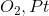Redox Chemistry
Help Questions
Organic Chemistry › Redox Chemistry
A student reacts sodium chloride and lithium bromide. He collects the products in a jar and performs several tests on them. He concludes that product A has a metal and a nonmetal and that the metal has an oxidation number of 

The results seem invalid
The identity of product A is sodium bromide
The identity of product A is lithium chloride
The other product will have similar oxidation numbers (metal: 

Explanation
The reaction stated in this question is as follows.
This is a double replacement reaction. Both products contain a metal (an alkali metal) and a nonmetal (a halogen). The oxidation number of all alkali metals (first column of periodic table) is 


A student reacts sodium chloride and lithium bromide. He collects the products in a jar and performs several tests on them. He concludes that product A has a metal and a nonmetal and that the metal has an oxidation number of 

The results seem invalid
The identity of product A is sodium bromide
The identity of product A is lithium chloride
The other product will have similar oxidation numbers (metal: 

Explanation
The reaction stated in this question is as follows.
This is a double replacement reaction. Both products contain a metal (an alkali metal) and a nonmetal (a halogen). The oxidation number of all alkali metals (first column of periodic table) is 


A student reacts sodium chloride and lithium bromide. He collects the products in a jar and performs several tests on them. He concludes that product A has a metal and a nonmetal and that the metal has an oxidation number of 

The results seem invalid
The identity of product A is sodium bromide
The identity of product A is lithium chloride
The other product will have similar oxidation numbers (metal: 

Explanation
The reaction stated in this question is as follows.
This is a double replacement reaction. Both products contain a metal (an alkali metal) and a nonmetal (a halogen). The oxidation number of all alkali metals (first column of periodic table) is 


What is an appropriate reagent to convert a primary alcohol to an aldehyde?
Explanation
To form the aldehyde, the alcohol must be oxidized. However, potassium permanganate and chromic acid are too strong and would yield a carboxylic acid. Ozonolysis works with alkenes and oxygen over platinum would not react. PCC is correct because it will oxidize the alcohol to form an aldehyde but is too weak to continue on to form the carboxylic acid.
Which of the following compounds is not a reducing agent?
Explanation

What is an appropriate reagent to convert a primary alcohol to an aldehyde?
Explanation
To form the aldehyde, the alcohol must be oxidized. However, potassium permanganate and chromic acid are too strong and would yield a carboxylic acid. Ozonolysis works with alkenes and oxygen over platinum would not react. PCC is correct because it will oxidize the alcohol to form an aldehyde but is too weak to continue on to form the carboxylic acid.
Which of the following reagents can turn primary alcohols into a carboxylic acid?
Jones Reagent (chromic acid in acetone)
Tollen's test
PCC
Explanation
The Jones reagent can convert primary alcohol to acids and secondary alcohols to ketones. The Tollen's test only converts aldehydes to carboxylic acids. PCC can only convert primary and secondary alcohol to aldehydes and ketones, respectively. 

Which of the following compounds is not a reducing agent?
Explanation

What is an appropriate reagent to convert a primary alcohol to an aldehyde?
Explanation
To form the aldehyde, the alcohol must be oxidized. However, potassium permanganate and chromic acid are too strong and would yield a carboxylic acid. Ozonolysis works with alkenes and oxygen over platinum would not react. PCC is correct because it will oxidize the alcohol to form an aldehyde but is too weak to continue on to form the carboxylic acid.
Which of the following compounds is not a reducing agent?
Explanation