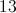Geometry
Help Questions
PSAT Math › Geometry
In order to get to work, Jeff leaves home and drives 4 miles due north, then 3 miles due east, followed by 6 miles due north and, finally, 7 miles due east. What is the straight line distance from Jeff’s work to his home?
2√5
11
10√2
15
6√2
Explanation
Jeff drives a total of 10 miles north and 10 miles east. Using the Pythagorean theorem (a2+b2=c2), the direct route from Jeff’s home to his work can be calculated. 102+102=c2. 200=c2. √200=c. √100√2=c. 10√2=c
What is the area of a square that has a diagonal whose endpoints in the coordinate plane are located at (-8, 6) and (2, -4)?
100
100√2
50√2
50
200√2
Explanation
100_π_
50_π_
25_π_
10_π_
20_π_
Explanation
100_π_
50_π_
25_π_
10_π_
20_π_
Explanation
A rectangular prism has a volume of 144 and a surface area of 192. If the shortest edge is 3, what is the length of the longest diagonal through the prism?
Explanation
The volume of a rectangular prism is 
We are told that the shortest edge is 3. Let us call this the height.
We now have 

Now we replace variables by known values:
Now we have:
We have thus determined that the other two edges of the rectangular prism will be 4 and 12. We now need to find the longest diagonal. This is equal to:
If you do not remember how to find this directly, you can also do it in steps. You first find the diagonal across one of the sides (in the plane), by using the Pythagorean Theorem. For example, we choose the side with edges 3 and 4. This diagonal will be:
We then use a plane with one side given by the diagonal we just found (length 5) and the other given by the distance of the 3rd edge (length 12).
This diagonal is then 
A certain cube has a side length of 25 m. How many square tiles, each with an area of 5 m2, are needed to fully cover the surface of the cube?
100
200
500
750
1000
Explanation
A cube with a side length of 25m has a surface area of:
25m * 25m * 6 = 3,750 m2
(The surface area of a cube is equal to the area of one face of the cube multiplied by 6 sides. In other words, if the side of a cube is s, then the surface area of the cube is 6_s_2.)
Each square tile has an area of 5 m2.
Therefore, the total number of square tiles needed to fully cover the surface of the cube is:
3,750m2/5m2 = 750
Note: the volume of a cube with side length s is equal to _s_3. Therefore, if asked how many mini-cubes with side length n are needed to fill the original cube, the answer would be:
s3/n3
A square with a side length of 4 inches is inscribed in a circle, as shown below. What is the area of the unshaded region inside of the circle, in square inches?

8π - 16
4π-4
8π-4
2π-4
8π-8
Explanation
Using the Pythagorean Theorem, the diameter of the circle (also the diagonal of the square) can be found to be 4√2. Thus, the radius of the circle is half of the diameter, or 2√2. The area of the circle is then π(2√2)2, which equals 8π. Next, the area of the square must be subtracted from the entire circle, yielding an area of 8π-16 square inches.
What is the hypotenuse of a right triangle with side lengths 

Explanation
The Pythagorean Theorem states that . This question gives us the values of



Take 



Now we can start solving for 
The length of the hypotenuse is 

Note: Figure NOT drawn to scale.
The above figure shows Rectangle 




What percent of Rectangle 
Explanation
The area of 


The answer is independent of the sidelengths of the rectangle, so to ease calculations - this will become more apparent later - we will arbitrarily assign to the rectangle the dimensions
and, subsequently,
and, since 


The area of Rectangle 

Since 


The area of 

The area of 
The area of the shaded region is therefore 

A square with a side length of 4 inches is inscribed in a circle, as shown below. What is the area of the unshaded region inside of the circle, in square inches?

8π - 16
4π-4
8π-4
2π-4
8π-8
Explanation
Using the Pythagorean Theorem, the diameter of the circle (also the diagonal of the square) can be found to be 4√2. Thus, the radius of the circle is half of the diameter, or 2√2. The area of the circle is then π(2√2)2, which equals 8π. Next, the area of the square must be subtracted from the entire circle, yielding an area of 8π-16 square inches.