Enzymes and Enzyme Inhibition
Help Questions
MCAT Biology › Enzymes and Enzyme Inhibition
Which of the following is not an example of positive feedback?
As blood calcium levels increase, parathyroid hormone (PTH) is reduced.
As more buffalo begin to run in a herd, the overall level of panic increases. This results in even more buffalo running.
A forest fire slowly expands outward, which provides it with even more fuel to burn.
During childbirth, oxytocin creates a stimulus which causes the hypothalamus to release more oxytocin.
Explanation
Negative feedback provides the body with a method for shutting down a reaction once sufficient product has been created. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is responsible for increasing blood calcium levels, but once the level is sufficient, the parathyroid glands detect the sufficient calcium level and no longer produce PTH. PTH works in coordination with calcitonin to maintain this balance via its negative feedback loop.
Positive feedback, in contrast, involves the exponential increase of a reaction upon detection. Very few examples of positive feedback exist in the body, though oxytocin follows this model during childbirth.
A student observes an enzymatic chemical reaction that normally takes place in human blood. She performs an experiment to see how certain conditions affect the reaction with the enzyme fully saturated with substrate. What should she do to speed the reaction up?
Increase the enzyme concentration
Increase the temperature to 40 degrees Celsius
Make the pH 7.0
Add more substrate
Remove some of the enzyme
Explanation
Adding more enzyme is the only way to make this reaction proceed faster. Since this is a reaction that takes place in the blood, the optimal conditions are 37 degrees Celsius and a pH of 7.4. Adding more substrate could help in certain conditions, but we know from the question that there is no free enzyme in the reaction so adding more would not help. Removing enzyme would obviously sow the reaction down.
Drain cleaners a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
Protein that forms the hair discussed in the preceeding passage is considered strucutral protein. Functional proteins, such as enzymes, are the other major class. Which of the following is expected in an enzymatic biological reaction?
I. Faster rate than non-enzymatic reaction
II. Enzymatic coupling to hydrolysis reactions
III. More product generation relative to amount of reactant than non-enzymatic reaction
I and II
I, only
II, only
I and III, only
I, II, and III
Explanation
Enzymatic reactions will always proceed faster than if there was no enzyme present. They will also often be coupled to hydrolysis reactions to drive them forward thermodynamically, such as ATP hyrodlysis to make an otherwise unfavorable reaction proceed. The equilibrium constant of an enzymatic reaction is never different than the constant for the same reaction without enyzme, however, and thus choice III is incorrect.
Sildenafil (commonly called Viagra) is a common drug used to treat erectile dysfunction and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Sildenafil's effect comes from its ability to cause vasodilation in smooth muscle cells. For this problem, we're only going to consider its effects on erections in males.
Erectile dysfunction is a common medical problem in older men. Its most significant effect is the prevention of erections. Erections occur when there is an increase in blood flow via enlargement of an artery (vasodilation). Understanding the mechanism by which vasodilations occur is important in order to treat erectile dysfunction.
Erections occur when nitric oxide 
Which of the following reactions would you expect PDE5 to catalyze?
Explanation
For this problem, we need to know what phosphodiesterases do. Phosphodiesterases catalyze the breakdown of phosphodiester bonds via hydrolysis. Cyclic GMP contains an internal phosphodiester bond. Therefore its breakdown would result in the formation of GMP. The hydrolysis of cGMP should not yield GMP and a phosphate, since cyclic GMP only has one phosphate group.
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
Carbonic anhydrase is an organic enzyme. Which of the following is true of carbonic anhydrase? Assume no CO2 or bicarbonate is lost in the reaction.
I. It lowers the activation energy for the conversion of carbon dioxide to carbonic acid
II. It shifts the equilibrium toward carbon dioxide in experimental conditions
III. It modifies chemical species at its allosteric site
I, only
III, only
I and II
I and III
I, II, and III
Explanation
Only choice I is correct. Carbonic anhydrase lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction, as does any catalyst. Thermodynamics, including equilibria, are not modified by catalysts, so choice II is incorrect. Choice III is also incorrect, as an allosteric site is typically used to bind regulators of enzymes to induce conformational changes, while an active site would be where the actual catalysis takes place.
Which statement is true about noncompetitive inhibitors?
They alter the conformation of the enzyme.
They bind at the active site of the enzyme.
They actively block the enzyme from attaching to the substrate.
They bind covalently to the enzyme and disrupt the substrate from attaching.
Explanation
Noncompetitive inhibitors do not bind at the active site of an enzyme. Instead, they bind at another position on the enzyme and alter its conformation. This passive approach to inhibition makes an enzyme unable to attach to the substrate at the active site. Only irreversible inhibitors bond covalently; both competitive and noncompetitive inhibitors bind noncovalently.
Scientists use a process called Flourescent In-Situ Hybridization, or FISH, to study genetic disorders in humans. FISH is a technique that uses spectrographic analysis to determine the presence or absence, as well as the relative abundance, of genetic material in human cells.
To use FISH, scientists apply fluorescently-labeled bits of DNA of a known color, called probes, to samples of test DNA. These probes anneal to the sample DNA, and scientists can read the colors that result using laboratory equipment. One common use of FISH is to determine the presence of extra DNA in conditions of aneuploidy, a state in which a human cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes. Chromosomes are collections of DNA, the totality of which makes up a cell’s genome. Another typical use is in the study of cancer cells, where scientists use FISH labels to ascertain if genes have moved inappropriately in a cell’s genome.
Using red fluorescent tags, scientists label probe DNA for a gene known to be expressed more heavily in cancer cells than normal cells. They then label a probe for an immediately adjacent DNA sequence with a green fluorescent tag. Both probes are then added to three dishes, shown below. In dish 1 human bladder cells are incubated with the probes, in dish 2 human epithelial cells are incubated, and in dish 3 known non-cancerous cells are used. The relative luminescence observed in regions of interest in all dishes is shown below.
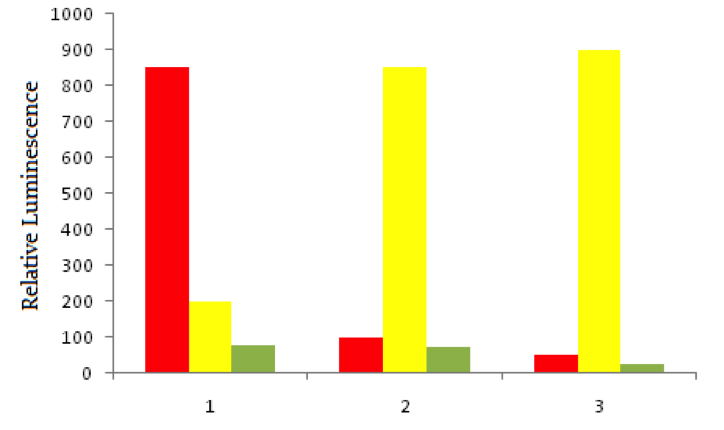
Cancer cells often invade by breaking through the collagen of a basement membrane of epithelial tissue. Considering the composition of basement membranes, which of the following compounds is most likely to be used by cancer cells for this purpose?
Protease
Peroxidase
Lipase
Amylase
Synthase
Explanation
The basement membrane and sub-basement structures are predominately made of protein (connective tissue). To infiltrate this region, a protease would be most appropriate. The remaining choices are all enzymes, but would not be capable of digesting appropriate proteins.
Fetal hemoglobin has a higher binding affinity for oxygen than does adult hemoglobin.
In comparison to the adult oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve, the fetal oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve will __________.
be shifted to the left and display a lower Km
be shifted to the right and display a lower Km
be shifted to the right and display a higher Km
be shifted to the left and display a higher Km
Explanation
Fetal hemoglobin is associated with a left-shift due to its greater binding affinity for oxygen. The Michaelis constant, Km, is defined as the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is 0.5 * Vmax. A low Km indicates high substrate affinity.
Which of the following changes could lead to loss of enzymatic function?
Increase in pH of the reaction
Change in overall free energy of the reaction
Change in overall enthalpy of the reaction
Decrease in activation energy of the reaction
Increase in enzyme concentration
Explanation
Enzymes are pH and temperature sensitive., and only function in optimal ranges of these conditions. Certain enzymes will only function in acidic environments, while others require basic conditions.
The overall free energy and enthalpy of the reaction, activation energy, and enzyme concentration do not have a bearing on enzymatic activity.
A supercoiled helix is described by which level of peptide structure?
Secondary
Primary
Tertiary
Quartenary
There is not enough information to tell
Explanation
Secondary peptide structure refers to alpha-helices and beta-sheets, which are formed by hydrogen bonding. A supercoiled helix is due to the secondary structure of a peptide. Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids, tertiary structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of the protein, and quatenary structure arises when more than one peptide subunit interacts.






