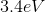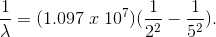Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics
Help Questions
GRE Subject Test: Physics › Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics
What is the energy of the photon emitted when a Hydrogen atom makes a transition from the 

Explanation


However, since the question asked what is the energy of the photon, it is the absolute value of the energy calculated above because of conservation of energy. The photon carries away the energy lost by the atom.
What is the energy of the photon emitted when a Hydrogen atom makes a transition from the 

Explanation


However, since the question asked what is the energy of the photon, it is the absolute value of the energy calculated above because of conservation of energy. The photon carries away the energy lost by the atom.
If a ground state particle is in a one-dimension square well, where is the probability of finding the particle equal to zero?
At the boundary.
In the middle.


None of these
Explanation
This is a fundamental concept question. For a ground state particle, the only place where the probability is equal to zero is at the boundary because the particle cannot be found there. He has to be in the box (not unlike a cat).
What is the energy of the photon emitted when a Hydrogen atom makes a transition from the 

Explanation


However, since the question asked what is the energy of the photon, it is the absolute value of the energy calculated above because of conservation of energy. The photon carries away the energy lost by the atom.
If a ground state particle is in a one-dimension square well, where is the probability of finding the particle equal to zero?
At the boundary.
In the middle.


None of these
Explanation
This is a fundamental concept question. For a ground state particle, the only place where the probability is equal to zero is at the boundary because the particle cannot be found there. He has to be in the box (not unlike a cat).
What wavelength will result in the most accurate measurement of the momentum of an electron?
Radio
Red light
X-ray
Gamma-ray
Infrared
Explanation
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that:

If a ground state particle is in a one-dimension square well, where is the probability of finding the particle equal to zero?
At the boundary.
In the middle.


None of these
Explanation
This is a fundamental concept question. For a ground state particle, the only place where the probability is equal to zero is at the boundary because the particle cannot be found there. He has to be in the box (not unlike a cat).
What wavelength will result in the most accurate measurement of the momentum of an electron?
Radio
Red light
X-ray
Gamma-ray
Infrared
Explanation
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that:

What wavelength will result in the most accurate measurement of the momentum of an electron?
Radio
Red light
X-ray
Gamma-ray
Infrared
Explanation
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that:

What color will be emitted in the 

Violet
Red
Yellow
Blue
Green
Explanation

Here, 




By inverting,