Plane Geometry
Help Questions
Math › Plane Geometry


True or false: From the given information, it follows that 
True
False
Explanation
As we are establishing whether or not 






A triangle is equilateral (having three sides of the same length) if and only if it is also equiangular (having three angles of the same measure, each of which is 

Specifically, 



The above figure shows a rhombus 
Explanation
Construct the other diagonal of the rhombus, which, along with the first one, form a pair of mutual perpendicular bisectors.

By the Pythagorean Theorem,
The rhombus can be seen as the composite of four congruent right triangles, each with legs 10 and 

A square with a side length of 4 inches is inscribed in a circle, as shown below. What is the area of the unshaded region inside of the circle, in square inches?

8π - 16
4π-4
8π-4
2π-4
8π-8
Explanation
Using the Pythagorean Theorem, the diameter of the circle (also the diagonal of the square) can be found to be 4√2. Thus, the radius of the circle is half of the diameter, or 2√2. The area of the circle is then π(2√2)2, which equals 8π. Next, the area of the square must be subtracted from the entire circle, yielding an area of 8π-16 square inches.
Each side of this pentagon has a length of 
Solve for the area of the pentagon.

Explanation
The formula for area of a pentagon is 


To find the apothem, we can convert our one pentagon into five triangles and solve for the height of the triangle:

Each of these triangles have angle measures of 



To solve for the apothem, we can use basic trigonometric ratios:
Now that we know the apothem length, we can plug in all our values to solve for area:
Find the perimeter.

Explanation
How do you find the perimeter of a right triangle?
There are three primary methods used to find the perimeter of a right triangle.
- When side lengths are given, add them together.
- Solve for a missing side using the Pythagorean theorem.
- If we know side-angle-side information, solve for the missing side using the Law of Cosines.
Method 1:
This method will show you how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle when all sides lengths are known. Consider the following figure:

If we know the lengths of sides 


Method 2:
In right triangles, we can calculate the perimeter of a triangle when we are provided only two sides. We can do this by using the Pythagorean theorem. Let's first discuss right triangles in a general sense. A right triangle is a triangle that has one 





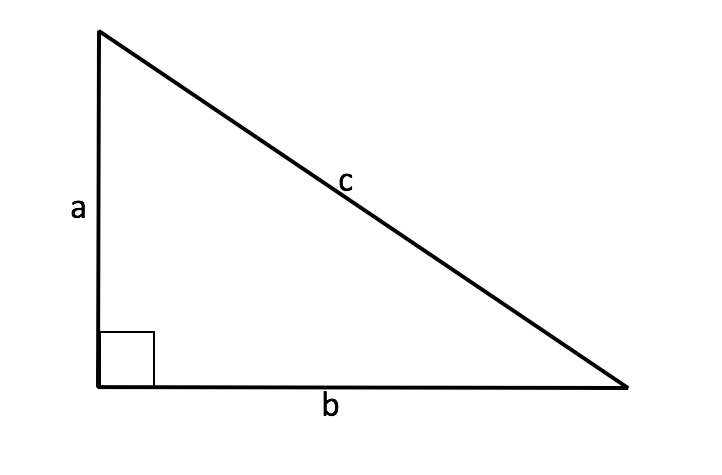
If a triangle appears in this format, then we can use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for any missing side. This formula is written in the following manner:
We can rearrange it in a number of ways to solve for each of the sides of the triangle. Let's rearrange it to solve for the hypotenuse, 
Rearrange and take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
Now, let's use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for one of the legs, 
Subtract 
Take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
Last, let's use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for the adjacent leg, 
Subtract 
Take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
It is important to note that we can only use the following formulas to solve for the missing side of a right triangle when two other sides are known:
After we find the missing side, we can use the perimeter formula to calculate the triangle's perimeter.
Method 3:
This method is the most complicated method and can only be used when we know two side lengths of a triangle as well as the measure of the angle that is between them. When we know side-angle-side (SAS) information, we can use the Law of Cosines to find the missing side. In order for this formula to accurately calculate the missing side we need to label the triangle in the following manner:

When the triangle is labeled in this way each side directly corresponds to the angle directly opposite of it. If we label our triangle carefully, then we can use the following formulas to find missing sides in any triangle given SAS information:
After, we calculate the right side of the equation, we need to take the square root of both sides in order to obtain the final side length of the missing side. Last, we need to use the perimeter formula to obtain the distance of the side lengths of the polygon.
Solution:
Now, that we have discussed the three methods used to calculate the perimeter of a triangle, we can use this information to solve the problem.

In order to find the perimeter, we must first find the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle.
Use Pythagorean's theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse:
Plug in the values of the lengths of the legs of the given triangle.
Now, recall how to find the perimeter of a triangle:
Plug in all the values of the sides of the triangle to find the perimeter.
Make sure to round to 
Find the perimeter.

