How to find the length of the hypotenuse of a 45/45/90 right isosceles triangle : Pythagorean Theorem - Math
Card 1 of 244
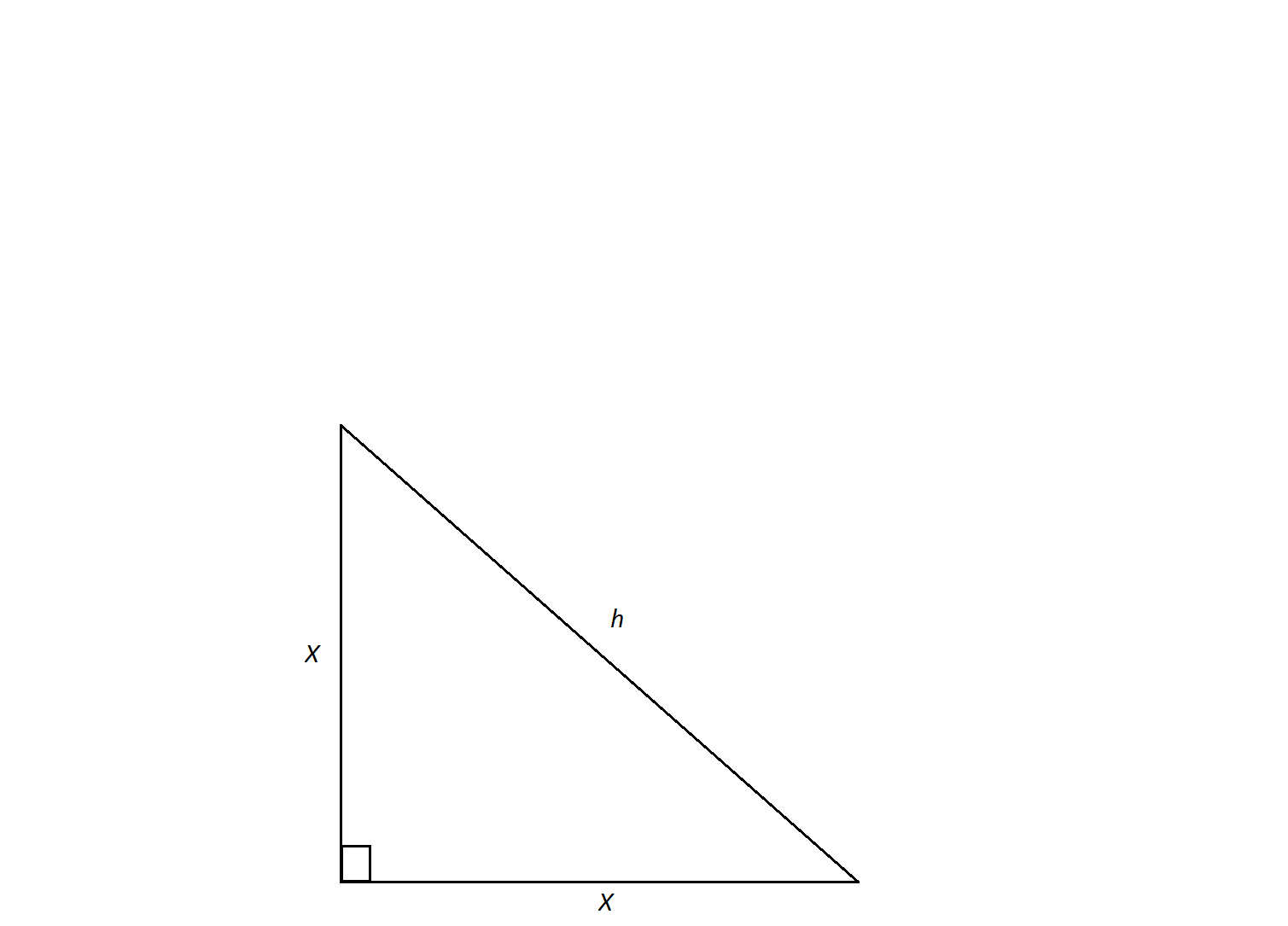
In an isosceles right triangle, two sides equal  . Find the length of side
. Find the length of side  .
.

In an isosceles right triangle, two sides equal 

Tap to reveal answer
This problem represents the definition of the side lengths of an isosceles right triangle. By definition the sides equal  ,
,  , and
, and  . However, if you did not remember this definition one can also find the length of the side using the Pythagorean theorem
. However, if you did not remember this definition one can also find the length of the side using the Pythagorean theorem  .
.




