Biological Molecules - Organic Chemistry
Card 1 of 176
Chemists and biochemists have many ways of representing sugars. Glucose, the most common hexose, is shown below in various linear and cyclic projections. Using the linear and cyclic projection of your choice, can you indicate which colored oxygen in the linear form corresponds to the circled hemiacetal oxygen once the cyclization reaction is complete?
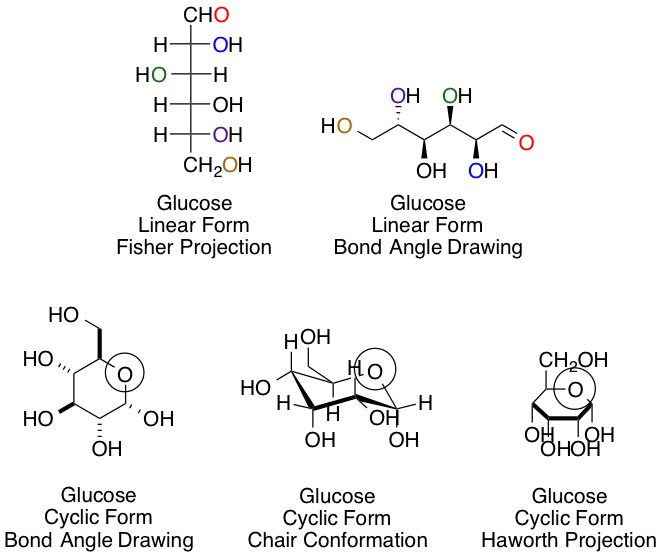
Chemists and biochemists have many ways of representing sugars. Glucose, the most common hexose, is shown below in various linear and cyclic projections. Using the linear and cyclic projection of your choice, can you indicate which colored oxygen in the linear form corresponds to the circled hemiacetal oxygen once the cyclization reaction is complete?

Tap to reveal answer
This answer, regardless of your preference of projection type, is easiest to obtain using arrow pushing for the cyclization reaction to keep track of each carbon and oxygen:

The purple carbon in the linear projection ends in the circled hemiacetal position.
This answer, regardless of your preference of projection type, is easiest to obtain using arrow pushing for the cyclization reaction to keep track of each carbon and oxygen:

The purple carbon in the linear projection ends in the circled hemiacetal position.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following structures represents the anomeric alpha ring structure of D-glucose?

Which of the following structures represents the anomeric alpha ring structure of D-glucose?

Tap to reveal answer
When converting a linear sugar to its ring form, a bond is formed between the oxygen attached to carbon 5 and the carbon at position 1. All hydroxyl groups that are not attached to the carbon in position 1 and are oriented to the right end up trans to the  attached to carbon 5, while those that are in the left position end up cis to the
attached to carbon 5, while those that are in the left position end up cis to the  attached to carbon 5.
attached to carbon 5.
If the hydroxyl group attached to carbon 1 ends up trans to the  attached to carbon 5, the ring structure is considered alpha. If the hydroxyl group attached to carbon 1 is cis to the
attached to carbon 5, the ring structure is considered alpha. If the hydroxyl group attached to carbon 1 is cis to the  attached to carbon 5, the ring structure is considered beta.
attached to carbon 5, the ring structure is considered beta.
The alpha ring structure of D-glucose bonds the carbon 1 hydroxyl group trans to the carbon 5  group. The hyroxyl groups on carbons 2, 3, and 4 will be trans, cis, and trans with respect to the
group. The hyroxyl groups on carbons 2, 3, and 4 will be trans, cis, and trans with respect to the  .
.
When converting a linear sugar to its ring form, a bond is formed between the oxygen attached to carbon 5 and the carbon at position 1. All hydroxyl groups that are not attached to the carbon in position 1 and are oriented to the right end up trans to the 

If the hydroxyl group attached to carbon 1 ends up trans to the 

The alpha ring structure of D-glucose bonds the carbon 1 hydroxyl group trans to the carbon 5 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following structures represents the anomeric alpha ring structure of D-galactose?

Which of the following structures represents the anomeric alpha ring structure of D-galactose?

Tap to reveal answer
When converting a linear sugar to its ring form, a bond is formed between the oxygen attached to carbon 5 and the carbon at position 1. All hydroxyl groups that are not attached to the carbon in position 1 and are oriented to the right end up trans to the  attached to carbon 5, while those that are in the left position end up cis to the
attached to carbon 5, while those that are in the left position end up cis to the  attached to carbon 5.
attached to carbon 5.
If the hydroxyl group attached to carbon 1 ends up trans to the  attached to carbon 5, the ring structure is considered alpha. If the hydroxyl group attached to carbon 1 is cis to the
attached to carbon 5, the ring structure is considered alpha. If the hydroxyl group attached to carbon 1 is cis to the  attached to carbon 5, the ring structure is considered beta.
attached to carbon 5, the ring structure is considered beta.
The alpha ring structure of D-galactose bonds the carbon 1 hydroxyl group trans to the carbon 5  group. The hyroxyl groups on carbons 2, 3, and 4 will be trans, cis, and cis with respect to the
group. The hyroxyl groups on carbons 2, 3, and 4 will be trans, cis, and cis with respect to the  .
.
When converting a linear sugar to its ring form, a bond is formed between the oxygen attached to carbon 5 and the carbon at position 1. All hydroxyl groups that are not attached to the carbon in position 1 and are oriented to the right end up trans to the 

