Introduction for Reactions
Help Questions
AP Chemistry › Introduction for Reactions
What is the chemical formula of the salt formed when a chemist mixes solvated Potassium and Arsenic ions in solution?
Explanation
Potassium is a Group I element, so to get to a filled valence shell, it will lost one electron, yielding 
Arsenic is a Group 5 element, so it needs to gain three electrons to obtain a filled valence shell, yielding 
In order to balance out the charges, the resultant salt will be 
What is the balanced chemical equation for the combustion of butane 
Explanation
Combustion is the chemical reaction of a hydrocarbon with molecular oxygen, and it always produces carbon dioxide and water. Knowing the reactants and products, the unbalanced equation must be:
We start by balancing the hydrogens. Since there are 10 on the left and only 2 on the right, we put a coefficient of 5 on water.
Similarly, we balance carbons by putting a 4 on the carbon dioxide.
To find the number of oxygens on the right, we multiply the 4 coefficient by the 2 subscript on O (which gets us 8 oxygens) and then add the 5 oxygens from the 5 water molecules to get a total of 13. The needed coefficient for 
Because fractional coefficients are not allowed, we mutiply every coefficient by 2 to find our final reaction:
For single replacement reactions, which of the following sets of guidelines are most helpful?
Activity series
Solubility rules
Oxidation-reduction
Octet rule
Boyle's law
Explanation
When writing/balancing a single replacement reaction, make sure to consult the activity series, because that will tell us if a reaction will actually take place. Remember to look at the cations (metals and hydrogen) and where they are in relation to each other on the activity series. The higher one on the activity series is the most reactive; so if the cation by itself is the most reactive, it will replace the other cation and a reaction will occur. Boyle's law explains the inverse relationship between volume and pressure with respect to certain amount of an ideal gas at constant temperature.
What is the coefficient for 
Explanation
The best way to solve this problem is to try all the possible answers. When we try 8, 






What is the net ionic equation for the ion exchange reaction between ferrous sulfate and calcium iodide? Assume all compounds are soluble.
None of the available answers
Explanation
First, we must know what ferrous sulfate is. Ferrous refers to 


Calcium is a divatent cation and iodide is a monovalent anion, so their salt is 
Given that lithium is higher on the activity series than hydrogen, what should be seen when solid lithium and hydrochloric acid are mixed?
Bubbles
Increase in test tube's temperature
No change
Change in color
None of these
Explanation
Given that lithium is more reactive than hydrogen, expect a single replacement reaction to take place, so lithium will replace hydrogen.
All ionic compounds are solids at room temperature, which is why lithium chloride has the solid phase label. Remember that hydrogen is a diatomic element which is a gas a room temperature. When observing reactions in which gasses are produced from a solution, bubbles are seen. There is no indication whether this reaction is endothermic or exothermic, nor is there any information that suggests the reaction should change color.
Determine whether or not solid aluminum reacts with aqueous zinc chloride. If it does, determine the balanced equation for the reaction.
No reaction occurs
Explanation
When we check the activity series, it is fairly easy to see that aluminum metal is more reactive than zinc metal. So, in this case, the two metals undergo a redox reaction, where the aqueous 



Because 

We note that there are 2 chlorine atoms on the left and 3 chlorine atoms on the right. To balance, we use a 3 coefficient on the left and a 2 coefficient on the right. This gives a total of 6 chlorine atoms on eahc side.
However, now we have also increased the amounts of zinc and aluminum. We copy the necessary coefficients to balance those—2 for aluminum on the left, 3 for zinc on the right—and we are done:
What is used as guidelines to determine the phase labels for double displacement/double replacement reactions?
Solubility rules
Activity series
Oxidation-reduction
Octet rule
Huckel number
Explanation
For double displacement, the solubility rules determine the phase labels. Make sure the correct set of rules/guidelines for the type of reaction that is being written/balanced are used. The octet rule refers to the stability atoms achieve by filling their outer shell of electrons. Huckel number is 4n+2 where n is any integer, and is involved in assigning aromaticity.
Which of the following represents a combustion reaction?
Explanation
Combustion reactions always produce 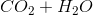
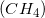

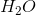
What type of reaction is shown above?
Double replacement
Single replacement
Combustion
Decomposition
Explanation
The typical double replacement reaction is as follows:
The anions are the chemical species being exchanged (both sulfur and chloride). Hence, the name double replacement is given to this particular reaction.