This problem represents the definition of the side lengths of an isosceles right triangle. By definition the sides equal 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
ABCD is a square whose side is  units. Find the length of diagonal AC.
units. Find the length of diagonal AC.
ABCD is a square whose side is 
Tap to reveal answer
To find the length of the diagonal, given two sides of the square, we can create two equal triangles from the square. The diagonal line splits the right angles of the square in half, creating two triangles with the angles of  ,
,  , and
, and  degrees. This type of triangle is a special right triangle, with the relationship between the side opposite the
degrees. This type of triangle is a special right triangle, with the relationship between the side opposite the  degree angles serving as x, and the side opposite the
degree angles serving as x, and the side opposite the  degree angle serving as
degree angle serving as  .
.
Appyling this, if we plug  in for
in for  we get that the side opposite the right angle (aka the diagonal) is
we get that the side opposite the right angle (aka the diagonal) is 
To find the length of the diagonal, given two sides of the square, we can create two equal triangles from the square. The diagonal line splits the right angles of the square in half, creating two triangles with the angles of 





Appyling this, if we plug 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The area of a square is  . Find the length of the diagonal of the square.
. Find the length of the diagonal of the square.
The area of a square is 
Tap to reveal answer
If the area of the square is  , we know that each side of the square is
, we know that each side of the square is  , because the area of a square is
, because the area of a square is  .
.
Then, the diagonal creates two  special right triangles. Knowing that the sides =
special right triangles. Knowing that the sides =  , we can find that the hypotenuse (aka diagonal) is
, we can find that the hypotenuse (aka diagonal) is 
If the area of the square is 


Then, the diagonal creates two 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →

In an isosceles right triangle, two sides equal  . Find the length of side
. Find the length of side  .
.

In an isosceles right triangle, two sides equal 

Tap to reveal answer
This problem represents the definition of the side lengths of an isosceles right triangle. By definition the sides equal  ,
,  , and
, and  . However, if you did not remember this definition one can also find the length of the side using the Pythagorean theorem
. However, if you did not remember this definition one can also find the length of the side using the Pythagorean theorem  .
.




This problem represents the definition of the side lengths of an isosceles right triangle. By definition the sides equal 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
ABCD is a square whose side is  units. Find the length of diagonal AC.
units. Find the length of diagonal AC.
ABCD is a square whose side is 
Tap to reveal answer
To find the length of the diagonal, given two sides of the square, we can create two equal triangles from the square. The diagonal line splits the right angles of the square in half, creating two triangles with the angles of  ,
,  , and
, and  degrees. This type of triangle is a special right triangle, with the relationship between the side opposite the
degrees. This type of triangle is a special right triangle, with the relationship between the side opposite the  degree angles serving as x, and the side opposite the
degree angles serving as x, and the side opposite the  degree angle serving as
degree angle serving as  .
.
Appyling this, if we plug  in for
in for  we get that the side opposite the right angle (aka the diagonal) is
we get that the side opposite the right angle (aka the diagonal) is 
To find the length of the diagonal, given two sides of the square, we can create two equal triangles from the square. The diagonal line splits the right angles of the square in half, creating two triangles with the angles of 





Appyling this, if we plug 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The area of a square is  . Find the length of the diagonal of the square.
. Find the length of the diagonal of the square.
The area of a square is 
Tap to reveal answer
If the area of the square is  , we know that each side of the square is
, we know that each side of the square is  , because the area of a square is
, because the area of a square is  .
.
Then, the diagonal creates two  special right triangles. Knowing that the sides =
special right triangles. Knowing that the sides =  , we can find that the hypotenuse (aka diagonal) is
, we can find that the hypotenuse (aka diagonal) is 
If the area of the square is 


Then, the diagonal creates two 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the length of the diagonal of a square with sides of  ?
?
What is the length of the diagonal of a square with sides of 
Tap to reveal answer
The diagonal cuts a square into two  right triangles with the legs of the triangle being the sides of the square and the hypotenuse is the diagonal of the triangle.
right triangles with the legs of the triangle being the sides of the square and the hypotenuse is the diagonal of the triangle.
Using Pythagorean Theorem we get:
 or
or 
The diagonal cuts a square into two 
Using Pythagorean Theorem we get:

← Didn't Know|Knew It →

Tap to reveal answer
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A right triangle has two sides of length  ; what is the correct formula for finding the length of the hypotenuse
; what is the correct formula for finding the length of the hypotenuse  ?
?
A right triangle has two sides of length 

Tap to reveal answer
The Pythagorean Theorem states that the sum of the squares of the sides of the triangle are equal to the square of the hypotenuse, summed up as  but for the case of right isoceles triangles where a and b are equal, it can be rewritten as:
but for the case of right isoceles triangles where a and b are equal, it can be rewritten as:
 ,
,
which simplifies to
 .
.