If the hydroxyl group attached to carbon 1 ends up trans to the 

The alpha ring structure of D-galactose bonds the carbon 1 hydroxyl group trans to the carbon 5 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following ring structures represents the anomeric alpha ring structure of D-mannose?

Which of the following ring structures represents the anomeric alpha ring structure of D-mannose?

Tap to reveal answer
When converting a linear sugar to its ring form, a bond is formed between the oxygen attached to carbon 5 and the carbon at position 1. All hydroxyl groups that are not attached to the carbon in position 1 and are oriented to the right end up trans to the  attached to carbon 5, while those that are in the left position end up cis to the
attached to carbon 5, while those that are in the left position end up cis to the  attached to carbon 5.
attached to carbon 5.
If the hydroxyl group attached to carbon 1 ends up trans to the  attached to carbon 5, the ring structure is considered alpha. If the hydroxyl group attached to carbon 1 is cis to the
attached to carbon 5, the ring structure is considered alpha. If the hydroxyl group attached to carbon 1 is cis to the  attached to carbon 5, the ring structure is considered beta.
attached to carbon 5, the ring structure is considered beta.
The alpha ring structure of D-mannose bonds the carbon 1 hydroxyl group trans to the carbon 5  group. The hyroxyl groups on carbons 2, 3, and 4 will be cis, cis, and trans with respect to the
group. The hyroxyl groups on carbons 2, 3, and 4 will be cis, cis, and trans with respect to the  .
.
When converting a linear sugar to its ring form, a bond is formed between the oxygen attached to carbon 5 and the carbon at position 1. All hydroxyl groups that are not attached to the carbon in position 1 and are oriented to the right end up trans to the 

If the hydroxyl group attached to carbon 1 ends up trans to the 

The alpha ring structure of D-mannose bonds the carbon 1 hydroxyl group trans to the carbon 5 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Identify the aldose pictured, including its alpha or beta designation.

Identify the aldose pictured, including its alpha or beta designation.

Tap to reveal answer
The structure pictured is mannose because the hydroxyl groups at carbons 2, 3, and 4 are situated cis, cis, and trans (respectively) to the  attached to carbon 5.
attached to carbon 5.
The mannose pictured is in alpha form because the hydroxyl group at carbon 1 is trans to the  attached to carbon 5.
attached to carbon 5.
The structure pictured is mannose because the hydroxyl groups at carbons 2, 3, and 4 are situated cis, cis, and trans (respectively) to the 
The mannose pictured is in alpha form because the hydroxyl group at carbon 1 is trans to the 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The Fischer projection pictured is a form of glucose. The carbon labeled "x" is the chiral carbon farthest away from carbon 1 and the hydroxyl group connected to carbon "x" is on the right. This fact designates that the glucose as what configuration?

The Fischer projection pictured is a form of glucose. The carbon labeled "x" is the chiral carbon farthest away from carbon 1 and the hydroxyl group connected to carbon "x" is on the right. This fact designates that the glucose as what configuration?

Tap to reveal answer
The chiral carbon farthest away from carbon 1 is designated as "D" if its hydroxyl group is on the right side in the Fischer projection. In other words, this is D-glucose because the hyroxyl group on carbon "x" is oriented to the right.
The chiral carbon farthest away from carbon 1 is designated as "D" if its hydroxyl group is on the right side in the Fischer projection. In other words, this is D-glucose because the hyroxyl group on carbon "x" is oriented to the right.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the name of the aldose pictured in this Fischer projection?

What is the name of the aldose pictured in this Fischer projection?

Tap to reveal answer
The structure is D-ribose because it is a five-carbon aldose with the hydroxyl groups on carbons 2, 3, and 4 all on the right in the Fischer projection.
The structure is D-ribose because it is a five-carbon aldose with the hydroxyl groups on carbons 2, 3, and 4 all on the right in the Fischer projection.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following statements is true regarding carbohydrates?
Which of the following statements is true regarding carbohydrates?
Tap to reveal answer
All of these statements are true. A carbohydrate is said to have a "D" conformation in its acyclic form when the alcohol group on the carbohydrate's top stereocenter is on the right side in a Fischer projection. Most carbohydrates that we deal with in organic chemistry are aldoses, which means that they contain an aldehyde. The anomeric carbon is the site of attachment from one monosaccharide to another, and can be used to create polysaccharides.
All of these statements are true. A carbohydrate is said to have a "D" conformation in its acyclic form when the alcohol group on the carbohydrate's top stereocenter is on the right side in a Fischer projection. Most carbohydrates that we deal with in organic chemistry are aldoses, which means that they contain an aldehyde. The anomeric carbon is the site of attachment from one monosaccharide to another, and can be used to create polysaccharides.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the name of the following carbohydrate?

What is the name of the following carbohydrate?

Tap to reveal answer
Stereochemistry from second to fifth carbon is R, S, S, R, which indicates D-galactose. The Haworth structure is a six-membered ring, so the molecule is in its pyranose form. The molecule has its anomeric hydroxyl group pointing down, so it's the alpha anomer.
Stereochemistry from second to fifth carbon is R, S, S, R, which indicates D-galactose. The Haworth structure is a six-membered ring, so the molecule is in its pyranose form. The molecule has its anomeric hydroxyl group pointing down, so it's the alpha anomer.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the name of the following molecule?

What is the name of the following molecule?

Tap to reveal answer
Stereochemistry from second to fifth carbon is R, S, R, R, which indicates D-glucose. The Haworth structure is a five-membered ring, so the molecule is in its furanose form. The molecule has its anomeric hydroxyl group pointing down, so it's the alpha anomer.
Stereochemistry from second to fifth carbon is R, S, R, R, which indicates D-glucose. The Haworth structure is a five-membered ring, so the molecule is in its furanose form. The molecule has its anomeric hydroxyl group pointing down, so it's the alpha anomer.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following correctly describes a reducing sugar?
Which of the following correctly describes a reducing sugar?
Tap to reveal answer
A reducing sugar contains a hemiacetal/hemiketal group which means that in its open chain form it contains a ketone/aldehyde group. Sugars containing a free aldehyde group can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid, while sugars containing a free ketone group must be tautomerized to an aldehyde group through an ene-diol intermediate (shown below), and this can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid.

Reducing sugars are detectable with the formation of either a precipitate or a solution color change after addition of Tollens' Reagent, Benedict's solution, or Fehling's solution.
A reducing sugar contains a hemiacetal/hemiketal group which means that in its open chain form it contains a ketone/aldehyde group. Sugars containing a free aldehyde group can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid, while sugars containing a free ketone group must be tautomerized to an aldehyde group through an ene-diol intermediate (shown below), and this can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid.

Reducing sugars are detectable with the formation of either a precipitate or a solution color change after addition of Tollens' Reagent, Benedict's solution, or Fehling's solution.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Alpha-D-glucopyranose:

Glucose (pictured) is defined as which of the following?
Alpha-D-glucopyranose:

Glucose (pictured) is defined as which of the following?
Tap to reveal answer
Glucose in its open chain form (shown below), has a free aldehyde group (an aldose), and it contains six carbons (a hexose). Together, glucose is shown to be an aldohexose.

Glucose in its open chain form (shown below), has a free aldehyde group (an aldose), and it contains six carbons (a hexose). Together, glucose is shown to be an aldohexose.

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Alpha-D-glucopyranose

Which of the labelled carbon atoms is the anomeric carbon?
Alpha-D-glucopyranose

Which of the labelled carbon atoms is the anomeric carbon?
Tap to reveal answer
The anomeric carbon is formed from the original carbonyl carbon in the straight-chain form of the molecule being attacked by a hydroxyl group to form a hemiacetal. This is seen as a carbon that is bonded to two oxygen atoms. In the case of glucose, the carbon labelled A is a hemiacetal, and is considered to be the anomeric carbon.
The anomeric carbon is formed from the original carbonyl carbon in the straight-chain form of the molecule being attacked by a hydroxyl group to form a hemiacetal. This is seen as a carbon that is bonded to two oxygen atoms. In the case of glucose, the carbon labelled A is a hemiacetal, and is considered to be the anomeric carbon.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Shown below is the structure of a sugar molecule.

Which of the following is the most appropriate classification of this sugar?
Shown below is the structure of a sugar molecule.

