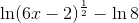Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
Help Questions
Math › Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
Solve for 
Explanation
First, let's begin by simplifying the left hand side.







Now, our expression is
From this, we can cancel out the 2's and an x from both sides.
Thus our answer becomes:

Determine whether each function represents exponential decay or growth.
a) decay
b) growth
a) growth
b) growth
a) decay
b) decay
a) growth
b) decay
Explanation
a)
This is exponential decay since the base, 


b)
This is exponential growth since the base, 

Solve:
Explanation
Rewrite the right side as base 2.
Replace the term into the equation.
With similar bases, we can set the exponents equal.
Subtract six from both sides.
Divide by negative three on both sides.
The answer is:
Solve the following function:

Explanation
You must get 


You must get the square root of both side to undue the exponent.
This leaves you with 
But since you square the 
This means your answer can be 

Solve:
None of the other answers.
Explanation
Combine the constants:
Isolate the exponential function by dividing:
Take the natural log of both sides:
Finally isolate x:
Condense the logarithm
Explanation
In order to condense the logarithmic expression, we use the following properties
As such
Solve for 
No solution
Explanation
Because both sides of the equation have the same base, set the terms equal to each other.
Add 9 to both sides:
Then, subtract 2x from both sides:
Finally, divide both sides by 3:
Match each function with its graph.
1.
2.
3.
a.
b.
c.
1.
2.
3.
1.
2.
3.
1.
2.
3.
1.
2.
3.
Explanation
For 





For 



For 



Completely expand this logarithm:
The answer is not present.
Explanation
We expand logarithms using the same rules that we use to condense them.
Here we will use the quotient property
and the power property
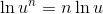
Use the quotient property:
Rewrite the radical:
Now use the power property:
Solve the equation for 
Explanation
The key to this is that 




Now take the natural log (ln) of the two equations.