Covalent Bonds and Hybrid Orbitals
Help Questions
MCAT Biology › Covalent Bonds and Hybrid Orbitals
The compound below is reacted with 

Explanation
The initially chiral carbon has an 




How many pi bonds are present in benzylamine?
Three
Eight
Four
Seventeen
Explanation
Benzylamine consists of a benzene ring with a -CH2NH2 substituent. The benzene ring contains three double bonds, and the substituent has none.
Each bond in a compound represents a sigma bond. Each additional bond represents a pi bond; thus, double binds result from one sigma and one pi bond, and triple bonds from one sigma and two pi bonds. In benzylamine, there are three double bonds and seventeen total bonds, three of which are double bonds. The compound will have a total of seventeen sigma bonds and three pi bonds.
Compound A has a molecular formula of 

Two
One
Zero
Four
Five
Explanation
Recall the formula for degrees of unsaturation as the sum of the number of pi bonds and the number of rings. This value is equivalent to the below formula.
C is the number of carbons, H is the number of hydrogens, X is the number of halogens, and N is the number of nitrogens. Using this formula, compound A has four degrees of unsaturation, while the product only has two.
The reaction described is a hydrogenation reaction, which will reduce double bonds. The reaction saturates two pi bonds of compound A, meaning the remaining degrees of unsaturation in that compound have to come from two rings. Essentially, due to the reaction given, we know that the product contains no double bonds but still has two degrees of unsaturation. These unsaturation points must correspond to rings.
Which compound contains the most stable carbon bonds?
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Acetone
Ethene
Explanation
The stability of a bond can be compared to others by determining the hybridization of the bond. It helps to remember that the bond with the most s character is considered the most stable.
Carbon dioxide has a carbon that is connected to two oxygens by two double bonds. This means that the carbon has sp hybridization. Since the bond has 50% s character, it is the most stable out of the available compounds.
Methane contains only single bonds and will have an sp3 hybridized carbon, with only 25% s character. Acetone and ethene each contain one double bond and will contain an sp2 hybridized carbon with 33% s character.
A and C
B, C, and D
B and C
C
Explanation
The answer is arrows A and C. The carbon that is pointed to by arrow C is 



We can quickly tell the hybridization of atoms by observing their double bonds and unbonded electrons. As a rule of thumb, any carbon, nitrogen, or oxygen involved in a double bond will be 


A
A, B, and C
D
A and C
Explanation
For a compound to be considered aromatic, it must be flat, cyclic, and conjugated and it must obey Huckel's rule. Huckel's rule states that an aromatic compound must have 
Drain cleaners are a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
The C–N bond in the original protein, before reaction with drain cleaner is __________.
weaker and longer than the carbonyl bond in the same molecule
stronger and longer than the carbonyl bond in the same molecule
weaker and shorter than the carbonyl bond in the same molecule
stronger and shorter than the carbonyl bond in the same molecule
nonpolar due to electron interaction with the lone pair on the N atom
Explanation
The C–N bond is a single bond, and the carbonyl bond is a double bond. Double bonds are stronger and shorter than single bonds.
Which compound has the largest bond energy between carbons?
Ethyne
Benzene
Propane
1,3-butadiene
Explanation
It helps to remember that bond energy is inversely proportional to bond length. In other words, the shorter the bond, the higher the bond energy.
Bond length is shortened when pi bonds are involved, so double and triple bonds are much shorter than simple sigma bonds. The bond length between the carbons in ethyne is the shortest out of all options because they are triple bonded to one another. This also makes it the most stable bond, and gives it the largest bond energy.
Benzene and 1,3-butadiene will have relatively high energy stored in double bonds, but will be unable to match a triple bond. Propane has only single bonds and will have the lowest bond energy of these answers.
Which of the following compounds has five degrees of unsaturation?

Compounds A and C
Compound A
Compound C
Compounds A, B, and C
Compounds B and C
Explanation
A degree of unsaturation results from either a ring or a double bond. In the case of a benzene ring or phenyl substituent, four degrees of unsaturation are present: the ring itself and the three included double bonds.
Compounds A, B, and C all possess a benzene ring, but compounds A and C also have one additional degree of unsaturation. Compound A contains a carbon-oxygen double bond in the ketone group and compound C contains a carbon-carbon double bond in the alkene group. In addition to the four degrees from the ring, these additions bring their total degrees of unsaturation to five. Compound B has no additional double bond, and therefore has four degrees of unsaturation.
When formic acid is completely reduced, methanol is formed.
What is the hybridization of the carbon in formic acid, compared to the carbon in methanol?
The carboxylic acid has sp2 hybridization and the alcohol has sp3 hybridization.
The carboxylic acid has sp2 hybridization and the alcohol has sp2 hybridization.
The carboxylic acid has sp3 hybridization and the alcohol has sp2 hybridization.
The carboxylic acid has sp3 hybridization and the alcohol has sp3 hybridization.
Explanation
In order to find the hybridization of an atom, simply count the number of sigma bonds and lone pair electrons around the atom. The carbon in formic acid is double bonded to an oxygen, and has two single bonds. This means that it has sp2 hybridization. Upon being reduced to methanol, the carbon now has four single bonds surrounding it. As a result, the carbon now has sp3 hybridization.
Remember that a triple bond corresponds to sp hydrization, a double bond to sp2, and single bonds to sp3 for a carbon atom.



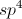





 hybridized?
hybridized?




