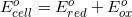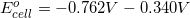Thermochemistry and Kinetics
Help Questions
AP Chemistry › Thermochemistry and Kinetics


The mechanism for decomposition of ozone is shown. What is the intermediate of the process?
Explanation
Intermediate is created and destroyed, and therefore does not appear on the net equation, which is 

The following galvanic cell is created:

Which of the following takes place at the cathode?
Gold ions receive electrons
Copper loses electrons
Gold loses electrons
Copper gains electrons
Explanation
Reduction always takes place at the cathode. This means that a substance is receiving electrons.
In the reaction, the gold ions are receiving electrons in order to create gold atoms. This takes place at the cathode.
Copper ions and gold are products, and will not be oxidized or reduced. Copper is reduced at the anode during this reaction.
How many grams of Cr can be obtained by the electrolysis of a Cr(NO3)3 if 10 amps are passed through the cell for 6 hours?
38.8 g
19.4 g
103 g
12.5 g
56.3 g
Explanation
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 




Explanation
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Given the reaction A + B → C. What is the rate law for the following experiment?
\[A\] \[B\] Rate
0.05 0.05 0.0125
0.05 0.1 0.0250
0.1 0.05 0.0125
rate = k\[A\]\[B\]2
rate = k\[A\]2\[B\]
rate = k\[A\]\[B\]
rate = k\[A\]
rate = k\[B\]
Explanation
When the concentration of B doubles, the rate doubles. Making this reaction first order in regards to compound B. When the concentration of A doubles the rate is unaffected, making this reaction zero order in regards to compound A. This leaves a rate law of rate=k\[B\]
The rate law of the reaction, 
![\textup{Rate} = k\left [ A\right ]^{3}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/770593/gif.latex)
Increasing the concentration of
Adding the catalyst to the reaction
Increasing the temperature of the reaction
Increasing the concentration of
Explanation
The reactant 

Chaning which of the following factors can alter the rate of a zero-order reaction?
Temperature
Increasing the concentration of reactants
Increasing the concentration of products
Decreasing the concentration of products
Explanation
A zero-order reaction has a rate of formation of product that is independent of changes in concentrations of any of the reactants; however, since the rate constant itself is dependent on temperture, changing the temperature can alter the rate.


The mechanism for decomposition of ozone is shown. What is the intermediate of the process?
Explanation
Intermediate is created and destroyed, and therefore does not appear on the net equation, which is 

Which of the following is a classic example of a first-order reaction?
Radioactive decay
A collision between 2 reactant molecules
A change in temperature
None of the other answers
Explanation
First order reactions have rates that are directly proportional to only 1 reactant. In radioactive decay, the rate of decrease of a radioactive material is proportional only to the amount of the material.
Which of the following is a law of thermodynamics?
ΔH (system) + ΔH (surroundings) = ΔH (universe)
ΔS (system) + ΔS (surroundings) = ΔS (universe)
ΔE (surroundings) = ΔE (system)
The entropy of the universe is always decreasing
Explanation
The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of the system and the entropy of the surroundings is equal to the entropy of the universe. The rest of the answer choices are not one of the fundamental laws of themodynamics.