Help with Intermolecular Forces
Help Questions
Organic Chemistry › Help with Intermolecular Forces
Which of the following statements is true of alkynes?
Internal alkynes are more stable than terminal alkynes
Terminal alkynes are less acidic than internal alkynes
Alkynes are very soluble in water
The triple bond of an alkyne consists of three pi-bonds
Terminal alkynes are stronger compounds than internal alkynes
Explanation
The answer is "Internal alkynes are more stable than terminal alkynes" as it is the only true statement in regards to alkynes. Internal alkynes are more stable because they have a better conjugated system than terminal alkynes. A conjugated system is a system of a single bond, then a multiple bond, then a single bond, and so on. A conjugated system will always be more stable than an unconjugated system. It is evident that the internal alkyne follows the conjugated system and the terminal alkyne does not based on the picture below.

Which of the following will have the highest vapor pressure?
Pentane
Octane
Ethanol
Acetic acid
Explanation
The compound with the highest vapor pressure will have the weakest intermolecular forces. Octane and pentane have only London dispersion forces; ethanol and acetic acid have hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is much stronger than London dispersion forces. Because octane is larger than pentane, it will have more London dispersion forces, thus pentane has the weakest intermolecular forces.
Which of the following molecules has the highest boiling point?
Explanation

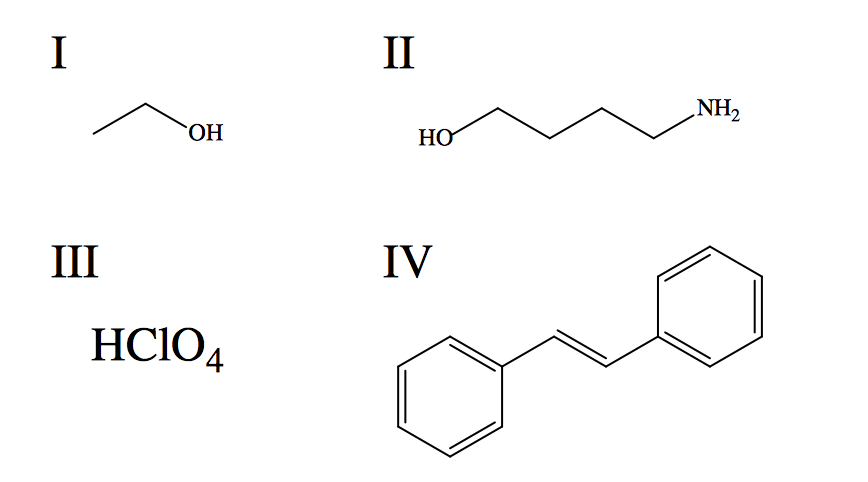
Rank the given species in terms of increasing aqueous solubility.
IV, II, I, III
II, IV, III, I
II, IV, I, III
IV, I, II, III
I, II, III, IV
Explanation
"Like dissolves like" is a good guiding principle to keep in mind in dealing with solubility trends. In other words, polar solvents will more easily dissolve polar solutes than nonpolar; and vice versa. Water is a polar solute that forms strong hydrogen bonds (intramolecular and intermolecular), which are energetically favorable interactions. Solutes that are also capable of hydrogen bonding are readily dissolved in water since they do not significantly disrupt the network of intramolecular hydrogen bonds. In order to predict the solubilities of the given compounds, it is useful to define the primary intermolecular forces each experiences when introduced to water. I: Hydrogen bonding dominates interaction between methanol and water (the two are miscible). II: Hydrogen bonding is present, but solubility is reduced by the presence of a multi-carbon chain, which adds significant nonpolar character to the structure. III: Perchloric acid is a strong acid (stronger than nitric acid and sulfuric acid), meaning it completely dissociates in water, forming verystrong ion-dipole interactions with water. Assessment of the given interactions leads to the correct trend of increasing solubility: IV, II, I, III.
Which of the following element(s) is/are not involved in hydrogen bonds?
I. Nitrogen
II. Oxygen
III. Chlorine
III only
I only
I and II
I and III
Explanation
Hydrogen bonds are strong intermolecular bonds between hydrogen and one of three atoms: nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine. A typical hydrogen bond occurs between a hydrogen atom on one molecule and one of the three atoms listed on another molecule. These bonds are reversible; however, they serve as strong interactions that stabilize a mixture of molecules.
Which of the following compounds are not able to form hydrogen bonds with water?
Alkanes
Carboxylic acids
Aldehydes
Ethers
Explanation
This question is rather straightforward, asking us which class of compounds will not form hydrogen bonds with water.
In order to form a hydrogen bond, whether it is intermolecular or intramolecular, there needs to be a partial positively charged hydrogen atom in between two other partial negative charged atoms. These atoms tend to be highly electronegative, and are usually either nitrogen, oxygen, or flourine.
Carboxylic acids will certainly engage in hydrogen bonds. The oxygen that is double bonded to the carbon has a partial negative charge, while the carbon has a partial positive charge, just as in aldehydes and ketones. Furthermore, the hydroxyl group attached to the carbon atom can also take part in hydrogen bonds.
Ethers are compounds in which an oxygen atom is situated between two carbon atoms via single bonds. Because there is a sufficient difference in the electronegativity of oxygen and carbon, ethers are also capable of hydrogen bonding.
Alkanes are hydrocarbons. This means that the only atoms found in these molecules are carbon and hydrogen. Because there is little difference in electronegativity between carbon and hydrogen, alkanes are incapable of hydrogen bonding with water.
Which of these accurately describes hydrogen bonds?
They play an important role in the solvent properties of water.
They may occur between hydrogen and chlorine.
They are not involved in protein structure.
They decrease the boiling point of water.
Explanation
A hydrogen bond forms when a hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule becomes attracted to an electronegative atom of another molecule (the electronegative atoms that may form hydrogen bonds are oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine). Hydrogen bonds are extremely important in water molecules. The hydrogen atoms attached to the electronegative oxygen atom in water can form hydrogen bonds with the oxygen atoms of other water molecules, giving water many of its properties as a solvent.
Hydrogen bonds are also important in protein secondary structure, which is defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds that form between the carbonyl oxygen and amine hydrogen atoms in the peptide backbone of proteins. Lastly, hydrogen bonds increase boiling point because they increase the strength of different substances.
Which of the following molecules would have the highest boiling point?
Explanation
Boiling point increases as the strength of intermolecular forces of a substance increases. The strength of intermolecular forces of a substance increases with a longer carbon chain, branching of elements off of the carbon chain, and the addition of 






