How to find the area of an equilateral triangle
Help Questions
Math › How to find the area of an equilateral triangle
Triangle A: A right triangle with sides length 

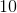
Triangle B: An equilateral triangle with side lengths 
Which triangle has a greater area?
Triangle B
Triangle A
The areas of the two triangles are the same.
There is not enough information given to determine which triangle has a greater area.
Explanation
The formula for the area of a right triangle is 


The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle is 

To determine which of the two areas is greater without using a calculator, rewrite the areas of the two triangles with comparable factors. Triangle A's area can be expressed as 



A circle is placed in an equilateral triangle as shown by the figure.

If the radius of the circle is 
Explanation

In order to find the area of the shaded region, you must first find the areas of the triangle and circle.
First, recall how to find the area of an equilateral triangle:
Substitute in the value of the side to find the area of the triangle.
Next, recall how to find the area of a circle.
Substitue in the value of the radius to find the area of the circle.
Finally, find the area of the shaded region.
Solve and round to two decimal places.
An equilateral triangle is placed on top of a regular hexagon as shown by the figure below.

Find the area of the entire figure.
Explanation

Recall that a regular hexagon can be divided into 
Since the extra equilateral triangle on top has the same side lengths as of the equilateral triangles made by dividing the hexagon, the entire figure has a total of 
Thus, to find the area of the entire figure, we must first find the area of the equilateral triangle.
Recall how to find the area of an equilateral triangle:
Plug in the length of a side of the equilateral triangle.
Now, multiply this area by 
Make sure to round to 
A circle with a radius of 


Find the area of the shaded region.
Explanation
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we must first find the area of the circle and the area of the equilateral triangle.
Recall how to find the area of a circle:
Plug in the given radius to find the area of the circle.
Next, recall how to find the area of an equilateral triangle:
Plug in the length of the side of the triangle to find the area.
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we will need to subtract the area of the circle from the area of the triangle.
Make sure to round to 
An equilateral triangle has sides of length 6cm. If the height of the triangle is 4.5cm what is the area of the triangle?
Explanation
To find the area of any triangle we can use the formula 1/2 (base x height) , that is the base times the height divided by two. It is important to remember any of the sides of an equaliateral triangle can be used as the base when the hieght is given. The area can be found by (6 x 4.5) divided by 2; which gives 13.5 square centimeters.
A circle is placed in an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure.

If the radius of the circle is 
Explanation

In order to find the area of the shaded region, you must first find the areas of the triangle and circle.
First, recall how to find the area of an equilateral triangle:
Substitute in the value of the side to find the area of the triangle.
Next, recall how to find the area of a circle.
Substitute in the value of the radius to find the area of the circle.
Finally, find the area of the shaded region.
Solve and round to two decimal places.
An equilateral triangle is placed on top of a regular hexagon as shown by the figure below.

Find the area of the entire figure.
The area of the entire figure cannot be determined by the given information.
Explanation

Recall that a regular hexagon can be divided into 
Since the extra equilateral triangle on top has the same side lengths as of the equilateral triangles made by dividing the hexagon, the entire figure has a total of 
Thus, to find the area of the entire figure, we must first find the area of the equilateral triangle.
Recall how to find the area of an equilateral triangle:
Plug in the length of a side of the equilateral triangle.
Now, multiply this area by 
Make sure to round to 
What is the area of an equilateral triangle with side 11?
Explanation
Since the area of a triangle is
you need to find the height of the triangle first. Because of the 30-60-90 relationship, you can determine that the height is 
Then, multiply that by the base (11).
Finally, divide it by two to get 52.4.
Find the area of an equilateral triangle whose perimeter is
Explanation
The formula for the perimeter of an equilateral triangle is:
Plugging in our values, we get
The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle is:
Plugging in our values, we get
A circle with a radius of 


Find the area of the shaded region.
Explanation
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we must first find the area of the circle and the area of the equilateral triangle.
Recall how to find the area of a circle:
Plug in the given radius to find the area of the circle.
Next, recall how to find the area of an equilateral triangle:
Plug in the length of the side of the triangle to find the area.
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we will need to subtract the area of the circle from the area of the triangle.
Make sure to round to 























































































