MCAT Social and Behavioral
Help Questions
MCAT Social and Behavioral Sciences › MCAT Social and Behavioral
Excerpt from "The Social Problems of American Farmers" by Kenyon L. Butterfield, 1905
Butterfield, Kenyon L. "The Social Problems of American Farmers." American Journal of Sociology 10.5 (1905): 606-22.
Perhaps the one great underlying social difficulty among American farmers is their comparatively isolated mode of life. The farmer's family is isolated from other families. A small city of perhaps twenty thousand population will contain from four hundred to six hundred families per square mile, whereas a typical agricultural community in a prosperous agricultural state will hardly average more than ten families per square mile. The farming class is isolated from other classes. Farmers, of course, mingle considerably in a business and political way with the men of their trading town and county seat; but, broadly speaking, farmers do not associate freely with people living under urban conditions and possessing other than the rural point of view. It would be venturesome to suggest very definite generalizations with respect to the precise influence of these conditions, because, so far as the writer is aware, the psychology of isolation has not been worked out. But two or three conclusions seem to be admissible, and for that matter rather generally accepted.
The well-known conservatism of the farming class is doubtless largely due to class isolation. Habits, ideas, traditions, and ideals have long life in the rural community. Changes come slowly. There is a tendency to tread the well-worn paths. The farmer does not easily keep in touch with rapid modern development, unless the movements or methods directly affect him. Physical agencies which improve social conditions, such as electric lights, telephones, and pavements, come to the city first. The atmosphere of the country speaks peace and quiet. Nature's routine of sunshine and storm, of summer and winter, encourages routine and repetition in the man who works with her…
There is time to brood over wrongs, real and imaginary. Personal prejudices often grow to be rank and coarse-fibered. Neighborhood feuds are not uncommon and are often virulent. Leadership is made difficult and sometimes impossible. It is easy to fall into personal habits that may mark off the farmer from other classes of similar intelligence, and that bar him from his rightful social place.
It would, however, be distinctly unfair to the farm community if we did not emphasize some of the advantages that grow out of the rural mode of life. Farmers have time to think, and the typical American farmer is a man who has thought much and often deeply. A spirit of sturdy independence is generated, and freedom of will and of action is encouraged. Family life is nowhere so educative as in the country. The whole family cooperates for common ends, and in its individual members are bred the qualities of industry, patience, and perseverance. The manual work of the schools is but a makeshift for the old-fashioned training of the country-grown boy. Country life is an admirable preparation for the modern industrial and professional career.
According to the author, life on a farm can be extremely based around the family. It is in the family that most children learn morals from their parents. Kohlberg described several stages of moral development. In which of the following stages are most adults found?
Conventional
Pre-conventional
Post-conventional
Concrete operational
Explanation
Most adults and adolescents are found on the conventional stage of Kohlberg’s Stages of Moral Reasoning. In this stage, people generally follow the rules because they believe it will benefit themselves and the society more than breaking the rules. Those in the post-conventional stage follow the rules based solely on their moral ideas of right and wrong, not necessarily the consequences. Most people do not reach this stage. Children are found in the pre-conventional stage. The concrete operational stage is part of Piaget’s stages of development.
Russian psychologist Ivan Pavlov extensively studied learning in animals. Most significantly, he contributed to the idea that is currently referred to as classical conditioning. Many know him from the popularly cited Pavlovian dog study from the greater experiment known as Lectures on the Function of the Principle Digestive Glands (1897).
In the Pavlovian dog experiment, Pavlov paired a neutral stimulus with a pleasurable one. The neutral stimulus was the ringing sound of a metronome, while the pleasurable stimulus was food. Pavlov never fed his dogs without ringing the metronome first, and as a result, his dogs would later salivate upon hearing the sound of the metronome. This learning process is known as conditioning, and this this specific instance, classical conditioning.
Later, Pavlov began ringing the metronome without feeding the dogs. As a result, the dogs eventually stopped salivating upon hearing the metronome. This is known as extinction. Finally, upon reintroducing the metronome/food pairing, the dogs quickly began salivating again, which is known as spontaneous recovery.
The passage describes classical conditioning, which of the following best describes the relationship between classical conditioning and operant conditioning.
Classical conditioning pairs a behavior with an arbitrary stimulus, while operant conditioning pairs a behavior with a punishment or a reward.
Operant conditioning pairs a behavior with an arbitrary stimulus, while classical conditioning pairs a behavior with a punishment or a reward.
Both operant and classical conditioning pair a behavior with a punishment or a reward.
Both operant and classical conditioning pair a behavior with an arbitrary stimulus.