Which of the following is the most appropriate classification of this sugar?
Tap to reveal answer
In this question, we're given the structure of a sugar molecule, and we're asked to identify which answer choice represents the correct identification of this molecule.
To answer this question, there are two things we need to look at. For one, we need to determine whether it is an aldehyde sugar (aldose) or a ketone sugar (ketose). The first carbon atom in the molecule (shown at the very top in the image) is shown as  . This means that the carbon contains a double bond to the oxygen. Furthermore, since it also contains a bond to a hydrogen, we can conclude that this is an aldehyde functional group. Consequently, we know that this must be an aldose sugar.
. This means that the carbon contains a double bond to the oxygen. Furthermore, since it also contains a bond to a hydrogen, we can conclude that this is an aldehyde functional group. Consequently, we know that this must be an aldose sugar.
Next, we need to look at the number of carbon atoms in the molecule. In the image shown in the question, there are a total of seven carbon atoms. Thus, this sugar would be classified as a heptose sugar (seven carbons) rather than a hexose sugar (six carbons).
Putting these two pieces of information together, we know that the sugar is both an aldose and a heptose. Therefore, this sugar is an aldoheptose.
In this question, we're given the structure of a sugar molecule, and we're asked to identify which answer choice represents the correct identification of this molecule.
To answer this question, there are two things we need to look at. For one, we need to determine whether it is an aldehyde sugar (aldose) or a ketone sugar (ketose). The first carbon atom in the molecule (shown at the very top in the image) is shown as 
Next, we need to look at the number of carbon atoms in the molecule. In the image shown in the question, there are a total of seven carbon atoms. Thus, this sugar would be classified as a heptose sugar (seven carbons) rather than a hexose sugar (six carbons).
Putting these two pieces of information together, we know that the sugar is both an aldose and a heptose. Therefore, this sugar is an aldoheptose.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following is an example of a basic amino acid?
Which of the following is an example of a basic amino acid?
Tap to reveal answer
Lysine's R-group includes an amine (-NH2), which can be ionized by picking up a hydrogen. This ability classifies lysine as basic.
Lysine's R-group includes an amine (-NH2), which can be ionized by picking up a hydrogen. This ability classifies lysine as basic.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following amino acids can participate in the formation of a disulfide bridge?
Which of the following amino acids can participate in the formation of a disulfide bridge?
Tap to reveal answer
Cysteine's R-group contains a sulfhydryl group (-SH), which can participate in the formation of a disulfide bridge in a protein's tertiary and/or quaternary structure. Cysteine is the only amino acid to contain a sulfur atom.
Cysteine's R-group contains a sulfhydryl group (-SH), which can participate in the formation of a disulfide bridge in a protein's tertiary and/or quaternary structure. Cysteine is the only amino acid to contain a sulfur atom.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
How many essential amino acids are there?
How many essential amino acids are there?
Tap to reveal answer
The nine essential amino acids are valine, leucine, isoleucine, histidine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, methionine, threonine, and lysine. These amino acids must be consumed in the diet, since they cannot be synthesized by adult humans.
The nine essential amino acids are valine, leucine, isoleucine, histidine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, methionine, threonine, and lysine. These amino acids must be consumed in the diet, since they cannot be synthesized by adult humans.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following amino acids is the only one to contain a side chain that results in an achiral amino acid?
Which of the following amino acids is the only one to contain a side chain that results in an achiral amino acid?
Tap to reveal answer
The only achiral amino acid is Glycene. Glycene's side chain is simply a hydrogen. Because a hydrogen already exists on the fundamental structure of an amino acid backbone, a side chain of a single hydrogen atom causes glycene to be achiral.
The only achiral amino acid is Glycene. Glycene's side chain is simply a hydrogen. Because a hydrogen already exists on the fundamental structure of an amino acid backbone, a side chain of a single hydrogen atom causes glycene to be achiral.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the D/L configuration and the absolute (R/S) configuration of the following amino acid (cysteine)?

What is the D/L configuration and the absolute (R/S) configuration of the following amino acid (cysteine)?

Tap to reveal answer
Cysteine is an unusual amino acid. Although each of the normal biological amino acids have the L configuration (with the exception of glycine, which is achiral), meaning they can be drawn with the Fischer projection as shown:

the fact that cysteine contains a sulfur group makes the side chain a higher priority than the carboxylic acid. Therefore, the absolute configuration of cysteine will be R, and not S like the other amino acids.
Cysteine is an unusual amino acid. Although each of the normal biological amino acids have the L configuration (with the exception of glycine, which is achiral), meaning they can be drawn with the Fischer projection as shown:

the fact that cysteine contains a sulfur group makes the side chain a higher priority than the carboxylic acid. Therefore, the absolute configuration of cysteine will be R, and not S like the other amino acids.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Consider L-glutamate, which is shown below.

Using the pKa information provided, what is the isoelectric point (pI) of the given molecule?
Consider L-glutamate, which is shown below.

Using the pKa information provided, what is the isoelectric point (pI) of the given molecule?
Tap to reveal answer
The isoelectric point is the average of the two pKa values around which the molecule has an overall neutral charge. In the case of glutamate, the amino acid is in its neutral (zwitterion) form in between the lower two pKa values. Taking the average of the two values gives the pI.

The isoelectric point is the average of the two pKa values around which the molecule has an overall neutral charge. In the case of glutamate, the amino acid is in its neutral (zwitterion) form in between the lower two pKa values. Taking the average of the two values gives the pI.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →