Solubility and Solution Equilibrium - MCAT Physical
Card 0 of 105
Which of the following will not increase the solubility of a solution?
Which of the following will not increase the solubility of a solution?
Increasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent will decrease solubility. While dissolved, the gas is in equilibrium with the liquid. Adding heat will push the equilibrium in favor of the gas, causing it to precipitate from solution in the form of bubbles.
Increasing the pressure of a gas solute in a liquid solvent, decreasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent, and increasing the temperature of a solid solute in a liquid solvent will all increase the solubility.
Increasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent will decrease solubility. While dissolved, the gas is in equilibrium with the liquid. Adding heat will push the equilibrium in favor of the gas, causing it to precipitate from solution in the form of bubbles.
Increasing the pressure of a gas solute in a liquid solvent, decreasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent, and increasing the temperature of a solid solute in a liquid solvent will all increase the solubility.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following compounds makes the least effective electrolyte?
Which of the following compounds makes the least effective electrolyte?
An electrolyte is a substance that creates ions when in solution. These compounds conduct electricity very well by donating ions to an aqueous solution. The worst electrolyte will be the compound that creates the smallest amount of ions in solution. Silver chloride is relatively insoluble in solution, meaning that it will make the smallest amount of ions out of the given options.
Van't Hoff factor can also be useful in determining electrolyte effectiveness, but is irrelevant in this particular question.
An electrolyte is a substance that creates ions when in solution. These compounds conduct electricity very well by donating ions to an aqueous solution. The worst electrolyte will be the compound that creates the smallest amount of ions in solution. Silver chloride is relatively insoluble in solution, meaning that it will make the smallest amount of ions out of the given options.
Van't Hoff factor can also be useful in determining electrolyte effectiveness, but is irrelevant in this particular question.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Electronegativity is an important concept in physical chemistry, and often used to help quantify the dipole moment of polar compounds. Polar compounds are different from those compounds that are purely nonpolar or purely ionic. An example can be seen by contrasting sodium chloride, NaCl, with an organic molecule, R-C-OH. The former is purely ionic, and the latter is polar covalent.
When comparing more than one polar covalent molecule, we use the dipole moment value to help us determine relative strength of polarity. Dipole moment, however, is dependent on the electronegativity of the atoms making up the bond. Electronegativity is a property inherent to the atom in question, whereas dipole moment is a property of the bond between them.
For example, oxygen has an electronegativity of 3.44, and hydrogen of 2.20. In other words, oxygen more strongly attracts electrons when in a bond with hydrogen. This leads to the O-H bond having a dipole moment.
When all the dipole moments of polar bonds in a molecule are summed, the molecular dipole moment results, as per the following equation.
Dipole moment = charge * separation distance
Given the polarity of O-H bonds in water described in the passage, what is the Ksp expression for the following reaction, assuming it takes place in an aqueous environment?

Electronegativity is an important concept in physical chemistry, and often used to help quantify the dipole moment of polar compounds. Polar compounds are different from those compounds that are purely nonpolar or purely ionic. An example can be seen by contrasting sodium chloride, NaCl, with an organic molecule, R-C-OH. The former is purely ionic, and the latter is polar covalent.
When comparing more than one polar covalent molecule, we use the dipole moment value to help us determine relative strength of polarity. Dipole moment, however, is dependent on the electronegativity of the atoms making up the bond. Electronegativity is a property inherent to the atom in question, whereas dipole moment is a property of the bond between them.
For example, oxygen has an electronegativity of 3.44, and hydrogen of 2.20. In other words, oxygen more strongly attracts electrons when in a bond with hydrogen. This leads to the O-H bond having a dipole moment.
When all the dipole moments of polar bonds in a molecule are summed, the molecular dipole moment results, as per the following equation.
Dipole moment = charge * separation distance
Given the polarity of O-H bonds in water described in the passage, what is the Ksp expression for the following reaction, assuming it takes place in an aqueous environment?
The Ksp is a standard equilibrium constant for the dissolution reaction of a solute. As such, it follows the standard formula for equilibrium constants, and excludes pure liquids and solids (like water and calcium sulfate!).
![K_{eq}=K_{sp}=\frac{[Products]}{[Reactants]}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/25761/gif.latex)
The Ksp is a standard equilibrium constant for the dissolution reaction of a solute. As such, it follows the standard formula for equilibrium constants, and excludes pure liquids and solids (like water and calcium sulfate!).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Barium fluoride dissolves in solution according to the following equation.