Explanation
Classical conditioning, as described in the passage, pairs a stimulus (e.g. the sound of a bell) with another behavior (e.g. receiving food). Eventually, according to the precepts of classical conditioning the bell will elicit a response (e.g. salivating in anticipation of receiving food). On the other hand, operant conditioning is a type of learning that is mediated by punishments and rewards/reinforcements. The punishment or reinforcement either encourages or discourages the learner from repeating a certain behavior.
From most basic to most complex, what is the correct order of movement types that occur during human development?
Reflexive, rudimentary, fundamental, specialized, lifelong application
Rudimentary, reflexive, fundamental, specialized, lifelong application
Reflexive, fundamental, rudimentary, specialized, lifelong application
Reflexive, rudimentary, specialized, fundamental, lifelong application
Explanation
The earliest movements humans perform during motor development are known as reflexive movements. These are followed by rudimentary movements, and then fundamental movements. The final stage is known as the lifelong application stage in which movements are continually adjusted and refined for efficiency. Last, the specialized movement stage is sometimes broken up into two stages: the transitional substage and the application substage; however, none of the answer choices mention either of those substages.
Alan Baddeley's model for working memory is comprised of four parts. Which of the following is not one of the four components of the model?
Semantic buffer
Phonological loop
Visuospatial sketchpad
Episodic buffer
Central executive
Explanation
Baddeley's Model of Working Memory consists of the following four parts: the central executive, phonological loop, episodic buffer, and visuospatial sketchpad. The semantic buffer does not exist in his model, and is the correct answer. The central executive acts like the "boss" of the other three components and directs our attention. The phonologial loop gives us the ability to temporarily hold spoken or written information in our memory through repetition; for example, you use this when trying to remember a phone number. The visuospatial sketchpad allows us to temporarily remember visuospatial information via mental images. For example, you may use this when navigating through a room to remember there is a chair to your left even when it is out of sight. Last, the episodic buffer is used to relate current experiences to memories of the past. For example, if you see a house and realize it looks similar to your childhood home.
Jimmy and Nate both volunteer at the dog pound. Jimmy loves animals of all kinds and loves the chance to be around dogs. Nate doesn’t particularly like animals, but he needs service hours for a club he is in at school.
The managers of the dog pound offer to start paying Jimmy and Nate. Who is more likely to experience a decrease in job satisfaction?
Jimmy; the intrinsic value of being with dogs is decreased by the overjustification of being paid
Jimmy; the extrinsic value of being with dogs is decreased by the overjustification of being paid
Nate; the intrinsic value of being with dogs is decreased by the overjustification of being paid
Nate; the extrinsic value of being with dogs is decreased by the overjustification of being paid
Explanation
The value of being with dogs is an intrinsic value for Jimmy; he genuinely likes being with them. Nate’s value associated with being with dogs has an extrinsic value of obtaining service hours. Overjustification is a sociological effect that occurs when intrinsic value decreases because extrinsic values, such as money, are introduced to the situation. Since Jimmy’s value is highly intrinsic, he is more likely to experience the effects of overjustification.
American psychologist B.F. Skinner is best known for his work in operant conditioning.Like all great academics, Skinner was not without influence. His work was inspired primarily based on Thorndike's Law of Effect. This law states that behaviors paired with positive consequences/effects/rewards are likely to be repeated, while behaviors paired with unpleasant consequences/effects/rewards are likely to be avoided.
While this principal inspired Skinner, he researched it further and named this principle operant conditioning. Skinner's research showed that conditioning/learning could occur through the use of punishments and rewards. The two important concepts of operant conditioning include punishment and reinforcement. Finally, Skinner also discussed the possibility of a neutral operant, which neither increased nor decreased the likelihood of a behavior occurring.
In operant conditioning, what is the term used to describe taking away a desired stimulus in order to decrease the likelihood of a behavior occurring?
Negative punishment
Positive punishment
Negative reinforcement
Positive reinforcement
Explanation
Reinforcement always acts to increase the likelihood of a behavior occurring; therefore, "positive reinforcement" and "negative reinforcement" can be eliminated. "Positive punishment" acts to add an undesirable stimulus in order to decrease the likelihood of a behavior occurring. On the other hand, "negative punishment" acts to remove a desired stimulus to reduce the likelihood of a behavior occurring, like the question asks.
Excerpt from "The Chicago Employment Agency and the Immigrant Worker," Grace Abbott, American Journal of Sociology 1908 14:3, 289-305
In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, immigrants poured into the United States without knowledge of English or American customs. They were also usually unaware of the local cost of living or typical wage. These immigrants turned to employment agencies that would help them find work, for a fee. The extreme dependence of immigrants on the employment agencies coupled with their general ignorance of the American system brought about an ethical dilemma for the employment agent in which it became very easy to take advantage of people seeking a job. This resulted in an extreme prejudice directed at immigrants by the American employment system. A study was conducted in the early 1900s gauged the degree of corruption among employment agents and the results of this study have been provided (see Tables 1, 2, and 3)
Table 1
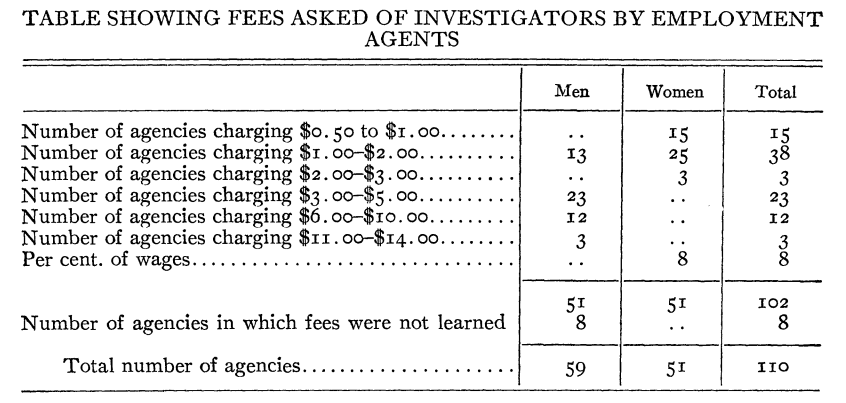
Table 2

Table 3

People are often concerned with meeting basic needs, such as food and clothing, before pursuing recreational or religious desires. Who is best known for describing this motivational prioritization?
Maslow
Piaget
Erickson
Pavlov
Explanation
Abraham Maslow is well known for the “Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.” It describes a prioritization of human needs ranging from homeostasis (breathing, staying warm), making up the broad bottom of the pyramid, to self-transcendence at the top. Piaget and Erickson both studied human development. Pavlov’s motivational theories centered around classical conditioning.
Excerpt from "The Social Problems of American Farmers" by Kenyon L. Butterfield, 1905
Butterfield, Kenyon L. "The Social Problems of American Farmers." American Journal of Sociology 10.5 (1905): 606-22.
Perhaps the one great underlying social difficulty among American farmers is their comparatively isolated mode of life. The farmer's family is isolated from other families. A small city of perhaps twenty thousand population will contain from four hundred to six hundred families per square mile, whereas a typical agricultural community in a prosperous agricultural state will hardly average more than ten families per square mile. The farming class is isolated from other classes. Farmers, of course, mingle considerably in a business and political way with the men of their trading town and county seat; but, broadly speaking, farmers do not associate freely with people living under urban conditions and possessing other than the rural point of view. It would be venturesome to suggest very definite generalizations with respect to the precise influence of these conditions, because, so far as the writer is aware, the psychology of isolation has not been worked out. But two or three conclusions seem to be admissible, and for that matter rather generally accepted.
The well-known conservatism of the farming class is doubtless largely due to class isolation. Habits, ideas, traditions, and ideals have long life in the rural community. Changes come slowly. There is a tendency to tread the well-worn paths. The farmer does not easily keep in touch with rapid modern development, unless the movements or methods directly affect him. Physical agencies which improve social conditions, such as electric lights, telephones, and pavements, come to the city first. The atmosphere of the country speaks peace and quiet. Nature's routine of sunshine and storm, of summer and winter, encourages routine and repetition in the man who works with her…
There is time to brood over wrongs, real and imaginary. Personal prejudices often grow to be rank and coarse-fibered. Neighborhood feuds are not uncommon and are often virulent. Leadership is made difficult and sometimes impossible. It is easy to fall into personal habits that may mark off the farmer from other classes of similar intelligence, and that bar him from his rightful social place.
It would, however, be distinctly unfair to the farm community if we did not emphasize some of the advantages that grow out of the rural mode of life. Farmers have time to think, and the typical American farmer is a man who has thought much and often deeply. A spirit of sturdy independence is generated, and freedom of will and of action is encouraged. Family life is nowhere so educative as in the country. The whole family cooperates for common ends, and in its individual members are bred the qualities of industry, patience, and perseverance. The manual work of the schools is but a makeshift for the old-fashioned training of the country-grown boy. Country life is an admirable preparation for the modern industrial and professional career.
According to the author, life on a farm can be extremely based around the family. It is in the family that most children learn morals from their parents. Kohlberg described several stages of moral development. In which of the following stages are most adults found?
Conventional
Pre-conventional
Post-conventional
Concrete operational
Explanation
Most adults and adolescents are found on the conventional stage of Kohlberg’s Stages of Moral Reasoning. In this stage, people generally follow the rules because they believe it will benefit themselves and the society more than breaking the rules. Those in the post-conventional stage follow the rules based solely on their moral ideas of right and wrong, not necessarily the consequences. Most people do not reach this stage. Children are found in the pre-conventional stage. The concrete operational stage is part of Piaget’s stages of development.
