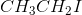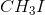Reaction Mechanisms, Energetics, and Kinematics
Help Questions
Organic Chemistry › Reaction Mechanisms, Energetics, and Kinematics
Which of the following substrates would have the fastest reaction rate for an SN1 mechanism?
Explanation
The SN1 mechanism involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate in the rate-determining step. The most stable carbocation will produce the fastest reaction. We can immediately eliminate any answer choices that will produce primary or secondary carbocations, since a tertiary carbocation will be much more stable. When comparing tertiary carbocations, larger and more electronegative substituents will allow for more charge stabilization.
Since the tertiary carbocation formed by the dissociation of iodide from 
Which of the following substrates would have the fastest reaction rate for an SN1 mechanism?
Explanation
The SN1 mechanism involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate in the rate-determining step. The most stable carbocation will produce the fastest reaction. We can immediately eliminate any answer choices that will produce primary or secondary carbocations, since a tertiary carbocation will be much more stable. When comparing tertiary carbocations, larger and more electronegative substituents will allow for more charge stabilization.
Since the tertiary carbocation formed by the dissociation of iodide from 
Which of the following substrates would have the fastest reaction rate for an SN1 mechanism?
Explanation
The SN1 mechanism involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate in the rate-determining step. The most stable carbocation will produce the fastest reaction. We can immediately eliminate any answer choices that will produce primary or secondary carbocations, since a tertiary carbocation will be much more stable. When comparing tertiary carbocations, larger and more electronegative substituents will allow for more charge stabilization.
Since the tertiary carbocation formed by the dissociation of iodide from 
Which of the following compounds could NEVER undergo an E2 reaction when treated with potassium tert-butoxide?
Benzylbromide
Bromoethane
Cyclopentylbromide
3-methyl-3-iodopentane
Cis-2-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane
Explanation
For an E2 reaction to occur, there must be a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbon with the leaving group. Benzyl bromide contains no hydrogens on the carbon next to the carbon with the bromide, and would therefore undergo only a substitution reaction.
Which SN2 reaction would proceed the fastest?
1-bromopentane and sodium iodide
1-bromo-2-methylpentane and sodium iodide
1-chloropentane and sodium iodide
sec-butyl bromide and sodium iodide
tert-butyl bromide and sodium iodide
Explanation
SN2 reactions involve a backside nucleophilic attack on an electrophilic carbon. As a result, less steric congestion for this backside attack results in a faster reaction, meaning that SN2 reactions proceed fastest for primary carbons. In addition, beta-branching next to a primary carbon results in a slower reaction, as does a poorer leaving group (i.e. chloride instead of bromide).
1-bromopentane has a good leaving group (bromine) attached to a primary carbon with no beta-branching, meaning it will proceed the fastest.
Which of the following compounds could NEVER undergo an E2 reaction when treated with potassium tert-butoxide?
Benzylbromide
Bromoethane
Cyclopentylbromide
3-methyl-3-iodopentane
Cis-2-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane
Explanation
For an E2 reaction to occur, there must be a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbon with the leaving group. Benzyl bromide contains no hydrogens on the carbon next to the carbon with the bromide, and would therefore undergo only a substitution reaction.
Which SN2 reaction would proceed the fastest?
1-bromopentane and sodium iodide
1-bromo-2-methylpentane and sodium iodide
1-chloropentane and sodium iodide
sec-butyl bromide and sodium iodide
tert-butyl bromide and sodium iodide
Explanation
SN2 reactions involve a backside nucleophilic attack on an electrophilic carbon. As a result, less steric congestion for this backside attack results in a faster reaction, meaning that SN2 reactions proceed fastest for primary carbons. In addition, beta-branching next to a primary carbon results in a slower reaction, as does a poorer leaving group (i.e. chloride instead of bromide).
1-bromopentane has a good leaving group (bromine) attached to a primary carbon with no beta-branching, meaning it will proceed the fastest.
Which of the following compounds could NEVER undergo an E2 reaction when treated with potassium tert-butoxide?
Benzylbromide
Bromoethane
Cyclopentylbromide
3-methyl-3-iodopentane
Cis-2-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane
Explanation
For an E2 reaction to occur, there must be a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbon with the leaving group. Benzyl bromide contains no hydrogens on the carbon next to the carbon with the bromide, and would therefore undergo only a substitution reaction.
Which SN2 reaction would proceed the fastest?
1-bromopentane and sodium iodide
1-bromo-2-methylpentane and sodium iodide
1-chloropentane and sodium iodide
sec-butyl bromide and sodium iodide
tert-butyl bromide and sodium iodide
Explanation
SN2 reactions involve a backside nucleophilic attack on an electrophilic carbon. As a result, less steric congestion for this backside attack results in a faster reaction, meaning that SN2 reactions proceed fastest for primary carbons. In addition, beta-branching next to a primary carbon results in a slower reaction, as does a poorer leaving group (i.e. chloride instead of bromide).
1-bromopentane has a good leaving group (bromine) attached to a primary carbon with no beta-branching, meaning it will proceed the fastest.
In reactions involving the alkylation of acetylide ions, it is preferred that the alkyl halide be primary. What is the reason for this?
The mechanism for these reactions is SN2
The reactions generally occur in two steps
The reaction involves a carbocation as intermediate
The mechanism for these reactions is SN1
An answer cannot be determined without more information about the reaction conditions
Explanation
The reason that the alkyl halide is preferred to be primary is because the mechanism for these reactions is SN2. SN2 indicates a substitution reaction that takes place in one step. A primary alcohol is preferred to prevent steric congestion caused by the simultaneous binding of the nucleophile and release of the leaving group. This reaction mechanism is faster because it omits the formation of a carbocation intermediate.
In contrast, SN1 reactions take place in two steps and involve the formation of a carbocation intermediate.