Explanation
How do you find the perimeter of a right triangle?
There are three primary methods used to find the perimeter of a right triangle.
- When side lengths are given, add them together.
- Solve for a missing side using the Pythagorean theorem.
- If we know side-angle-side information, solve for the missing side using the Law of Cosines.
Method 1:
This method will show you how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle when all sides lengths are known. Consider the following figure:

If we know the lengths of sides 


Method 2:
In right triangles, we can calculate the perimeter of a triangle when we are provided only two sides. We can do this by using the Pythagorean theorem. Let's first discuss right triangles in a general sense. A right triangle is a triangle that has one 






If a triangle appears in this format, then we can use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for any missing side. This formula is written in the following manner:
We can rearrange it in a number of ways to solve for each of the sides of the triangle. Let's rearrange it to solve for the hypotenuse, 
Rearrange and take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
Now, let's use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for one of the legs, 
Subtract 
Take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
Last, let's use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for the adjacent leg, 
Subtract 
Take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
It is important to note that we can only use the following formulas to solve for the missing side of a right triangle when two other sides are known:
After we find the missing side, we can use the perimeter formula to calculate the triangle's perimeter.
Method 3:
This method is the most complicated method and can only be used when we know two side lengths of a triangle as well as the measure of the angle that is between them. When we know side-angle-side (SAS) information, we can use the Law of Cosines to find the missing side. In order for this formula to accurately calculate the missing side we need to label the triangle in the following manner:

When the triangle is labeled in this way each side directly corresponds to the angle directly opposite of it. If we label our triangle carefully, then we can use the following formulas to find missing sides in any triangle given SAS information:
After, we calculate the right side of the equation, we need to take the square root of both sides in order to obtain the final side length of the missing side. Last, we need to use the perimeter formula to obtain the distance of the side lengths of the polygon.
Solution:
Now, that we have discussed the three methods used to calculate the perimeter of a triangle, we can use this information to solve the problem.
Recall how to find the perimeter of a triangle:
The given triangle has 
Recall the Pythagorean theorem:

Since we are finding the length of the hypotenuse, 
Plug in the values of 

Now, plug in all three values into the equation to find the perimeter. Use a calculator and round to 
Find the perimeter.

Explanation
How do you find the perimeter of a right triangle?
There are three primary methods used to find the perimeter of a right triangle.
- When side lengths are given, add them together.
- Solve for a missing side using the Pythagorean theorem.
- If we know side-angle-side information, solve for the missing side using the Law of Cosines.
Method 1:
This method will show you how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle when all sides lengths are known. Consider the following figure:

If we know the lengths of sides 


Method 2:
In right triangles, we can calculate the perimeter of a triangle when we are provided only two sides. We can do this by using the Pythagorean theorem. Let's first discuss right triangles in a general sense. A right triangle is a triangle that has one 






If a triangle appears in this format, then we can use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for any missing side. This formula is written in the following manner:
We can rearrange it in a number of ways to solve for each of the sides of the triangle. Let's rearrange it to solve for the hypotenuse, 
Rearrange and take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
Now, let's use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for one of the legs, 
Subtract 
Take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
Last, let's use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for the adjacent leg, 
Subtract 
Take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
It is important to note that we can only use the following formulas to solve for the missing side of a right triangle when two other sides are known:
After we find the missing side, we can use the perimeter formula to calculate the triangle's perimeter.
Method 3:
This method is the most complicated method and can only be used when we know two side lengths of a triangle as well as the measure of the angle that is between them. When we know side-angle-side (SAS) information, we can use the Law of Cosines to find the missing side. In order for this formula to accurately calculate the missing side we need to label the triangle in the following manner:

