How to find if two acute / obtuse triangles are similar - Math
Card 1 of 104
The ratio of the side lengths of a triangle is 7:10:11. In a similar triangle, the middle side is 9 inches long. What is the length of the longest side of the second triangle?
The ratio of the side lengths of a triangle is 7:10:11. In a similar triangle, the middle side is 9 inches long. What is the length of the longest side of the second triangle?
Tap to reveal answer
Side lengths of similar triangles can be expressed in proportions. Establish a proportion comparing the middle and long sides of your triangles.
10/11 = 9/x
Cross multiply and solve for x.
10x = 99
x = 9.9
Side lengths of similar triangles can be expressed in proportions. Establish a proportion comparing the middle and long sides of your triangles.
10/11 = 9/x
Cross multiply and solve for x.
10x = 99
x = 9.9
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
 and
and  are similar triangles. The perimeter of Triangle A is 45” and the length of two of its sides are 15” and 10”. If the perimeter of Triangle B is 135” and what are lengths of two of its sides?
are similar triangles. The perimeter of Triangle A is 45” and the length of two of its sides are 15” and 10”. If the perimeter of Triangle B is 135” and what are lengths of two of its sides?


Tap to reveal answer
The perimeter is equal to the sum of the three sides. In similar triangles, each side is in proportion to its correlating side. The perimeters are also in equal proportion.
Perimeter A = 45” and perimeter B = 135”
The proportion of Perimeter A to Perimeter B is 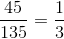 .
.
This applies to the sides of the triangle. Therefore to get the any side of Triangle B, just multiply the correlating side by 3.
15” x 3 = 45”
10” x 3 = 30“

The perimeter is equal to the sum of the three sides. In similar triangles, each side is in proportion to its correlating side. The perimeters are also in equal proportion.
Perimeter A = 45” and perimeter B = 135”
The proportion of Perimeter A to Perimeter B is 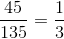
This applies to the sides of the triangle. Therefore to get the any side of Triangle B, just multiply the correlating side by 3.
15” x 3 = 45”
10” x 3 = 30“

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Two triangles are similar to each other. The bigger one has side lengths of 12, 3, and 14.
The smaller triangle's shortest side is 1 unit in length. What is the length of the smaller triangle's longest side?
Two triangles are similar to each other. The bigger one has side lengths of 12, 3, and 14.
The smaller triangle's shortest side is 1 unit in length. What is the length of the smaller triangle's longest side?
Tap to reveal answer
Because the triangles are similar, a ratio can be set up between the triangles' longest sides and shortest sides as such: 14/3 = x/1. Solving for x, we obtain that the shortest side of the triangle is 14/3 units long.
Because the triangles are similar, a ratio can be set up between the triangles' longest sides and shortest sides as such: 14/3 = x/1. Solving for x, we obtain that the shortest side of the triangle is 14/3 units long.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A triangle with two equal angles is called a(n) .
A triangle with two equal angles is called a(n) .
Tap to reveal answer
An isoceles triangle is a triangle that has at least two congruent sides (and therefore, at least two congruent angles as well).
An isoceles triangle is a triangle that has at least two congruent sides (and therefore, at least two congruent angles as well).
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Are the triangles similar? If so, solve for  . (Not drawn to scale).
. (Not drawn to scale).

Are the triangles similar? If so, solve for 

Tap to reveal answer
The triangles are similar because of the side-angle-side postulate.
Side: 
Angle: 
Side: 
The third side must also have a 2:3 ratio.

Cross-multiply, and solve for  .
.


The triangles are similar because of the side-angle-side postulate.
Side:
Angle:
Side:
The third side must also have a 2:3 ratio.
Cross-multiply, and solve for 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Are the triangles similar? If so, solve for  . (Not drawn to scale).
. (Not drawn to scale).
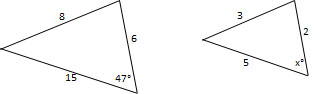
Are the triangles similar? If so, solve for 

Tap to reveal answer
The triangles are not similar, as proven by the side-side-side postulate.



The third side does not follow the same ratio of the other two, thus the triangles are not similar.
The triangles are not similar, as proven by the side-side-side postulate.
The third side does not follow the same ratio of the other two, thus the triangles are not similar.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Angle-Angle Postulate: if two angles of one triangle are equal to two corresponding angles of another triangle, the triangles must be similar.
In this example, the triangles share one angle, which must be equal. Additionally, the triangles contain segments that are parallel to each other. When two parallel lines are crossed by another line, the corresponding angles must be equal. Each angle in one triangle is congruent with its corresponding angle in the other triangle, indicating that they are similar.
Angle-Angle Postulate: if two angles of one triangle are equal to two corresponding angles of another triangle, the triangles must be similar.
In this example, the triangles share one angle, which must be equal. Additionally, the triangles contain segments that are parallel to each other. When two parallel lines are crossed by another line, the corresponding angles must be equal. Each angle in one triangle is congruent with its corresponding angle in the other triangle, indicating that they are similar.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The Side-Angle-Side Postulate considers two corresponding sides and the included angle. The included angles must be congruent, and the ratios of the two corresponding sides must be equal. If both criteria are satisfied, then the triangles are similar.
In this problem, there is a shared angle, making it equal for the two triangles. Now, consider the ratios of the sides.

