Analyzing Solids
Help Questions
GRE › Analyzing Solids
Household vinegar contains the organic compound acetic acid with chemical formula, 



Density of vinegar is the following:
Explanation
Convert the moles of 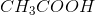
To calculate the percentage of 
Therefore,
Household vinegar contains the organic compound acetic acid with chemical formula, 



Density of vinegar is the following:
Explanation
Convert the moles of 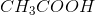
To calculate the percentage of 
Therefore,
Determining the molecular ion peak (parent peak) in mass spectroscopy allows you to determine what characteristic of a mystery molecule?
Molecular weight
Molecular charge
Functional groups
Nuclear charge
Explanation
The molecular ion peak is determined using mass spectrometry. The parent peak is formed when a mystery molecule does not fragment, and simply loses an electron. This means that the mass to charge ratio of this peak will allow us to determine the molecular weight of the compound.
Determining the molecular ion peak (parent peak) in mass spectroscopy allows you to determine what characteristic of a mystery molecule?
Molecular weight
Molecular charge
Functional groups
Nuclear charge
Explanation
The molecular ion peak is determined using mass spectrometry. The parent peak is formed when a mystery molecule does not fragment, and simply loses an electron. This means that the mass to charge ratio of this peak will allow us to determine the molecular weight of the compound.
The 



Explanation
The equation for the dissolution of 
The 
Due to the molar ratios of the species of 


Plugging 

Therefore, the solubility of 
The 



Explanation
The equation for the dissolution of 
The 
Due to the molar ratios of the species of 


Plugging 

Therefore, the solubility of 
For the titration of 




Explanation
The equivalence point is when enough titrant has been added so that the number of moles of titrant equals the number of moles of analyte. We must first determine the number of moles of silver ions at the equivalence point.
At the equivalence point the following occurs in solution:
The number of moles of silver ions at equivalence point is calculated as follows:
Plugging these values into the equation gives:
For the titration of 




Explanation
The equivalence point is when enough titrant has been added so that the number of moles of titrant equals the number of moles of analyte. We must first determine the number of moles of silver ions at the equivalence point.
At the equivalence point the following occurs in solution:
The number of moles of silver ions at equivalence point is calculated as follows:
Plugging these values into the equation gives:
Write the solubility product, 

Explanation
The solubility product constant (

The denominator represents solid barium sulfate which is considered a constant. When the equation is rearranged, it becomes:
The product, ![K_{eq}*[BaSO_{4}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/553151/gif.latex)

Write the solubility product, 

Explanation
The solubility product constant (

The denominator represents solid barium sulfate which is considered a constant. When the equation is rearranged, it becomes:
The product, ![K_{eq}*[BaSO_{4}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/553151/gif.latex)


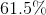


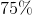









![K_{sp}=[Cd^{2+}][CO_{3}^{2-}]=1.8 *10^{-14}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/704265/gif.latex)
![[Cd^{2+}]=[CO_{3}^{2-}]=X](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/704269/gif.latex)












![K_{sp} = [Ba^{2+}][SO_{4^}^{}^{2-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/541638/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ba][SO_{4}]^{2-}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/541639/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ba][SO_{4}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/541640/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ba]^{2+}[SO_{4}]^{2-}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/541641/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ba]^{4+}[SO_{4}]^{2-}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/553588/gif.latex)
![K_{eq} = \frac{[Ba^{2+}][SO_{4^}^{}^{2-}]}{[BaSO_{4}(s)]}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/541651/gif.latex)
![K_{eq}*[BaSO_{4}]=[Ba^{2+}][SO_{4^}^{}^{2-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/553150/gif.latex)
![K_{sp} = [Ba^{2+}][SO_{4^}^{}^{2-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/541654/gif.latex)