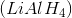Reaction Types
Help Questions
MCAT Biology › Reaction Types
Which of the following statements is true concerning the Hofmann elimination reaction?
The least substituted alkene is the major product in the reaction
The ammonium is eliminated following an E1 mechanism
The Zaitsev product is favored in the elimination reaction
The quaternary ammonium salt is a poor leaving group
Explanation
The Hofmann product is the most favored product in a Hofmann elimination reaction. The reaction follows an E2 mechanism, where a quaternary ammonium salt is able to be removed from a hydrocarbon, resulting in an alkene product. This reaction results in the least substituted alkene being the primary product.
Which of the following statements is true concerning the Hofmann elimination reaction?
The least substituted alkene is the major product in the reaction
The ammonium is eliminated following an E1 mechanism
The Zaitsev product is favored in the elimination reaction
The quaternary ammonium salt is a poor leaving group
Explanation
The Hofmann product is the most favored product in a Hofmann elimination reaction. The reaction follows an E2 mechanism, where a quaternary ammonium salt is able to be removed from a hydrocarbon, resulting in an alkene product. This reaction results in the least substituted alkene being the primary product.
Carbonic anhydrase is a very important enzyme that is utilized by the body. The enzyme catalyzes the following reaction:
A class of drugs that inhibits this enzyme is carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (eg. acetazolamide, brinzolamide, dorzolamide). These drugs are commonly prescribed in patients with glaucoma, hypertension, heart failure, high altitude sickness and for the treatment of basic drugs overdose.
In patients with hypertension, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors will prevent the reabsorption of sodium chloride 
When mountain climbing, the atmospheric pressure is lowered as the altitude increases. As a result of less oxygen into the lungs, ventilation increases. From the equation above, hyperventilation will result in more 
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are useful in patients with a drug overdose that is acidic. The lumen of the collecting tubule is nonpolar. Due to the lumen's characteristic, molecules that are also nonpolar and uncharged are able to cross the membrane and re-enter the circulatory system. Since carbonic anhydrase inhibitors alkalize the urine, acidic molecules stay in a charged state.
When a patient is not ventilating efficiently, the kidneys try to compensate by producing more bicarbonate to buffer the decreasing pH of the blood due to the buildup of 

I. Increase 
II. Increase 
III. Increase metabolism
I and III
I only
II only
III only
I, II, and III
Explanation
To answer this question, we must understand Le Chatelier’s principle. The reaction favorites the product when there is more of the reactants. The opposite is also true in that when there is a buildup of the products, the reaction will reverse and favorite the reactants. Increasing the metabolism will produce more 
Carbonic anhydrase is a very important enzyme that is utilized by the body. The enzyme catalyzes the following reaction:
A class of drugs that inhibits this enzyme is carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (eg. acetazolamide, brinzolamide, dorzolamide). These drugs are commonly prescribed in patients with glaucoma, hypertension, heart failure, high altitude sickness and for the treatment of basic drugs overdose.
In patients with hypertension, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors will prevent the reabsorption of sodium chloride 
When mountain climbing, the atmospheric pressure is lowered as the altitude increases. As a result of less oxygen into the lungs, ventilation increases. From the equation above, hyperventilation will result in more 
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are useful in patients with a drug overdose that is acidic. The lumen of the collecting tubule is nonpolar. Due to the lumen's characteristic, molecules that are also nonpolar and uncharged are able to cross the membrane and re-enter the circulatory system. Since carbonic anhydrase inhibitors alkalize the urine, acidic molecules stay in a charged state.
When a patient is not ventilating efficiently, the kidneys try to compensate by producing more bicarbonate to buffer the decreasing pH of the blood due to the buildup of 

I. Increase 
II. Increase 
III. Increase metabolism
I and III
I only
II only
III only
I, II, and III
Explanation
To answer this question, we must understand Le Chatelier’s principle. The reaction favorites the product when there is more of the reactants. The opposite is also true in that when there is a buildup of the products, the reaction will reverse and favorite the reactants. Increasing the metabolism will produce more 
Which of the following is not capable of oxidizing a secondary alcohol to a ketone?
Lithium aluminum hydride
Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)


All of these answers can oxidize secondary alcohols to ketones
Explanation
Lithium aluminum hydride is correct because it is a reducing agent, and is therefore not capable of oxidizing secondary alcohols. Instead, LAH could be used to perform the reverse reaction, reducing a ketone to an alcohol. The other answer choices are oxidizing agents.
Carbonic anhydrase is a very important enzyme that is utilized by the body. The enzyme catalyzes the following reaction:
A class of drugs that inhibits this enzyme is carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (eg. acetazolamide, brinzolamide, dorzolamide). These drugs are commonly prescribed in patients with glaucoma, hypertension, heart failure, high altitude sickness and for the treatment of basic drugs overdose.
In patients with hypertension, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors will prevent the reabsorption of sodium chloride 
When mountain climbing, the atmospheric pressure is lowered as the altitude increases. As a result of less oxygen into the lungs, ventilation increases. From the equation above, hyperventilation will result in more 
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are useful in patients with a drug overdose that is acidic. The lumen of the collecting tubule is nonpolar. Due to the lumen's characteristic, molecules that are also nonpolar and uncharged are able to cross the membrane and re-enter the circulatory system. Since carbonic anhydrase inhibitors alkalize the urine, acidic molecules stay in a charged state.
Based on the passage, which of the following statements, if true, will contradict the effectiveness of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as a treatment?
Acidic molecules will not release its proton in the basic environment of the lumen of the collecting tubule
Acidic molecules will release its proton in the basic environment of the lumen of the collecting tubule
Basic Molecules will not release its proton in the basic environment of the lumen of the collecting tubule.
Basic molecules will release its proton in the basic environment of the lumen of the collecting tubule
Acidic molecules have a better ability to cross the membrane than basic molecules
Explanation
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are used to alkalinize the urine. When the urine is alkalinized, acidic molecules will lose its proton and go into a charged state. Charged molecules are unable to cross the membrane of the lumen of the collecting tubule. Without the ability to cross the membrane, the molecule is therefore unable to be reabsorbed. Therefore, if the statement "Acidic molecules will not release its proton in the basic environment of the lumen of the collecting tubule" was true, then alkalinizing the urine will have no effect.
What intermediate is involved in the conversion of compound B to compound C?

Tertiary carbocation
Tertiary radical
Tertiary carbanion
Secondary carbocation
Secondary radical
Explanation
The strong sulfuric acid protonates the hydroxyl group of compound B, resulting in the loss of water as a leaving group and the generation of a carbocation intermediate. Since this carbocation carbon is attached to three other carbons, this is a tertiary carbocation. It is bound to the phenyl substituent, a methyl group, and the branched carbon chain.
Which of the following is not capable of oxidizing a secondary alcohol to a ketone?
Lithium aluminum hydride
Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)


All of these answers can oxidize secondary alcohols to ketones
Explanation
Lithium aluminum hydride is correct because it is a reducing agent, and is therefore not capable of oxidizing secondary alcohols. Instead, LAH could be used to perform the reverse reaction, reducing a ketone to an alcohol. The other answer choices are oxidizing agents.
What intermediate is involved in the conversion of compound B to compound C?

Tertiary carbocation
Tertiary radical
Tertiary carbanion
Secondary carbocation
Secondary radical
Explanation
The strong sulfuric acid protonates the hydroxyl group of compound B, resulting in the loss of water as a leaving group and the generation of a carbocation intermediate. Since this carbocation carbon is attached to three other carbons, this is a tertiary carbocation. It is bound to the phenyl substituent, a methyl group, and the branched carbon chain.
Carbonic anhydrase is a very important enzyme that is utilized by the body. The enzyme catalyzes the following reaction:
A class of drugs that inhibits this enzyme is carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (eg. acetazolamide, brinzolamide, dorzolamide). These drugs are commonly prescribed in patients with glaucoma, hypertension, heart failure, high altitude sickness and for the treatment of basic drugs overdose.
In patients with hypertension, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors will prevent the reabsorption of sodium chloride 
When mountain climbing, the atmospheric pressure is lowered as the altitude increases. As a result of less oxygen into the lungs, ventilation increases. From the equation above, hyperventilation will result in more 
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are useful in patients with a drug overdose that is acidic. The lumen of the collecting tubule is nonpolar. Due to the lumen's characteristic, molecules that are also nonpolar and uncharged are able to cross the membrane and re-enter the circulatory system. Since carbonic anhydrase inhibitors alkalize the urine, acidic molecules stay in a charged state.
Based on the passage, which of the following statements, if true, will contradict the effectiveness of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as a treatment?
Acidic molecules will not release its proton in the basic environment of the lumen of the collecting tubule
Acidic molecules will release its proton in the basic environment of the lumen of the collecting tubule
Basic Molecules will not release its proton in the basic environment of the lumen of the collecting tubule.
Basic molecules will release its proton in the basic environment of the lumen of the collecting tubule
Acidic molecules have a better ability to cross the membrane than basic molecules
Explanation
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are used to alkalinize the urine. When the urine is alkalinized, acidic molecules will lose its proton and go into a charged state. Charged molecules are unable to cross the membrane of the lumen of the collecting tubule. Without the ability to cross the membrane, the molecule is therefore unable to be reabsorbed. Therefore, if the statement "Acidic molecules will not release its proton in the basic environment of the lumen of the collecting tubule" was true, then alkalinizing the urine will have no effect.