelvin |
16, 628 Pascals |
|
400 Kelvin |
33, 256 Pascals |
|
600 Kelvin |
49, 884 Pascals |
|
800 Kelvin |
66, 512 Pascals |
TABLE 1
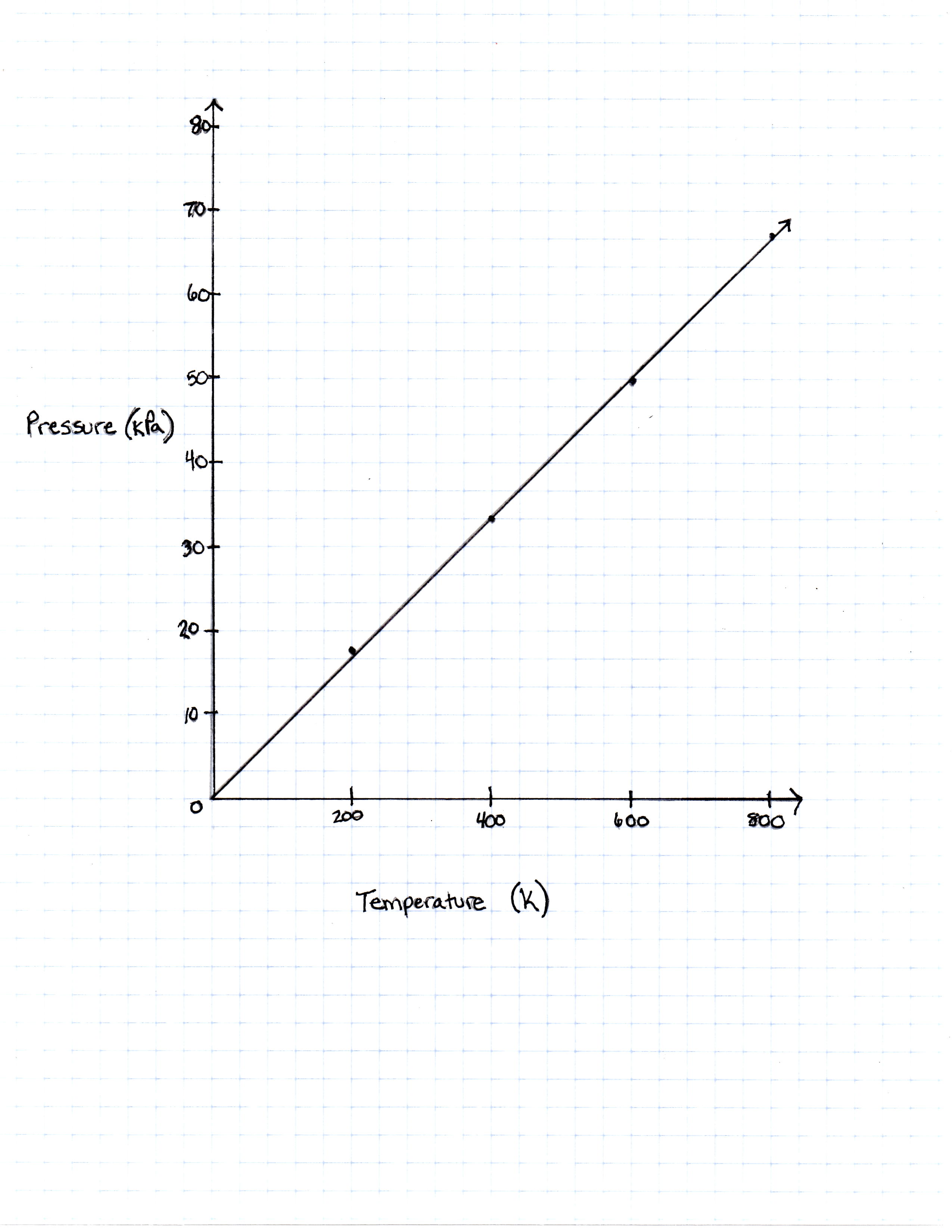
FIGURE 1
The graph the students made based on the data is seen in Figure 1.
Pressure is created by the movement of the gas molecules pushing against a container. 0 Kelvin is known as absolute 0, the temperature at which all molecule movement theoretically stops.
| 10. | Describe the relationship between the temperature and the pressure. |
The pressure remains the same no matter the temperature.
They are inversely related. As temperature decreases, pressure increases.
The relationship cannot be determined from the graph.
They are unrelated.
They are directly related. As temperature increases, so does pressure.




