Geometry
Help Questions
GMAT Quantitative › Geometry
Calculate the length of a chord in a circle with a radius of 

Explanation
We are given the radius of the circle and the perpendicular distance from its center to the chord, which is all we need to calculate the length of the chord. Using the formula for chord length that involves these two quantities, we find the solution as follows, where 


Calculate the length of a chord in a circle with a radius of 

Explanation
We are given the radius of the circle and the perpendicular distance from its center to the chord, which is all we need to calculate the length of the chord. Using the formula for chord length that involves these two quantities, we find the solution as follows, where 



This triangle cannot exist.
Explanation
We are looking for ways to add three primes to yield a sum of 43. Two or all three (since an equilateral triangle is considered isosceles) must be equal (although, since 43 is not a multiple of three, only two can be equal).
We will set the shared sidelength of the congruent sides to each prime number in turn up to 19:
By the Triangle Inequality, the sum of the lengths of the shortest two sides must exceed that of the greatest. We can therefore eliminate the first three. 



19 is the correct choice.
The perimeter of a regular pentagon is one-fifth of a mile. Give its sidelength in feet.
Explanation
One mile is 5,280 feet. The perimeter of the pentagon is one-fifth of this, or 

What is the area of the figure with vertices 
Explanation
This figure can be seen as a composite of two simple shapes: the rectangle with vertices 

The rectangle has length 


The triangle has as its base the length of the horizontal segment connecting 




Add the areas of the rectangle and the triangle to get the total area:
The perimeter of a regular octagon is two kilometers. Give its sidelength in meters.
Explanation
One kilometer is equal to 1,000 meters, so two kilometers comprise 2,000 meters. A regular octagon has eight sides of equal length, so divide by 8 to get the sidelength: 



Explanation
The three sides of a scalene triangle have different measures. One measure 
It cannot be true that 

Therefore, if 

What is the area of a triangle on the coordinate plane with its vertices on the points 
Explanation
The vertical segment connecting 





The arc 



Explanation
The figure referenced is below.
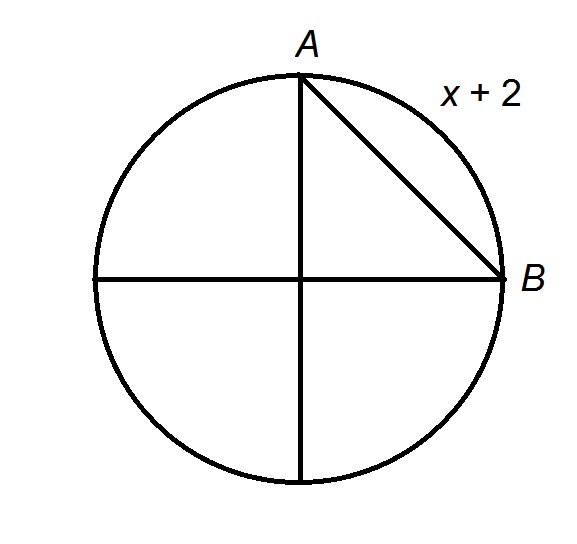
The arc is 

The radius is this circumference divided by 

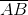


The chord of a 

Explanation
The radius 

The circle, the central angle, and the chord are shown below:

By way of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem, 





























































