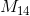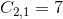Operations and Properties
Help Questions
Linear Algebra › Operations and Properties
Consider the matrix

Give cofactor 
Explanation
The minor of a matrix 



To find cofactor 



which is found by taking the product of the upper left and lower right entries and subtracting that of the other two entries:
In the cofactor equation, set 
Explanation
Let 
Cofactor 
Minor
The additive inverse of Minor
The reciprocal of Minor
The additive inverse of the reciprocal of Minor
None of the other choices gives a correct response.
Explanation
The minor of a matrix 



Set 

making the quantities equal.
Consider the matrix

Give cofactor 
Explanation
The minor of a matrix 



To find cofactor 



which is found by taking the product of the upper left and lower right entries and subtracting that of the other two entries:
In the cofactor equation, set 
True or False: If a 



True
False
Explanation
Since 






Find the rank of the following matrix.
Explanation
We need to get the matrix into reduced echelon form, and then count all the non all zero rows.
The rank is 2, since there are 2 non all zero rows.
Explanation
True or false: A matrix with five rows and four columns has as its inverse a matrix with four rows and five columns.
False
True
Explanation
Only a square matrix - a matrix with an equal number of rows and columns - has an inverse. Therefore, a matrix with five rows and four columns cannot even have an inverse.
Let 
Cofactor 
The additive inverse of Minor
Minor
The additive inverse of the reciprocal of Minor
The reciprocal of Minor
None of the other choices gives a correct response.
Explanation
The minor of a matrix 



Set 

Therefore, the cofactor 

Consider the matrix
Calculate the cofactor 
Explanation
The cofactor 


where 







The minor is therefore equal to
This is equal to the product of the upper-left and lower-right elements minus the product of the upper-right to lower-right elements, which is
Setting 


so