The Pythagorean Theorem states that the sum of the squares of the sides of the triangle are equal to the square of the hypotenuse, summed up as 

which simplifies to

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
 is a
is a  triangle.
triangle.



Using the Pythagorean Theorem, calculate the length of the hypotenuse of  .
.



Using the Pythagorean Theorem, calculate the length of the hypotenuse of 
Tap to reveal answer
The Pythagorean Theorem holds that, in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides. That is,

where  is the hypotenuse and
is the hypotenuse and  and
and  are the other two sides.
are the other two sides.
Here,  corresponds to
corresponds to  , and, since this is a
, and, since this is a  triangle, the length of
triangle, the length of  equals the length of
equals the length of  , so we know that
, so we know that  .
.
Apply the Pythagorean Theorem.







So the length of the hypotenuse is  .
.
The Pythagorean Theorem holds that, in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides. That is,
where 


Here, 





Apply the Pythagorean Theorem.
So the length of the hypotenuse is 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The following image is not to scale.
Find the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle:

The following image is not to scale.
Find the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle:
Tap to reveal answer
Because the problem states that this the triangle is a right triangle and provides the length of the two legs, the third side (hypotenuse) can be calculated using the Pythagorean Theorem.
 , where a and b can be arbitrarily chosen for either leg length and c represents the length of the hypotenuse.
, where a and b can be arbitrarily chosen for either leg length and c represents the length of the hypotenuse.



 but because the question requires to find the length of the hypotenuse, c cannot be a negative number. Therefore the final answer is +13.9.
but because the question requires to find the length of the hypotenuse, c cannot be a negative number. Therefore the final answer is +13.9.
Because the problem states that this the triangle is a right triangle and provides the length of the two legs, the third side (hypotenuse) can be calculated using the Pythagorean Theorem.


← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The following image is not to scale.
Find the length of the hypotenuse of the  right triangle.
right triangle.

The following image is not to scale.
Find the length of the hypotenuse of the 
Tap to reveal answer

45/45/90 triangles are always isosceles. This means that two of the legs of the triangle are congruent. In the figure, it's indicates which two sides are congruent.
From here, we can find the length of the hypotenuse through the Pythagorean Theorem. We can confirm this because the problem has given us no angle measures to perform trig functions with.






c also equals -2√2, but because the hypotenuse is a physical length, the value cannot be negative distance.
45/45/90 triangles are always isosceles. This means that two of the legs of the triangle are congruent. In the figure, it's indicates which two sides are congruent.
From here, we can find the length of the hypotenuse through the Pythagorean Theorem. We can confirm this because the problem has given us no angle measures to perform trig functions with.
c also equals -2√2, but because the hypotenuse is a physical length, the value cannot be negative distance.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Square  has a side length of
has a side length of  . What is the length of its diagonal?
. What is the length of its diagonal?
Square 

Tap to reveal answer
The answer can be found two different ways. The first step is to realize that this is really a triangle question, even though it starts with a square. By drawing the square out and adding the diagonal, you can see that you form two right triangles. Furthermore, the diagonal bisects two ninety-degree angles, thereby making the resulting triangles a  triangle.
triangle.
From here you can go one of two ways: using the Pythagorean Theorem to find the diagonal, or recognizing the triangle as a  triangle.
triangle.
- Using the Pythagorean Theorem
Once you recognize the right triangle in this question, you can begin to use the Pythagorean Theorem. Remember the formula:  , where
, where  and
and  are the lengths of the legs of the triangle, and
are the lengths of the legs of the triangle, and  is the length of the triangle's hypotenuse.
is the length of the triangle's hypotenuse.
In this case,  . We can substitute these values into the equation and then solve for
. We can substitute these values into the equation and then solve for  , the hypotenuse of the triangle and the diagonal of the square:
, the hypotenuse of the triangle and the diagonal of the square:







The length of the diagonal is  .
.
- Using Properties of
 Triangles
Triangles
The second approach relies on recognizing a  triangle. Although one could solve this rather easily with Pythagorean Theorem, the following method could be faster.
triangle. Although one could solve this rather easily with Pythagorean Theorem, the following method could be faster.
 triangles have side length ratios of
triangles have side length ratios of  , where
, where  represents the side lengths of the triangle's legs and
represents the side lengths of the triangle's legs and  represents the length of the hypotenuse.
represents the length of the hypotenuse.
In this case,  because it is the side length of our square and the triangles formed by the square's diagonal.
because it is the side length of our square and the triangles formed by the square's diagonal.
Therefore, using the  triangle ratios, we have
triangle ratios, we have  for the hypotenuse of our triangle, which is also the diagonal of our square.
for the hypotenuse of our triangle, which is also the diagonal of our square.
The answer can be found two different ways. The first step is to realize that this is really a triangle question, even though it starts with a square. By drawing the square out and adding the diagonal, you can see that you form two right triangles. Furthermore, the diagonal bisects two ninety-degree angles, thereby making the resulting triangles a 
From here you can go one of two ways: using the Pythagorean Theorem to find the diagonal, or recognizing the triangle as a 
- Using the Pythagorean Theorem
Once you recognize the right triangle in this question, you can begin to use the Pythagorean Theorem. Remember the formula: 



