Phases and Properties of Matter
Help Questions
Physical Chemistry › Phases and Properties of Matter
Which of the following is not an intensive property?
Volume
Temperature
Density
Melting point
Pressure
Explanation
Intensive properties are not dependent on the amount of substance. Melting point, pressure, temperature, and density are some examples of intensive properties. Therefore, volume of a substance is not an example of an intensive property, rather, it is an extensive property which depends on the amount of substance. Some other examples of extensive properties include weight, energy, and electric charge.
Which of the following is not an intensive property?
Volume
Temperature
Density
Melting point
Pressure
Explanation
Intensive properties are not dependent on the amount of substance. Melting point, pressure, temperature, and density are some examples of intensive properties. Therefore, volume of a substance is not an example of an intensive property, rather, it is an extensive property which depends on the amount of substance. Some other examples of extensive properties include weight, energy, and electric charge.
Which of the following is not an intensive property?
Volume
Temperature
Density
Melting point
Pressure
Explanation
Intensive properties are not dependent on the amount of substance. Melting point, pressure, temperature, and density are some examples of intensive properties. Therefore, volume of a substance is not an example of an intensive property, rather, it is an extensive property which depends on the amount of substance. Some other examples of extensive properties include weight, energy, and electric charge.
You freeze a sample of nitrogen. Compared to the reactant, the end product has density and mass.
a higher . . . the same
a higher . . . a higher
a lower . . . the same
the same . . . the same
Explanation
Freezing the is process of converting a liquid to a solid. This question is asking about the freezing process of liquid nitrogen to solid nitrogen; therefore, the end product of the reaction is solid nitrogen. Recall that solids are more tightly packed. This means that the volume taken up by the molecules in solid is lower than in liquid; therefore, solids generally have a lower volume. Mass, on the other hand, depends on the number of molecules present. Phase changes do not alter the amount of molecules present. For example, the end product in this question (solid nitrogen) will have the same amount of molecules as its liquid counterpart; therefore, the mass doesn’t change when the phase changes.
Density is defined as follows.
Since its volume decreases and the mass stays the same, a solid will have a lower density than liquid. Note that water is an exception to this general rule, as solid ice has a lower density (higher volume) than the same mass of liquid water. This is due to the arrangement of its hydrogen bonds throughout its crystalline structure.
You freeze a sample of nitrogen. Compared to the reactant, the end product has density and mass.
a higher . . . the same
a higher . . . a higher
a lower . . . the same
the same . . . the same
Explanation
Freezing the is process of converting a liquid to a solid. This question is asking about the freezing process of liquid nitrogen to solid nitrogen; therefore, the end product of the reaction is solid nitrogen. Recall that solids are more tightly packed. This means that the volume taken up by the molecules in solid is lower than in liquid; therefore, solids generally have a lower volume. Mass, on the other hand, depends on the number of molecules present. Phase changes do not alter the amount of molecules present. For example, the end product in this question (solid nitrogen) will have the same amount of molecules as its liquid counterpart; therefore, the mass doesn’t change when the phase changes.
Density is defined as follows.
Since its volume decreases and the mass stays the same, a solid will have a lower density than liquid. Note that water is an exception to this general rule, as solid ice has a lower density (higher volume) than the same mass of liquid water. This is due to the arrangement of its hydrogen bonds throughout its crystalline structure.
You freeze a sample of nitrogen. Compared to the reactant, the end product has density and mass.
a higher . . . the same
a higher . . . a higher
a lower . . . the same
the same . . . the same
Explanation
Freezing the is process of converting a liquid to a solid. This question is asking about the freezing process of liquid nitrogen to solid nitrogen; therefore, the end product of the reaction is solid nitrogen. Recall that solids are more tightly packed. This means that the volume taken up by the molecules in solid is lower than in liquid; therefore, solids generally have a lower volume. Mass, on the other hand, depends on the number of molecules present. Phase changes do not alter the amount of molecules present. For example, the end product in this question (solid nitrogen) will have the same amount of molecules as its liquid counterpart; therefore, the mass doesn’t change when the phase changes.
Density is defined as follows.
Since its volume decreases and the mass stays the same, a solid will have a lower density than liquid. Note that water is an exception to this general rule, as solid ice has a lower density (higher volume) than the same mass of liquid water. This is due to the arrangement of its hydrogen bonds throughout its crystalline structure.
An unknown molecule (molecule A), in its solid phase, is found to have a density of 

Liquid will overflow
No liquid will overflow
Solid will not fit in the container
The container will be about halfway full with liquid
Explanation
The dimensions of the cubic container are 
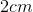

Recall that 


An unknown molecule (molecule A), in its solid phase, is found to have a density of 

Liquid will overflow
No liquid will overflow
Solid will not fit in the container
The container will be about halfway full with liquid
Explanation
The dimensions of the cubic container are 
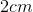

Recall that 


An unknown molecule (molecule A), in its solid phase, is found to have a density of 

Liquid will overflow
No liquid will overflow
Solid will not fit in the container
The container will be about halfway full with liquid
Explanation
The dimensions of the cubic container are 
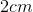

Recall that 


An unknown gas is being analyzed in lab. You place 



Oxygen
Nitrogen
Argon
Chlorine
Explanation
To solve this question we need to use the ideal gas law equation:
Above, 







Rearrange the ideal gas law and solve for 
The question states that you place one gram of gas in the container. Since we know the moles, we can solve for the molecular weight of the gas and figure out its identity from the molecular weight.
The molecular weight of oxygen gas, 