Jimmy and Nate both volunteer at the dog pound. Jimmy loves animals of all kinds and loves the chance to be around dogs. Nate doesn’t particularly like animals, but he needs service hours for a club he is in at school.
The managers of the dog pound offer to start paying Jimmy and Nate. Who is more likely to experience a decrease in job satisfaction?
Jimmy; the intrinsic value of being with dogs is decreased by the overjustification of being paid
Jimmy; the extrinsic value of being with dogs is decreased by the overjustification of being paid
Nate; the intrinsic value of being with dogs is decreased by the overjustification of being paid
Nate; the extrinsic value of being with dogs is decreased by the overjustification of being paid
Explanation
The value of being with dogs is an intrinsic value for Jimmy; he genuinely likes being with them. Nate’s value associated with being with dogs has an extrinsic value of obtaining service hours. Overjustification is a sociological effect that occurs when intrinsic value decreases because extrinsic values, such as money, are introduced to the situation. Since Jimmy’s value is highly intrinsic, he is more likely to experience the effects of overjustification.
Excerpt from “Institutional Competition,” Edward A. Ross, American Journal of Sociology 1919 25:2, 171-184
The first impulse of any organization or institution on the appearance of a serious competitor is to destroy competition. The "trust" regularly cuts the prices of its products to a point below cost of production in localities in which an "independent" seeks to sell. A shipping combine will have "fighting ships" which are called into play when a new steamship line enters their trade. As soon as the competitor announces a sailing date the combine advertises a steamer to sail on or near this date and offers a freight rate below the actual cost of carriage. In this way the competitor is prevented from securing a cargo.
The highest social class hobbles by minute sumptuary regulations the classes, which aspire to come up abreast of it. In feudal Japan, for example, one might not use his money as he pleased. The farmer, craftsman, or shopkeeper could not build a house as he liked or procure himself such articles of luxury as his taste might incline him to buy. The richest commoner might not order certain things to be made for him, might not imitate the habits or assume the privileges of his betters. Although urged on economic grounds, sumptuary restrictions are doubtless intended to protect the monopoly of prestige by the higher social orders.
The spread of anti-slavery feeling among the producing people of the North during the generation before the American Civil War was due to their perception that slavery is a menace to the free-labor system. In accounting for the early abolition of slavery in Massachusetts John Adams remarks: "Argument might have had some weight ... but the real cause was the multiplication of laboring white people who would not longer suffer the rich to employ these sable rivals so much to their injury."
The whole history of religious persecution is the history of an organization trying to establish itself as a monopoly by ruthless destruction of the spokesmen of competing doctrines and movements. In Diocletian's time Roman religious beliefs were weak while the Christian beliefs were vigorous and spreading. In desperation the old system made a ferocious attempt to exterminate all Christians. A thousand years later the church stamped certain sects out of existence and strangled heresies in the cradle. Says Coulton:
…What Darwin took at first for a smooth unbroken grassland proved, on nearer examination, to be thick-set with tiny self-sown firs, which the cattle regularly cropped as they grew. Similarly, that which some love to picture as the harmonious growth of one great body through the Middle Ages is really a history of many divergent opinions violently strangled at birth; while hundreds more, too vigorous to be killed by the adverse surroundings, and elastic enough to take something of the outward color of their environment, grew in spite of the hierarchy into organisms which, in their turn, profoundly modified the whole constitution of the Church. If the mediaeval theory and practice of persecution had still been in full force in the eighteenth century in England, nearly all the best Wesleyans would have chosen to remain within the Church rather than to shed blood in revolt; and the rest would have been killed off like wild beasts. The present unity of Romanism so far as it exists, is due less to tact than to naked force.
Suppose that Steve volunteers to help out on his uncle’s cargo ship. After two weeks of working for free, Steve’s uncle decides to start paying Steve. Steve is excited to be paid, but he finds the work much less satisfying than it was before. What motivational principle does this example best demonstrate?
Overjustification
Extrinsic motivation
Intrinsic motivation
Delayed gratifification
Explanation
Overjustification is the principle best illustrated in this example. Overjustification is defined as the effect of an extrinsic reward diminishing an intrinsic reward. In this example, Steve at first finds the work aboard his Uncle’s ship satisfying (intrinsic), but when he starts receiving pay (extrinsic), that satisfaction decreases. Thus, overjustification is best illustrated. Delayed gratification is not demonstrated in this example; it assumes that accessing a reward later will lead to more satisfaction than now.