Simplify the fractions.


because the ratios are equal, the triangles are similar by the Side-Angle-Side postulate.
The Side-Angle-Side Postulate considers two corresponding sides and the included angle. The included angles must be congruent, and the ratios of the two corresponding sides must be equal. If both criteria are satisfied, then the triangles are similar.
In this problem, there is a shared angle, making it equal for the two triangles. Now, consider the ratios of the sides.
Simplify the fractions.
because the ratios are equal, the triangles are similar by the Side-Angle-Side postulate.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The triangles are similar by the angle-angle postulate. 2 corresponding angles are equal to each other, therefore, the triangles must be similar.
The triangles are similar by the angle-angle postulate. 2 corresponding angles are equal to each other, therefore, the triangles must be similar.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The triangles are not similar, and it can be proven through the side-angle-side postulate. The SAS postulate states that two sides flanking a corresponding angle must be similar. In this case, the angles are congruent. However, the sides are not similar.



The triangles are not similar, and it can be proven through the side-angle-side postulate. The SAS postulate states that two sides flanking a corresponding angle must be similar. In this case, the angles are congruent. However, the sides are not similar.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →

If the two triangles shown above are similar, what is the measurements for angles  and
and  ?
?

If the two triangles shown above are similar, what is the measurements for angles 

Tap to reveal answer
In order for two triangles to be similar, they must have equivalent interior angles.
Thus, angle  degrees and angle
degrees and angle  degrees.
degrees.
In order for two triangles to be similar, they must have equivalent interior angles.
Thus, angle 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →

Using the similar triangles above, find a possible measurement for sides  and
and  .
.

Using the similar triangles above, find a possible measurement for sides 

Tap to reveal answer
Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The original ratio of side lengths is:

Thus a similar triangle will have this same ratio:

Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The original ratio of side lengths is:
Thus a similar triangle will have this same ratio:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Triangle one and triangle two are similar triangles. Triangle one has two sides with lengths  and
and  . What are possible measurements for the corresponding sides in triangle two?
. What are possible measurements for the corresponding sides in triangle two?
Triangle one and triangle two are similar triangles. Triangle one has two sides with lengths 

Tap to reveal answer
Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The ratio of side lengths for triangle one is:

Thus the ratio of side lengths for the second triangle must following this as well:
 , because both side lengths in triangle one have been multiplied by a factor of
, because both side lengths in triangle one have been multiplied by a factor of  .
.
Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The ratio of side lengths for triangle one is:
Thus the ratio of side lengths for the second triangle must following this as well:


← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Triangle one and triangle two are similar triangles. Triangle one has two sides with lengths  and
and  . What are possible measurements for the corresponding sides in triangle two?
. What are possible measurements for the corresponding sides in triangle two?
Triangle one and triangle two are similar triangles. Triangle one has two sides with lengths 

Tap to reveal answer
Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The ratio of triangle one is:

Therefore, looking at the possible solutions we see that one answer has the same ratio as triangle one.

Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The ratio of triangle one is:
Therefore, looking at the possible solutions we see that one answer has the same ratio as triangle one.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Triangle one and triangle two are similar triangles. Triangle one has two sides with lengths  and
and  . What are possible measurements for the corresponding sides in triangle two?
. What are possible measurements for the corresponding sides in triangle two?
Triangle one and triangle two are similar triangles. Triangle one has two sides with lengths 

Tap to reveal answer
Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The ratio of the side lengths in triangle one is:

If we take this ratio and look at the possible solutions we will see:


Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The ratio of the side lengths in triangle one is:
If we take this ratio and look at the possible solutions we will see:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Triangle one and triangle two are similar triangles. Triangle one has two sides with lengths  mm and
mm and  mm. What are possible measurements for the corresponding sides in triangle two?
mm. What are possible measurements for the corresponding sides in triangle two?
Triangle one and triangle two are similar triangles. Triangle one has two sides with lengths 

Tap to reveal answer
Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The ratio of triangle one is:

If we look at the possible solutions we will see that ratio that is in triangle one is also seen in the triangle with side lengths as follows:

Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The ratio of triangle one is:
If we look at the possible solutions we will see that ratio that is in triangle one is also seen in the triangle with side lengths as follows:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →

Using the triangle shown above, find possible measurements for the corresponding sides of a similar triangle?

Using the triangle shown above, find possible measurements for the corresponding sides of a similar triangle?
Tap to reveal answer
Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The ratio of the triangle is:

Applying this ratio we are able to find the lengths of a similar triangle.

Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The ratio of the triangle is:
Applying this ratio we are able to find the lengths of a similar triangle.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →

Using the triangle shown above, find possible measurements for the corresponding sides of a similar triangle?

Using the triangle shown above, find possible measurements for the corresponding sides of a similar triangle?
Tap to reveal answer
Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The ratio of the triangle is:

Applying this ratio we are able to find the lengths of a similar triangle.

Since the two triangles are similar, each triangles three corresponding sides must have the same ratio.
The ratio of the triangle is:
Applying this ratio we are able to find the lengths of a similar triangle.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Given:  and
and  .
.






True or false: It follows from the given information that  .
.
Given: 

True or false: It follows from the given information that 
Tap to reveal answer
As we are establishing whether or not  , then
, then  ,
,  , and
, and  correspond respectively to
correspond respectively to  ,
,  , and
, and  .
.
According to the Side-Angle-Side Similarity Theorem (SASS), if the lengths of two pairs of corresponding sides of two triangles are in proportion, and their included angles are congruent, then the triangles are similar.
 and
and  are corresponding sides, as are
are corresponding sides, as are  and
and  ;
;  and
and  are their included angles. Substituting
are their included angles. Substituting


Therefore,  , and corresponding sides are in proportion.
, and corresponding sides are in proportion.
 and
and  ; the included angles are congruent.
; the included angles are congruent.
The conditions of SASS are met, and it follows that  .
.
As we are establishing whether or not 






According to the Side-Angle-Side Similarity Theorem (SASS), if the lengths of two pairs of corresponding sides of two triangles are in proportion, and their included angles are congruent, then the triangles are similar.






Therefore, 


The conditions of SASS are met, and it follows that 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →







