Carbonyl Reactions
Help Questions
Organic Chemistry › Carbonyl Reactions
What is the product of the following reaction?

Explanation
The reaction uses a Grignard reagent's nucleophilic carbon to attack the carbon in carbon dioxide. Following treatment with water the resulting molecule (a carboxylate anion, of the form 
What is the product of the following reaction?

Explanation
The reaction uses a Grignard reagent's nucleophilic carbon to attack the carbon in carbon dioxide. Following treatment with water the resulting molecule (a carboxylate anion, of the form 

What is the product of this reaction?

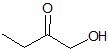
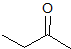
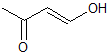

Explanation
This is a classic esterification reaction. Esterfication occurs when a carboxylic acid and an alcohol are reacted together. Only one answer choice is an ester.

What is the product of this reaction?





Explanation
This is a classic esterification reaction. Esterfication occurs when a carboxylic acid and an alcohol are reacted together. Only one answer choice is an ester.
What is the final organic product of the reaction shown?


III
I
II
IV
V
Explanation
First step: esterification
Second step: reduction
Third step: neutralization
Fourth step: oxidation to aldehyde
Fifth step: alkene metathesis
What is the final organic product of the reaction shown?


III
I
II
IV
V
Explanation
First step: esterification
Second step: reduction
Third step: neutralization
Fourth step: oxidation to aldehyde
Fifth step: alkene metathesis

Determine the major product of the given intramolecular aldol reaction.

II
I
III
IV
None of these
Explanation
Keep in mind the following principles: Cyclization is favored when a five/six-member ring may be formed. Addition at an aldehyde is favored relative to the same reaction at a ketone.
As a result, abstraction of a hydrogen bound to carbon 6 (an alpha-carbon) is favored since the resulting carbanion may attack the aldehyde (carbon 1) to form a six-member ring, resulting in compound II. Compound I results from abstracting a hydrogen from carbon 2, generating a carbanion which may then attack the ketone. Based on the latter of the above principles, this is a minor product.
What is the product of the reaction shown?

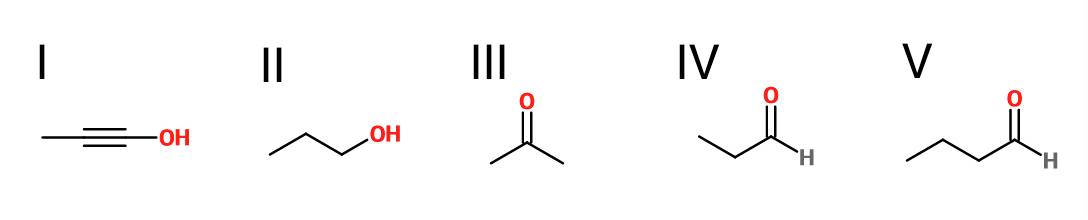
IV
I
II
III
V
Explanation
First step: bromination across the double bond
Second step: double dehydrohalogenation and removal of terminal alkyne hydrogen
Third step: neutralization of the molecule
Fourth/fifth step: hydroboration/oxidation, followed by keto/enol tautomerization

Determine the major product of the given intramolecular aldol reaction.

II
I
III
IV
None of these
Explanation
Keep in mind the following principles: Cyclization is favored when a five/six-member ring may be formed. Addition at an aldehyde is favored relative to the same reaction at a ketone.
As a result, abstraction of a hydrogen bound to carbon 6 (an alpha-carbon) is favored since the resulting carbanion may attack the aldehyde (carbon 1) to form a six-member ring, resulting in compound II. Compound I results from abstracting a hydrogen from carbon 2, generating a carbanion which may then attack the ketone. Based on the latter of the above principles, this is a minor product.
What is the product of the reaction shown?


IV
I
II
III
V
Explanation
First step: bromination across the double bond
Second step: double dehydrohalogenation and removal of terminal alkyne hydrogen
Third step: neutralization of the molecule
Fourth/fifth step: hydroboration/oxidation, followed by keto/enol tautomerization




