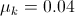Friction and Normal Force
Help Questions
MCAT Physical › Friction and Normal Force
When the force applied to a moving object is equal and opposite the force of kinetic friction, what happens to the object?
It moves with a constant velocity
It stops
It accelerates
It decelerates
It changes direction
Explanation
It is important to understand the difference between static and kinetic friction. When an object is at rest, it takes more force to get it to start moving than to keep it moving. If you match the amount of static friction that can be generated when the object is at rest, it will not move because there is zero net force; the force applied must be greater than the static friction in order to initiate motion. Once the object begins moving, the force required to keep it moving decreases. If you match the force of kinetic friction, the object moves at a constant velocity because there is again no net force. Any more force will cause acceleration, while any less will cause deceleration.
A 3kg book slides towards the right along a frictionless horizontal surface with initial velocity 5m/s, then suddenly encounters a long rough section with kinetic friction coefficient 

5.1m
4.4m
3.7m
2.9m
6.5m
Explanation
We'll need to use the kinematic equation 

-
Find the normal force on the book,
.
-
Plug this normal force into
to solve for frictional force.
-
Find the acceleration caused by this frictional force, with
.
Step 1 gives 


Returning to the original kinematic equation, 
Rearranging to solve for d gives
A 50kg block resting on the ground experiences an upward acceleration of 4m/s2. What is the normal force acting on the block?
300 N
200 N
700 N
500 N
Explanation
The block experiences the force of gravity, plus the force of the upward acceleration
If the block is resting on the ground, then its total force must be zero, and the normal force must cancel out the net force above. The normal force is 300N.
A 2kg box is at the top of a ramp at an angle of 60o. The top of the ramp is 30m above the ground. The box is sitting still while at the top of the ramp, and is then released.
Imagine that the net force on the box is 16.5N when sliding down the ramp. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction for the box?
The kinetic coefficient of friction cannot be determined while the box is moving
Explanation
Since the box is moving when the net force on the box is determined, we can calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction for the box. The first step is determining what the net force on the box would be in the absence of friction. The net force on the box is given by the equation 
The difference between the frictionless net force and the net force with friction is 0.8N. This means that the force of kinetic friction on the box is 0.8N, acting opposite the direction of motion. Knowing this, we can solve for the coefficient of kinetic friction using the equation
A 
The block will suddenly jerk to the right, and then stop
The block will move to the right proportional to the force applied to it
The block will not move until the spring scale reads
When the block begins to move, it will smoothly accelerate to the right
The block will move to the right at a uniform velocity
Explanation
This is a classic experiment to determine the coefficient of static friction, 
When the frictional force is just barely overcome, the block will start moving to the right, but as soon as it does, the tension in the spring diminishes and static frictional forces prevail. The block thus starts moving and almost immediately stops.
A 

Explanation
The coefficient of friction is a ratio of the force initiating horizontal displacement of an object and the downwards force of the object due to gravity
Note that the units cancel since we are finding the ratio of two forces. Although it is possible to have values for the coefficient of static friction greater than one, these systems are highly unusual.
A 


Explanation
The force of kinetic friction is given by the equation:
We can calculate the frictional force using the values from the question.
There are four force acting on the block: force from gravity, normal force, force of the spring scale, and force of friction. The normal force will be equal and opposite to the force of gravity, allowing us to cancel the forces in the vertical direction. This leaves us with a net force calculation for the horizontal force: the spring scale force and the force of friction. Note that the frictional force remains negative, as it acts in the opposite direction to the spring scale force.
Now that we know the net force and the mass of the block, we can calculate the acceleration using Newton's second law.
A 


Explanation
In this situation, we must simply remember how to calculate friction. Once the force of gravity overcomes the force of static friction, the object will slide. Our formula for friction is:
This means the force of friction is equal to the friction coefficient times the normal force. On an incline, the normal force is equal to the force of gravity times the cosine of the angle:
We can combine our formulas to give the force of friction.
Using the given coefficient of friction, mass, and angle, we can calculate the force of friction.
Two children are playing with sleds on a snow-covered hill. Sam weighs 50kg, and his sled weighs 10kg. Sally weighs 40kg, and her sled weighs 12kg. When they arrive, they climb up the hill using boots. Halfway up the 50-meter hill, Sally slips and rolls back down to the bottom. Sam continues climbing, and eventually Sally joins him at the top.
They then decide to sled down the hill, but disagree about who will go first.
Scenario 1:
Sam goes down the hill first, claiming that he will reach a higher velocity. If Sally had gone first, Sam says they could collide.
Scenario 2:
Sally goes down the hill first, claiming that she will experience lower friction and thus reach a higher velocity. If Sam had gone first, Sally says they could collide.
Scenario 3:
Unable to agree, Sam and Sally tether themselves with a rope and go down together.
Who would you expect to experience a greater force of friction while traveling down the hill?
Sam, because he experiences a greater normal force
Sally, because she travels more slowly
Sam, because he travels more quickly
Sally, because she experiences less normal force
They would experience equal forces of friction because the coeffecients of friction are the same for both.
Explanation
The force of friction can be found from the following equation.
Force of Friction = Normal Force * Coeffecient of Friction
Normal force here is the force that the Earth pushes back on Sam against his mass. Thus, because he is more massive, he will experience a greater normal force and greater frictional force as a result.
Which of the following could not influence the magnitude of frictional force acting on a book sliding across a horizontal table?
A pushing force exerted horizontally on the book
The mass of the book
The normal force of the table on the book
The materials of which the table and book are made
A pushing force exerted on the book at 
Explanation
Frictional force is given by the equation:
The only factors that can change frictional force are the coefficient of friction, which is determined by the materials of the surfaces in contact, and the normal force. Since the normal force must have a magnitude such that the sum of forces perpendicular to the table equals zero, both the mass of the book and any external vertical forces would influence the normal force, and thus also would influence the frictional force.