In this case, 

The length of the diagonal is 
- Using Properties of
Triangles
The second approach relies on recognizing a 




In this case, 
Therefore, using the 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the length of the hypotenuse of an isosceles right triangle with an area of  ?
?
What is the length of the hypotenuse of an isosceles right triangle with an area of 
Tap to reveal answer
Recall that an isosceles right triangle is also a  triangle. It has sides that appear as follows:
triangle. It has sides that appear as follows:

Therefore, the area of the triangle is:
 , since the base and the height are the same.
, since the base and the height are the same.
For our data, this means:

Solving for  , you get:
, you get:


So, your triangle looks like this:

Now, you can solve this with a ratio and easily find that it is  . You also can use the Pythagorean Theorem. To do the latter, it is:
. You also can use the Pythagorean Theorem. To do the latter, it is:


Now, just do your math carefully:

That is a weird kind of factoring, but it makes sense if you distribute back into the group. This means you can simplify:

Recall that an isosceles right triangle is also a 

Therefore, the area of the triangle is:

For our data, this means:
Solving for 
So, your triangle looks like this:

Now, you can solve this with a ratio and easily find that it is 
Now, just do your math carefully:
That is a weird kind of factoring, but it makes sense if you distribute back into the group. This means you can simplify:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
When the sun shines on a  pole, it leaves a shadow on the ground that is also
pole, it leaves a shadow on the ground that is also  . What is the distance from the top of the pole to the end of its shadow?
. What is the distance from the top of the pole to the end of its shadow?
When the sun shines on a 

Tap to reveal answer
The pole and its shadow make a right angle. Because they are the same length, they form an isosceles right triangle (45/45/90). We can use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the hypotenuse.  . In this case,
. In this case,  . Therefore, we do
. Therefore, we do  . So
. So  .
.
The pole and its shadow make a right angle. Because they are the same length, they form an isosceles right triangle (45/45/90). We can use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the hypotenuse. 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the length of the hypotenuse.

Find the length of the hypotenuse.

Tap to reveal answer
To find the hypotenuse of a triangle, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem. For any right triangle with leg lengths of  and
and  and a hypotenuse of
and a hypotenuse of  ,
,



Now, plug in the values of  and
and  from the question.
from the question.


Solve.

Simplify.

To find the hypotenuse of a triangle, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem. For any right triangle with leg lengths of 



Now, plug in the values of 

Solve.
Simplify.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the length of the hypotenuse.

Find the length of the hypotenuse.

Tap to reveal answer
To find the hypotenuse of a triangle, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem. For any right triangle with leg lengths of  and
and  and a hypotenuse of
and a hypotenuse of  ,
,



Now, plug in the values of  and
and  from the question.
from the question.


Solve.

Simplify.

To find the hypotenuse of a triangle, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem. For any right triangle with leg lengths of 



Now, plug in the values of 

Solve.
Simplify.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the length of the hypotenuse.

Find the length of the hypotenuse.

Tap to reveal answer
To find the hypotenuse of a triangle, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem. For any right triangle with leg lengths of  and
and  and a hypotenuse of
and a hypotenuse of  ,
,



Now, plug in the values of  and
and  from the question.
from the question.


Solve.

Simplify.

To find the hypotenuse of a triangle, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem. For any right triangle with leg lengths of 



Now, plug in the values of 

Solve.
Simplify.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the length of the hypotenuse.

Find the length of the hypotenuse.

Tap to reveal answer
To find the hypotenuse of a triangle, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem. For any right triangle with leg lengths of  and
and  and a hypotenuse of
and a hypotenuse of  ,
,



Now, plug in the values of  and
and  from the question.
from the question.


Solve.

Simplify.

To find the hypotenuse of a triangle, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem. For any right triangle with leg lengths of 



Now, plug in the values of 

Solve.
Simplify.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the length of the hypotenuse.

Find the length of the hypotenuse.

Tap to reveal answer
To find the hypotenuse of a triangle, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem. For any right triangle with leg lengths of  and
and  and a hypotenuse of
and a hypotenuse of  ,
,



Now, plug in the values of  and
and  from the question.
from the question.


Solve.

Simplify.

To find the hypotenuse of a triangle, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem. For any right triangle with leg lengths of 



Now, plug in the values of 

Solve.
Simplify.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →





