Entropy
Help Questions
AP Chemistry › Entropy
Which of the following does not represent an increase in entropy?
Boiling water
NaCl dissolving in water
Sublimation of CO2
Condensation of water on glass
Melting of mercury
Explanation
Of phases, from greatest to least entropy is gas>liquid>solid. Dissolving a salt into solution is an increase in entropy because the salt has greater space to move. The only decrease in entropy is condensation of water on glass (gas to liquid)
Which of the following reactions represents a negative change in entropy?
Water heating
Ice melting
Salt dissolving
Sublimation of dry ice
None of these represent a negative change in entropy
Explanation
Entropy for phases are Gas>Liquid>Solid. A salt dissolving into solution has a positive entropy change (the solution becomes more chaotic). Therefore all of the listed reactions are a positive change in entropy, making E the correct answer.
A reaction will reach equilibrium when the system's entropy .
is at a maximum
is at a minimum
is zero
entropy does not influence equilibrium at all
Explanation
Equilibrium is the basis of entropy, which can essentially be thought of as the distribution of energy in the system. For a reaction at a given temperature, the system's entropy will be at a maximum when it reaches equilbrium because this is the ideal energy state, and the forward and reverse reactions are occurring at a steady rate.
Which of the following scenarios describes a process with a negative entropy change?
Building a skyscraper
An igloo melting
Osmosis
A clean room becomes cluttered
Explanation
Entropy can be thought of as the tendency for a system to become disordered, or random. Osmosis, melting ice, and a clean room becoming dirty are all examples of entropy at work. Each of these processes will occur spontaneously without the input of outside energy or work.
If you make a skyscraper, you are incorporating a series of compounds and building products into a single, distinct formation. Think of it this way: what are the odds that mother nature would spontaneously build a building? This process is very ordered, which means that entropy of the universe has decreased.



What is the change in entropy for the following reaction?
Explanation
The change in entropy is calculated by:
When 



It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in entropy of a reaction.



What is the change in entropy for the following reaction?
Explanation
The change in entropy is calculated by:
When 



It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in entropy of a reaction.



What is the change in entropy for the following reaction?
Explanation
The change in entropy is calculated by:
When 



It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in entropy of a reaction.
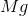

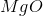
What is the change in entropy for the following reaction?
Explanation
The change in entropy is calculated by:
When 
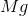

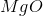
It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in entropy of a reaction.




What is the change in entropy for the following equation?
Explanation
The change in entropy is calculated by:
When 




It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in entropy of a reaction.




What is the entropy for the following reaction?
Explanation
The change in entropy is calculated by:
When 




It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in entropy of a reaction.













































