Write the solubility product constant (Ksp) for the reaction.
Barium fluoride dissolves in solution according to the following equation.
Write the solubility product constant (Ksp) for the reaction.
When writing the solubility product for a reaction, it is important to remember that solid and liquid compounds are not included in the expression. As a result, barium fluoride would not be included, because it is a solid. Just like the law of mass action, coefficients are the exponents in the expression.
Since only the products are used in the expression (the reactant is a pure solid), it is written as ![K_{sp} = [Ba^{2+}][F^{-}]^{2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/110627/gif.latex) .
.
When writing the solubility product for a reaction, it is important to remember that solid and liquid compounds are not included in the expression. As a result, barium fluoride would not be included, because it is a solid. Just like the law of mass action, coefficients are the exponents in the expression.
Since only the products are used in the expression (the reactant is a pure solid), it is written as ![K_{sp} = [Ba^{2+}][F^{-}]^{2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/110627/gif.latex)
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Barium fluoride dissolves in solution according to the following equation.


Assume an aqueous solution is saturated with BaF2. What is the solubility of BaF2?
Barium fluoride dissolves in solution according to the following equation.
Assume an aqueous solution is saturated with BaF2. What is the solubility of BaF2?
When the solution is saturated, we can determine the solubility of the salt in the solution. We can determine the solubility by using the solubility product constant and comparing it to the amount of ions predicted to be created in the dissolving of the salt. Since the dissolving of BaF2 will yield 1 Ba2+ ion and 2 F- ions, we can express their increases as X and 2X respectively. Plugging this in to the equation for the solubility product constant yields the calculations below.
![K_{sp}=[Ba^{2+}][F^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/86111/gif.latex)




When the solution is saturated, we can determine the solubility of the salt in the solution. We can determine the solubility by using the solubility product constant and comparing it to the amount of ions predicted to be created in the dissolving of the salt. Since the dissolving of BaF2 will yield 1 Ba2+ ion and 2 F- ions, we can express their increases as X and 2X respectively. Plugging this in to the equation for the solubility product constant yields the calculations below.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Barium fluoride dissolves in solution according to the following equation.


Enough BaF2 is added to create a saturated liter of aqueous solution.
Suppose that 0.5M of NaF is added to the solution. What will the solubility of BaF2 be in the new solution?
Barium fluoride dissolves in solution according to the following equation.
Enough BaF2 is added to create a saturated liter of aqueous solution.
Suppose that 0.5M of NaF is added to the solution. What will the solubility of BaF2 be in the new solution?
When 0.5M of NaF is added, it increases the amount of fluoride ions in the solution. As a result, we can expect the solubility of the salt to decrease (a result of the common ion effect).
To determine by how much the solubility will decrease, we must use the solubility product constant expression with the newfound fluoride concentration. The expression for the equation is ![K_{sp} = [Ba^{2+}][F^{-}]^{2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/131267/gif.latex)
 . Remeber that pure solids and liquids (such as solid barium flouride are not included in this expression).
. Remeber that pure solids and liquids (such as solid barium flouride are not included in this expression).
Since there is a starting concentration of 0.5M for the fluoride, the predicted increases in the ion concentrations for Ba2+ and F- are now X and (0.5 + X) respectively. We can plug these variables into out equation.

Since the value of X will be much smaller than 0.5, it is acceptable to simplify the fluoride portion of the equation to just (0.5)2.


When 0.5M of NaF is added, it increases the amount of fluoride ions in the solution. As a result, we can expect the solubility of the salt to decrease (a result of the common ion effect).
To determine by how much the solubility will decrease, we must use the solubility product constant expression with the newfound fluoride concentration. The expression for the equation is ![K_{sp} = [Ba^{2+}][F^{-}]^{2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/131267/gif.latex)

Since there is a starting concentration of 0.5M for the fluoride, the predicted increases in the ion concentrations for Ba2+ and F- are now X and (0.5 + X) respectively. We can plug these variables into out equation.
Since the value of X will be much smaller than 0.5, it is acceptable to simplify the fluoride portion of the equation to just (0.5)2.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following compounds would make a weak electrolyte in solution?
Which of the following compounds would make a weak electrolyte in solution?
A strong electrolyte is a compound that will conduct electricity while in solution. This is because it creates many charged ions in the solution. Because we want a weak electrolyte, the answer will be the compound that does not form many ions when in solution. NH3 is a weak base which does not dissociate completely. As a result, it creates few ions in solution, making it a weak electrolyte.
The other answer choices represent either ionic compounds or strong acids, and will dissociate completely in solution.
A strong electrolyte is a compound that will conduct electricity while in solution. This is because it creates many charged ions in the solution. Because we want a weak electrolyte, the answer will be the compound that does not form many ions when in solution. NH3 is a weak base which does not dissociate completely. As a result, it creates few ions in solution, making it a weak electrolyte.
The other answer choices represent either ionic compounds or strong acids, and will dissociate completely in solution.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is true of a saturated solution?
Which of the following is true of a saturated solution?
A saturated solution is a solution that is at equilibrium. The ionization product is equal to the Ksp in a saturated solution, and the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. In an unsaturated solution, the solute continues to dissolve until equilibrium is reached. In a supersaturated solution, salt will "crash out," or precipitate, from solution.
A saturated solution is a solution that is at equilibrium. The ionization product is equal to the Ksp in a saturated solution, and the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. In an unsaturated solution, the solute continues to dissolve until equilibrium is reached. In a supersaturated solution, salt will "crash out," or precipitate, from solution.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Scandium hydroxide,  , has a
, has a  value of
value of  . What is its solubility?
. What is its solubility?
Scandium hydroxide, 


Scandium hydroxide dissociates according to the following reaction.

The  for this dissociation is written as follows. Note that the solid is left out of the equation.
for this dissociation is written as follows. Note that the solid is left out of the equation.
![Ksp = [Sc^{3+}][OH^{-}]^{3}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/132011/gif.latex)
If  is the amount of
is the amount of  that forms when
that forms when  dissociates, then
dissociates, then  is the amount of
is the amount of  formed, based on stoichiometry.
formed, based on stoichiometry.
![8.0 * 10^{-31} = [x][3x]^{3} = 27x^{4}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/132014/gif.latex)
Solving this equation gives us the value of  .
.


This value is the solubility of scandium hydroxide.
Scandium hydroxide dissociates according to the following reaction.
The 
If 




Solving this equation gives us the value of 
This value is the solubility of scandium hydroxide.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Hypothetically, if calcium hydroxide, lithium hydroxide, and potassium hydroxide all had a  value of
value of  , which compound would have the greatest solubility?
, which compound would have the greatest solubility?
Hypothetically, if calcium hydroxide, lithium hydroxide, and potassium hydroxide all had a 

Solubility is the ability of a solute to dissolve into a solvent. It is calculated by creating an equilibrium equation and solving for the concentration of dissolved ions.
For this question, we will need to set up equilibrium constant equations for each compound.
![Ca(OH)_2\rightleftharpoons Ca^{2+}+2OH^-;\ K_{sp}=[Ca^{2+}][OH^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/113712/gif.latex)
![LiOH\rightleftharpoons Li^++OH^-;\ K_{sp}=[Li^+][OH^-]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/100505/gif.latex)
![KOH\rightleftharpoons K^++OH^-;\ K_{sp}=[K^+][OH^-]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/113713/gif.latex)
Note that the solid compounds are not included in the equilibrium expressions. Now we can work on finding the solubilities. For each mole of calcium hydroxide dissolved, one mole of calcium ions and two moles of hydroxide ions are released. For each mole of lithium hydroxide dissolved, one mole of lithium ions and one mole of hydroxide ions are released. For each mole of potassium hydroxide dissolved, one mole of potassium ions and one mole of hydroxide ions are released. Mathematically, we can equate these ratios to the ion concentrations in the equilibrium calculations.



In these calculations,  is the solubility. Given the solubility constants, we can solve for
is the solubility. Given the solubility constants, we can solve for  .
.



Calcium hydroxide has the greatest solubility.
Solubility is the ability of a solute to dissolve into a solvent. It is calculated by creating an equilibrium equation and solving for the concentration of dissolved ions.
For this question, we will need to set up equilibrium constant equations for each compound.
Note that the solid compounds are not included in the equilibrium expressions. Now we can work on finding the solubilities. For each mole of calcium hydroxide dissolved, one mole of calcium ions and two moles of hydroxide ions are released. For each mole of lithium hydroxide dissolved, one mole of lithium ions and one mole of hydroxide ions are released. For each mole of potassium hydroxide dissolved, one mole of potassium ions and one mole of hydroxide ions are released. Mathematically, we can equate these ratios to the ion concentrations in the equilibrium calculations.
In these calculations, 

Calcium hydroxide has the greatest solubility.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is true regarding the solubility product constant,  , for a reaction in the form:
, for a reaction in the form:

Which of the following is true regarding the solubility product constant, 
To determine the solubility product constant, we only need the concentrations and coefficients of the ions. The effective concentration of any pure substance (solid, liquid, or gas) is equal to one by definition, so does not influence the value of  . The equation for the solubility product constant of this reaction is:
. The equation for the solubility product constant of this reaction is:
![K_{sp}=[C]^c[D]^d](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/100575/gif.latex)
The units of the solubility product constant will depend on the coefficients of the products. 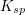 will be a constant for the reaction, and will not change as more solid dissolves or as the reaction progresses.
will be a constant for the reaction, and will not change as more solid dissolves or as the reaction progresses.
To determine the solubility product constant, we only need the concentrations and coefficients of the ions. The effective concentration of any pure substance (solid, liquid, or gas) is equal to one by definition, so does not influence the value of 
The units of the solubility product constant will depend on the coefficients of the products. 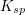
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The solubility product constant of  is
is  . What is the solubility of this compound?
. What is the solubility of this compound?
The solubility product constant of 

Solubility is the ability of a solute to dissolve into a solvent. It is calculated by creating an equilibrium equation and solving for the concentration of dissolved ions.
For this question, we will need to set up the equilibrium constant equation for calcium hydroxide.
![Ca(OH)_2\rightleftharpoons Ca^{2+}+2OH^-;\ K_{sp}=[Ca^{2+}][OH^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/100585/gif.latex)
Note that the solid compound is not included in the equilibrium expression. Now we can work on finding the solubility. For each mole of calcium hydroxide dissolved, one mole of calcium ions and two moles of hydroxide ions are released. Mathematically, we can equate this ratio to the ion concentrations in the equilibrium calculation.

In this calculation,  is the solubility. Given the solubility constant, we can solve for
is the solubility. Given the solubility constant, we can solve for  .
.

Solubility is the ability of a solute to dissolve into a solvent. It is calculated by creating an equilibrium equation and solving for the concentration of dissolved ions.
For this question, we will need to set up the equilibrium constant equation for calcium hydroxide.
Note that the solid compound is not included in the equilibrium expression. Now we can work on finding the solubility. For each mole of calcium hydroxide dissolved, one mole of calcium ions and two moles of hydroxide ions are released. Mathematically, we can equate this ratio to the ion concentrations in the equilibrium calculation.
In this calculation, 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is present in a solution of sodium cyanide?
Which of the following is present in a solution of sodium cyanide?
Salts are a type of strong electrolyte, as are strong acids and strong bases. Strong electrolytes break up completely into ions (or "ionize") when dissolved in water. A solution of sodium cyanide would contain almost entirely sodium and cyanide ions, and no salt molecules.

Salts are a type of strong electrolyte, as are strong acids and strong bases. Strong electrolytes break up completely into ions (or "ionize") when dissolved in water. A solution of sodium cyanide would contain almost entirely sodium and cyanide ions, and no salt molecules.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
How many moles of fluoride ions are present in  of a completely saturated solution of lead (II) fluoride?
of a completely saturated solution of lead (II) fluoride?


How many moles of fluoride ions are present in 
Recall that the solubility product constant is given by the equation below, for a reaction in the following format.

![K_{sp}=[C]^c[D]^d](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/126068/gif.latex)
Using our balanced reaction, we can find the solubility product equation for the dissociation of lead (II) fluoride.

![K_{sp}=[Pb^{2+}][F^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1053245/gif.latex)
For each molecule of lead (II) fluoride that dissolves, it produces one lead ion and two fluoride ions. We can conclude that the concentration of fluoride ions in solution will be twice the concentration of lead ions.
![[Pb^{2+}] = x](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/102001/gif.latex)
![[F^-]=2x](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/126071/gif.latex)
Use these variables in the solubility product equation, along with the given value from the question.

Now we can solve for the value of  .
.

![x = \sqrt[3]{\frac{3.7*10^{-8}}{4}}=2.1*10^{-3}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/126073/gif.latex)
Remember that this value is equal to the concentration of lead ions in solution and half the concentration of fluoride ions in solution.
![[Pb^{2+}]=x=2.1*10^{-3}M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/102004/gif.latex)
![[F^-]=2x=2(2.1*10^{-3}M)=4.2*10^{-3}M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1051540/gif.latex)
Recall that the solubility product constant is given by the equation below, for a reaction in the following format.
Using our balanced reaction, we can find the solubility product equation for the dissociation of lead (II) fluoride.
For each molecule of lead (II) fluoride that dissolves, it produces one lead ion and two fluoride ions. We can conclude that the concentration of fluoride ions in solution will be twice the concentration of lead ions.
Use these variables in the solubility product equation, along with the given value from the question.
Now we can solve for the value of 
Remember that this value is equal to the concentration of lead ions in solution and half the concentration of fluoride ions in solution.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which substance is more soluble in hydrochloric acid than sodium hydroxide?
Which substance is more soluble in hydrochloric acid than sodium hydroxide?
Though we are asking about solubility in a strong acid and in a strong base, this is not an acid-base chemistry question.
Instead, we are dealing with solubility, which is directly affected by the solubility product constant. The solubility product constant for each answer choice is given below.
![K_{spHI}=[H^+][I^-]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/116854/gif.latex)
![K_{spCaF_2}=[Ca^{2+}][F^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/102294/gif.latex)
![K_{spAgCl}=[Ag^+][Cl^-]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/116855/gif.latex)
![K_{spPb(OH)_2}=[Pb^{2+}][OH^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/102295/gif.latex)
Hydrochloric acid will contribute to hydrogen and chloride ion concentrations, while sodium hydroxide will contribute to sodium and hydroxide ion concentrations. The solubility product constant for hydroiodic acid incorporates the hydrogen ions, while the product constant for lead (II) hydroxide incorporates the hydroxide ions.
Increasing the ion concentration results in the common ion effect. Compounds are less soluble in solutions already containing ions that contribute to their solubility product constant. We can thus conclude that lead (II) hydroxide will be less soluble in sodium hydroxide because the sodium hydroxide contributes a common ion.
Though we are asking about solubility in a strong acid and in a strong base, this is not an acid-base chemistry question.
Instead, we are dealing with solubility, which is directly affected by the solubility product constant. The solubility product constant for each answer choice is given below.
Hydrochloric acid will contribute to hydrogen and chloride ion concentrations, while sodium hydroxide will contribute to sodium and hydroxide ion concentrations. The solubility product constant for hydroiodic acid incorporates the hydrogen ions, while the product constant for lead (II) hydroxide incorporates the hydroxide ions.
Increasing the ion concentration results in the common ion effect. Compounds are less soluble in solutions already containing ions that contribute to their solubility product constant. We can thus conclude that lead (II) hydroxide will be less soluble in sodium hydroxide because the sodium hydroxide contributes a common ion.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following will not increase the solubility of a solution?
Which of the following will not increase the solubility of a solution?
Increasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent will decrease solubility. While dissolved, the gas is in equilibrium with the liquid. Adding heat will push the equilibrium in favor of the gas, causing it to precipitate from solution in the form of bubbles.
Increasing the pressure of a gas solute in a liquid solvent, decreasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent, and increasing the temperature of a solid solute in a liquid solvent will all increase the solubility.
Increasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent will decrease solubility. While dissolved, the gas is in equilibrium with the liquid. Adding heat will push the equilibrium in favor of the gas, causing it to precipitate from solution in the form of bubbles.
Increasing the pressure of a gas solute in a liquid solvent, decreasing the temperature of a gas solute in a liquid solvent, and increasing the temperature of a solid solute in a liquid solvent will all increase the solubility.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following compounds makes the least effective electrolyte?
Which of the following compounds makes the least effective electrolyte?
An electrolyte is a substance that creates ions when in solution. These compounds conduct electricity very well by donating ions to an aqueous solution. The worst electrolyte will be the compound that creates the smallest amount of ions in solution. Silver chloride is relatively insoluble in solution, meaning that it will make the smallest amount of ions out of the given options.
Van't Hoff factor can also be useful in determining electrolyte effectiveness, but is irrelevant in this particular question.
An electrolyte is a substance that creates ions when in solution. These compounds conduct electricity very well by donating ions to an aqueous solution. The worst electrolyte will be the compound that creates the smallest amount of ions in solution. Silver chloride is relatively insoluble in solution, meaning that it will make the smallest amount of ions out of the given options.
Van't Hoff factor can also be useful in determining electrolyte effectiveness, but is irrelevant in this particular question.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Electronegativity is an important concept in physical chemistry, and often used to help quantify the dipole moment of polar compounds. Polar compounds are different from those compounds that are purely nonpolar or purely ionic. An example can be seen by contrasting sodium chloride, NaCl, with an organic molecule, R-C-OH. The former is purely ionic, and the latter is polar covalent.
When comparing more than one polar covalent molecule, we use the dipole moment value to help us determine relative strength of polarity. Dipole moment, however, is dependent on the electronegativity of the atoms making up the bond. Electronegativity is a property inherent to the atom in question, whereas dipole moment is a property of the bond between them.
For example, oxygen has an electronegativity of 3.44, and hydrogen of 2.20. In other words, oxygen more strongly attracts electrons when in a bond with hydrogen. This leads to the O-H bond having a dipole moment.
When all the dipole moments of polar bonds in a molecule are summed, the molecular dipole moment results, as per the following equation.
Dipole moment = charge * separation distance
Given the polarity of O-H bonds in water described in the passage, what is the Ksp expression for the following reaction, assuming it takes place in an aqueous environment?

Electronegativity is an important concept in physical chemistry, and often used to help quantify the dipole moment of polar compounds. Polar compounds are different from those compounds that are purely nonpolar or purely ionic. An example can be seen by contrasting sodium chloride, NaCl, with an organic molecule, R-C-OH. The former is purely ionic, and the latter is polar covalent.
When comparing more than one polar covalent molecule, we use the dipole moment value to help us determine relative strength of polarity. Dipole moment, however, is dependent on the electronegativity of the atoms making up the bond. Electronegativity is a property inherent to the atom in question, whereas dipole moment is a property of the bond between them.
For example, oxygen has an electronegativity of 3.44, and hydrogen of 2.20. In other words, oxygen more strongly attracts electrons when in a bond with hydrogen. This leads to the O-H bond having a dipole moment.
When all the dipole moments of polar bonds in a molecule are summed, the molecular dipole moment results, as per the following equation.
Dipole moment = charge * separation distance
Given the polarity of O-H bonds in water described in the passage, what is the Ksp expression for the following reaction, assuming it takes place in an aqueous environment?
The Ksp is a standard equilibrium constant for the dissolution reaction of a solute. As such, it follows the standard formula for equilibrium constants, and excludes pure liquids and solids (like water and calcium sulfate!).
![K_{eq}=K_{sp}=\frac{[Products]}{[Reactants]}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/25761/gif.latex)
The Ksp is a standard equilibrium constant for the dissolution reaction of a solute. As such, it follows the standard formula for equilibrium constants, and excludes pure liquids and solids (like water and calcium sulfate!).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Barium fluoride dissolves in solution according to the following equation.


Write the solubility product constant (Ksp) for the reaction.
Barium fluoride dissolves in solution according to the following equation.
Write the solubility product constant (Ksp) for the reaction.
When writing the solubility product for a reaction, it is important to remember that solid and liquid compounds are not included in the expression. As a result, barium fluoride would not be included, because it is a solid. Just like the law of mass action, coefficients are the exponents in the expression.
Since only the products are used in the expression (the reactant is a pure solid), it is written as ![K_{sp} = [Ba^{2+}][F^{-}]^{2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/110627/gif.latex) .
.
When writing the solubility product for a reaction, it is important to remember that solid and liquid compounds are not included in the expression. As a result, barium fluoride would not be included, because it is a solid. Just like the law of mass action, coefficients are the exponents in the expression.
Since only the products are used in the expression (the reactant is a pure solid), it is written as ![K_{sp} = [Ba^{2+}][F^{-}]^{2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/110627/gif.latex)
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Barium fluoride dissolves in solution according to the following equation.


Assume an aqueous solution is saturated with BaF2. What is the solubility of BaF2?
Barium fluoride dissolves in solution according to the following equation.
Assume an aqueous solution is saturated with BaF2. What is the solubility of BaF2?
When the solution is saturated, we can determine the solubility of the salt in the solution. We can determine the solubility by using the solubility product constant and comparing it to the amount of ions predicted to be created in the dissolving of the salt. Since the dissolving of BaF2 will yield 1 Ba2+ ion and 2 F- ions, we can express their increases as X and 2X respectively. Plugging this in to the equation for the solubility product constant yields the calculations below.
![K_{sp}=[Ba^{2+}][F^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/86111/gif.latex)




When the solution is saturated, we can determine the solubility of the salt in the solution. We can determine the solubility by using the solubility product constant and comparing it to the amount of ions predicted to be created in the dissolving of the salt. Since the dissolving of BaF2 will yield 1 Ba2+ ion and 2 F- ions, we can express their increases as X and 2X respectively. Plugging this in to the equation for the solubility product constant yields the calculations below.
Compare your answer with the correct one above