Optics - GRE Subject Test: Physics
Card 1 of 24
A beam of light travels through a medium with index of refraction  until it reaches an interface with another material, with index of refraction
until it reaches an interface with another material, with index of refraction 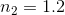 . No light is transmitted into the second material. At what angle (measured from the plane of the interface between the two materials) does the beam hit the second material?
. No light is transmitted into the second material. At what angle (measured from the plane of the interface between the two materials) does the beam hit the second material?
A beam of light travels through a medium with index of refraction 
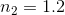
Tap to reveal answer
Total internal reflection occurs at the angle:

However, this angle is measured from a line normal to the plane of the interface; the angle we want, therefore, is  , which is
, which is  .
.
Total internal reflection occurs at the angle:
However, this angle is measured from a line normal to the plane of the interface; the angle we want, therefore, is 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A beam of light travels through a medium with index of refraction  until it reaches an interface with another material, with index of refraction
until it reaches an interface with another material, with index of refraction 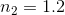 . No light is transmitted into the second material. At what angle (measured from the plane of the interface between the two materials) does the beam hit the second material?
. No light is transmitted into the second material. At what angle (measured from the plane of the interface between the two materials) does the beam hit the second material?
A beam of light travels through a medium with index of refraction 
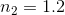
Tap to reveal answer
Total internal reflection occurs at the angle:

However, this angle is measured from a line normal to the plane of the interface; the angle we want, therefore, is  , which is
, which is  .
.
Total internal reflection occurs at the angle:
However, this angle is measured from a line normal to the plane of the interface; the angle we want, therefore, is 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The focal length of a thin convex lens is  . A candle is placed
. A candle is placed  to the left of the lens. Approximately where is the image of the candle?
to the left of the lens. Approximately where is the image of the candle?
The focal length of a thin convex lens is 

Tap to reveal answer
Because the object is beyond 2 focal lengths of the lens, the image must be between 1 and 2 focal lengths on the opposite side. Therefore, the image must be between  on the right side of the lens.
on the right side of the lens.
Alternatively, one can apply the thin lens equation:

Where  is the object distance
is the object distance  and
and  is the focal length
is the focal length  . Plug in these values and solve.
. Plug in these values and solve.



Because the object is beyond 2 focal lengths of the lens, the image must be between 1 and 2 focal lengths on the opposite side. Therefore, the image must be between 
Alternatively, one can apply the thin lens equation:
Where 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A candle  tall is placed
tall is placed  to the left of a thin convex lens with focal length
to the left of a thin convex lens with focal length  . What is the height and orientation of the image created?
. What is the height and orientation of the image created?
A candle 


Tap to reveal answer
First, find the image distance  from the thin lens equation:
from the thin lens equation:




Magnification of a lens is given by:

Where  and
and  are the image height and object height, respectively. The given object height is
are the image height and object height, respectively. The given object height is  , which we can use to solve for the image height:
, which we can use to solve for the image height:

Because the sign is negative, the image is inverted.
First, find the image distance 
Magnification of a lens is given by:
Where 


Because the sign is negative, the image is inverted.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Sirius is a binary star system, consisting of two white dwarfs with an angular separation of 3 arcseconds. What is the approximate minimum diameter lens needed to resolve the two stars in Sirius for an observation at  ?
?
Sirius is a binary star system, consisting of two white dwarfs with an angular separation of 3 arcseconds. What is the approximate minimum diameter lens needed to resolve the two stars in Sirius for an observation at 
Tap to reveal answer
The Rayleigh Criterion gives the diffraction limit on resolution of a particular lens at a particular wavelength:

Where theta is the angular resolution in radians,  is the wavelength of light, and
is the wavelength of light, and  is the diameter the lens in question. Solving for
is the diameter the lens in question. Solving for  and converting 3 arcseconds into radians, one can approximate the diameter to be about
and converting 3 arcseconds into radians, one can approximate the diameter to be about  :
:



The Rayleigh Criterion gives the diffraction limit on resolution of a particular lens at a particular wavelength:
Where theta is the angular resolution in radians, 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A beam of unpolarized light passes through two linear polarizers whose polarization axes are at an angle theta with each other. The light initially has an intensity  , and has an intensity of
, and has an intensity of  after passing through both polarizes. Find
after passing through both polarizes. Find  ?
?
A beam of unpolarized light passes through two linear polarizers whose polarization axes are at an angle theta with each other. The light initially has an intensity 


Tap to reveal answer
Initially unpolarized light passing though a linear polarizer decreases in intensity by a factor of two:

Malus's Law gives the change in intensity of polarized light passing through a linear polarizer in terms of the change in angle of polarization:

Combining the two equations, we get:

Solving for  :
:

Initially unpolarized light passing though a linear polarizer decreases in intensity by a factor of two:
Malus's Law gives the change in intensity of polarized light passing through a linear polarizer in terms of the change in angle of polarization:
Combining the two equations, we get:
Solving for 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The focal length of a thin convex lens is  . A candle is placed
. A candle is placed  to the left of the lens. Approximately where is the image of the candle?
to the left of the lens. Approximately where is the image of the candle?
The focal length of a thin convex lens is 

Tap to reveal answer
Because the object is beyond 2 focal lengths of the lens, the image must be between 1 and 2 focal lengths on the opposite side. Therefore, the image must be between  on the right side of the lens.
on the right side of the lens.
Alternatively, one can apply the thin lens equation:

Where  is the object distance
is the object distance  and
and  is the focal length
is the focal length  . Plug in these values and solve.
. Plug in these values and solve.



Because the object is beyond 2 focal lengths of the lens, the image must be between 1 and 2 focal lengths on the opposite side. Therefore, the image must be between 
Alternatively, one can apply the thin lens equation:
Where 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A candle  tall is placed
tall is placed  to the left of a thin convex lens with focal length
to the left of a thin convex lens with focal length  . What is the height and orientation of the image created?
. What is the height and orientation of the image created?
A candle 


Tap to reveal answer
First, find the image distance  from the thin lens equation:
from the thin lens equation:




Magnification of a lens is given by:

Where  and
and  are the image height and object height, respectively. The given object height is
are the image height and object height, respectively. The given object height is  , which we can use to solve for the image height:
, which we can use to solve for the image height:

Because the sign is negative, the image is inverted.
First, find the image distance 
Magnification of a lens is given by:
Where 


Because the sign is negative, the image is inverted.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Sirius is a binary star system, consisting of two white dwarfs with an angular separation of 3 arcseconds. What is the approximate minimum diameter lens needed to resolve the two stars in Sirius for an observation at  ?
?
Sirius is a binary star system, consisting of two white dwarfs with an angular separation of 3 arcseconds. What is the approximate minimum diameter lens needed to resolve the two stars in Sirius for an observation at 
Tap to reveal answer
The Rayleigh Criterion gives the diffraction limit on resolution of a particular lens at a particular wavelength:

Where theta is the angular resolution in radians,  is the wavelength of light, and
is the wavelength of light, and  is the diameter the lens in question. Solving for
is the diameter the lens in question. Solving for  and converting 3 arcseconds into radians, one can approximate the diameter to be about
and converting 3 arcseconds into radians, one can approximate the diameter to be about  :
:



The Rayleigh Criterion gives the diffraction limit on resolution of a particular lens at a particular wavelength:
Where theta is the angular resolution in radians, 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The focal length of a thin convex lens is  . A candle is placed
. A candle is placed  to the left of the lens. Approximately where is the image of the candle?
to the left of the lens. Approximately where is the image of the candle?
The focal length of a thin convex lens is 

Tap to reveal answer
Because the object is beyond 2 focal lengths of the lens, the image must be between 1 and 2 focal lengths on the opposite side. Therefore, the image must be between  on the right side of the lens.
on the right side of the lens.
Alternatively, one can apply the thin lens equation:

Where  is the object distance
is the object distance  and
and  is the focal length
is the focal length  . Plug in these values and solve.
. Plug in these values and solve.