When the triangle is labeled in this way each side directly corresponds to the angle directly opposite of it. If we label our triangle carefully, then we can use the following formulas to find missing sides in any triangle given SAS information:
After, we calculate the right side of the equation, we need to take the square root of both sides in order to obtain the final side length of the missing side. Last, we need to use the perimeter formula to obtain the distance of the side lengths of the polygon.
Solution:
Now, that we have discussed the three methods used to calculate the perimeter of a triangle, we can use this information to solve the problem.
Recall how to find the perimeter of a triangle:
The given triangle has 
Recall the Pythagorean theorem:
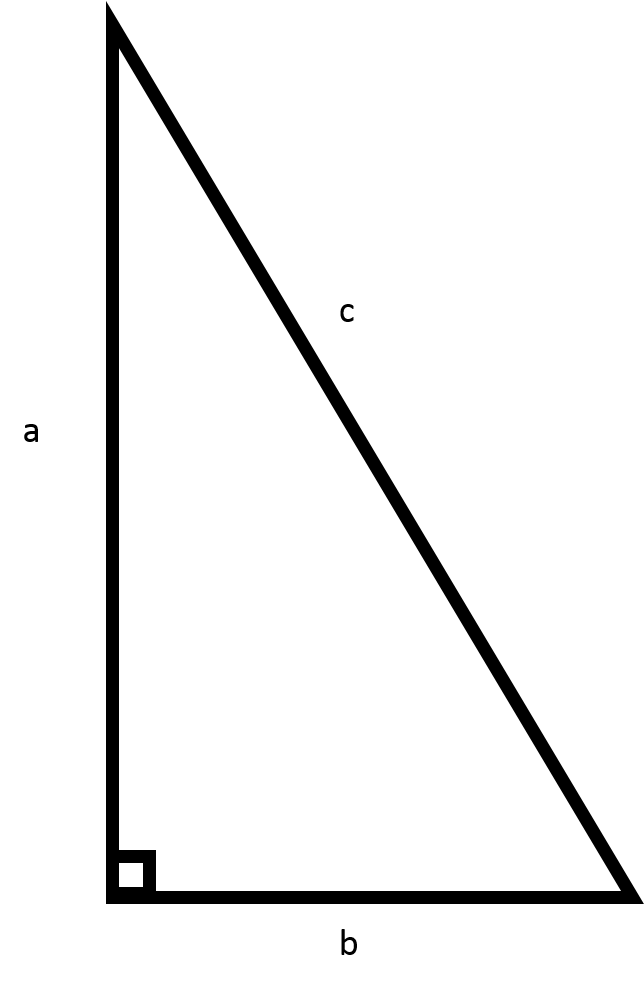
Since we are finding the length of side 
Plug in the values of 

Now, plug in all three values into the equation to find the perimeter. Use a calculator and round to 
A rectangle has an area of 
Explanation
For a rectangle, area is 



Let 

The area equation to solve becomes 

To factor, find two numbers the sum to -4 and multiply to -96. -12 and 8 will work:
x2 + 8x - 12x - 96 = 0
x(x + 8) - 12(x + 8) = 0
(x - 12)(x + 8) = 0
Set each factor equal to zero and solve:


Therefore the length is 


If the diagonal of a square is 
Explanation
The diagonal of a square is also the hypotenuse of a triangle whose legs are the sides of the square.

Thus, from knowing the length of the diagonal, we can use Pythagorean's Theorem to figure out the side lengths of the square.
We can now find the side length of the square in question.
Simplify.
Now, recall how to find the area of a square:
For the square in question,
Solve.
Find the perimeter.

Explanation
How do you find the perimeter of a right triangle?
There are three primary methods used to find the perimeter of a right triangle.
- When side lengths are given, add them together.
- Solve for a missing side using the Pythagorean theorem.
- If we know side-angle-side information, solve for the missing side using the Law of Cosines.
Method 1:
This method will show you how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle when all sides lengths are known. Consider the following figure:

If we know the lengths of sides 


Method 2:
In right triangles, we can calculate the perimeter of a triangle when we are provided only two sides. We can do this by using the Pythagorean theorem. Let's first discuss right triangles in a general sense. A right triangle is a triangle that has one 






If a triangle appears in this format, then we can use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for any missing side. This formula is written in the following manner:
We can rearrange it in a number of ways to solve for each of the sides of the triangle. Let's rearrange it to solve for the hypotenuse, 
Rearrange and take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
Now, let's use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for one of the legs, 
Subtract 
Take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
Last, let's use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for the adjacent leg, 
Subtract 
Take the square root of both sides.
Simplify.
It is important to note that we can only use the following formulas to solve for the missing side of a right triangle when two other sides are known:
After we find the missing side, we can use the perimeter formula to calculate the triangle's perimeter.
Method 3:
This method is the most complicated method and can only be used when we know two side lengths of a triangle as well as the measure of the angle that is between them. When we know side-angle-side (SAS) information, we can use the Law of Cosines to find the missing side. In order for this formula to accurately calculate the missing side we need to label the triangle in the following manner:

When the triangle is labeled in this way each side directly corresponds to the angle directly opposite of it. If we label our triangle carefully, then we can use the following formulas to find missing sides in any triangle given SAS information:
After, we calculate the right side of the equation, we need to take the square root of both sides in order to obtain the final side length of the missing side. Last, we need to use the perimeter formula to obtain the distance of the side lengths of the polygon.
Solution:
Now, that we have discussed the three methods used to calculate the perimeter of a triangle, we can use this information to solve the problem.

In order to find the perimeter, we must first find the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle.
Use Pythagorean's theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse:
Plug in the values of the lengths of the legs of the given triangle.
Now, recall how to find the perimeter of a triangle:
Plug in all the values of the sides of the triangle to find the perimeter.
Make sure to round to 

























































