Of the following intermolecular forces, which force would typically provide a pure compound with the highest possible boiling point?
Network covalent forces
Ionic bonding
Hydrogen bonding
Dipole-dipole interractions
Explanation
At first glance, we would be eager to jump to ionic bonding as the correct answer, as ionic bonding provides for very high boiling points. The correct answer, however, is a rare type of intermolecular force called network covalent bonding. Network covalent bonding is typically seen in diamond and quartz, and is a stronger intermolecular force than ionic bonding. Hydrogen bonding is the next strongest intermolecular force and also increases the boiling points of pure substances.
A researcher is trying to identify a molecule. He observes that there is a weak hydrophobic bond between adjacent molecules. He also notices a weak polar interaction between the molecules. Which of the following could be the identity of the molecule?
More than one of the above could be the identity of this molecule
Hexane
Hydrochloric acid
Hydrobromic acid
Explanation
Intermolecular bonds occur between adjacent molecules (recall that ‘inter’ means ‘between’). There are several types of intermolecular bonds. Hydrophobic bonds, or van der Waals forces, are the weakest intermolecular forces and occur between every molecule; therefore, all of the listed molecules in the question have hydrophobic bonds. Polar interactions between molecules occur between charged species or polar molecules. Recall that polar molecules are molecules that contain two or more atoms with very different electronegativities. The more electronegative atom pulls the electrons closer to itself, causing polarity in the molecule. The more electronegative atom will have a partial negative charge (due to the proximity to electrons) and the less electronegative atom will have a partial positive charge. This polarity in molecule allows for dipole-dipole interactions, a type of intermolecular force.
To solve this question, we need to determine which molecules are polar. Hexane, or 