Because the object is beyond 2 focal lengths of the lens, the image must be between 1 and 2 focal lengths on the opposite side. Therefore, the image must be between 
Alternatively, one can apply the thin lens equation:
Where 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A candle  tall is placed
tall is placed  to the left of a thin convex lens with focal length
to the left of a thin convex lens with focal length  . What is the height and orientation of the image created?
. What is the height and orientation of the image created?
A candle 


Tap to reveal answer
First, find the image distance  from the thin lens equation:
from the thin lens equation:




Magnification of a lens is given by:

Where  and
and  are the image height and object height, respectively. The given object height is
are the image height and object height, respectively. The given object height is  , which we can use to solve for the image height:
, which we can use to solve for the image height:

Because the sign is negative, the image is inverted.
First, find the image distance 
Magnification of a lens is given by:
Where 


Because the sign is negative, the image is inverted.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Sirius is a binary star system, consisting of two white dwarfs with an angular separation of 3 arcseconds. What is the approximate minimum diameter lens needed to resolve the two stars in Sirius for an observation at  ?
?
Sirius is a binary star system, consisting of two white dwarfs with an angular separation of 3 arcseconds. What is the approximate minimum diameter lens needed to resolve the two stars in Sirius for an observation at 
Tap to reveal answer
The Rayleigh Criterion gives the diffraction limit on resolution of a particular lens at a particular wavelength:

Where theta is the angular resolution in radians,  is the wavelength of light, and
is the wavelength of light, and  is the diameter the lens in question. Solving for
is the diameter the lens in question. Solving for  and converting 3 arcseconds into radians, one can approximate the diameter to be about
and converting 3 arcseconds into radians, one can approximate the diameter to be about  :
:



The Rayleigh Criterion gives the diffraction limit on resolution of a particular lens at a particular wavelength:
Where theta is the angular resolution in radians, 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A beam of light travels through a medium with index of refraction  until it reaches an interface with another material, with index of refraction
until it reaches an interface with another material, with index of refraction 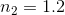 . No light is transmitted into the second material. At what angle (measured from the plane of the interface between the two materials) does the beam hit the second material?
. No light is transmitted into the second material. At what angle (measured from the plane of the interface between the two materials) does the beam hit the second material?
A beam of light travels through a medium with index of refraction 
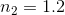
Tap to reveal answer
Total internal reflection occurs at the angle:

However, this angle is measured from a line normal to the plane of the interface; the angle we want, therefore, is  , which is
, which is  .
.
Total internal reflection occurs at the angle:
However, this angle is measured from a line normal to the plane of the interface; the angle we want, therefore, is 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The focal length of a thin convex lens is  . A candle is placed
. A candle is placed  to the left of the lens. Approximately where is the image of the candle?
to the left of the lens. Approximately where is the image of the candle?
The focal length of a thin convex lens is 

Tap to reveal answer
Because the object is beyond 2 focal lengths of the lens, the image must be between 1 and 2 focal lengths on the opposite side. Therefore, the image must be between  on the right side of the lens.
on the right side of the lens.
Alternatively, one can apply the thin lens equation:

Where  is the object distance
is the object distance  and
and  is the focal length
is the focal length  . Plug in these values and solve.
. Plug in these values and solve.



Because the object is beyond 2 focal lengths of the lens, the image must be between 1 and 2 focal lengths on the opposite side. Therefore, the image must be between 
Alternatively, one can apply the thin lens equation:
Where 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A candle  tall is placed
tall is placed  to the left of a thin convex lens with focal length
to the left of a thin convex lens with focal length  . What is the height and orientation of the image created?
. What is the height and orientation of the image created?
A candle 


Tap to reveal answer
First, find the image distance  from the thin lens equation:
from the thin lens equation:




Magnification of a lens is given by:

Where  and
and  are the image height and object height, respectively. The given object height is
are the image height and object height, respectively. The given object height is  , which we can use to solve for the image height:
, which we can use to solve for the image height:

Because the sign is negative, the image is inverted.
First, find the image distance 
Magnification of a lens is given by:
Where 


Because the sign is negative, the image is inverted.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Sirius is a binary star system, consisting of two white dwarfs with an angular separation of 3 arcseconds. What is the approximate minimum diameter lens needed to resolve the two stars in Sirius for an observation at  ?
?
Sirius is a binary star system, consisting of two white dwarfs with an angular separation of 3 arcseconds. What is the approximate minimum diameter lens needed to resolve the two stars in Sirius for an observation at 
Tap to reveal answer
The Rayleigh Criterion gives the diffraction limit on resolution of a particular lens at a particular wavelength:

Where theta is the angular resolution in radians,  is the wavelength of light, and
is the wavelength of light, and  is the diameter the lens in question. Solving for
is the diameter the lens in question. Solving for  and converting 3 arcseconds into radians, one can approximate the diameter to be about
and converting 3 arcseconds into radians, one can approximate the diameter to be about  :
:



The Rayleigh Criterion gives the diffraction limit on resolution of a particular lens at a particular wavelength:
Where theta is the angular resolution in radians, 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A reflective sphere has a diameter of  . The surface of the sphere makes a convex spherical mirror; what is its focal point?
. The surface of the sphere makes a convex spherical mirror; what is its focal point?
A reflective sphere has a diameter of 
Tap to reveal answer
The focal length of a spherical mirror is one half of the radius, which is one quarter of the diameter. In the case of convex mirrors, the focal point is considered behind the surface, which gives the answer its negative sign.
The focal length of a spherical mirror is one half of the radius, which is one quarter of the diameter. In the case of convex mirrors, the focal point is considered behind the surface, which gives the answer its negative sign.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A reflective sphere has a diameter of  . The surface of the sphere makes a convex spherical mirror; what is its focal point?
. The surface of the sphere makes a convex spherical mirror; what is its focal point?
A reflective sphere has a diameter of 
Tap to reveal answer
The focal length of a spherical mirror is one half of the radius, which is one quarter of the diameter. In the case of convex mirrors, the focal point is considered behind the surface, which gives the answer its negative sign.
The focal length of a spherical mirror is one half of the radius, which is one quarter of the diameter. In the case of convex mirrors, the focal point is considered behind the surface, which gives the answer its negative sign.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A beam of unpolarized light passes through two linear polarizers whose polarization axes are at an angle theta with each other. The light initially has an intensity  , and has an intensity of
, and has an intensity of  after passing through both polarizes. Find
after passing through both polarizes. Find  ?
?
A beam of unpolarized light passes through two linear polarizers whose polarization axes are at an angle theta with each other. The light initially has an intensity 


Tap to reveal answer
Initially unpolarized light passing though a linear polarizer decreases in intensity by a factor of two:

Malus's Law gives the change in intensity of polarized light passing through a linear polarizer in terms of the change in angle of polarization:

Combining the two equations, we get:

Solving for  :
:

Initially unpolarized light passing though a linear polarizer decreases in intensity by a factor of two:
Malus's Law gives the change in intensity of polarized light passing through a linear polarizer in terms of the change in angle of polarization:
Combining the two equations, we get:
Solving for 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A beam of light travels through a medium with index of refraction  until it reaches an interface with another material, with index of refraction
until it reaches an interface with another material, with index of refraction 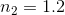 . No light is transmitted into the second material. At what angle (measured from the plane of the interface between the two materials) does the beam hit the second material?
. No light is transmitted into the second material. At what angle (measured from the plane of the interface between the two materials) does the beam hit the second material?
A beam of light travels through a medium with index of refraction 
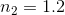
Tap to reveal answer
Total internal reflection occurs at the angle:

However, this angle is measured from a line normal to the plane of the interface; the angle we want, therefore, is  , which is
, which is  .
.
Total internal reflection occurs at the angle:
However, this angle is measured from a line normal to the plane of the interface; the angle we want, therefore, is 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →