Organic Chemistry - GRE Subject Test: Chemistry
Card 0 of 244
A molecule has three chiral centers. How many stereoisomers of this compound will have different boiling points compared to the original molecule?
A molecule has three chiral centers. How many stereoisomers of this compound will have different boiling points compared to the original molecule?
The first step is to determine how many stereoisomers there are for this molecule. Since the number of stereoisomers is dependent on the number of chiral carbons, we can solve according to the equation  , where
, where  is the number of chiral centers. Since there are three chiral centers, we determine that there are eight stereoisomers for this molecule. Keep in mind that this number includes the original molecule.
is the number of chiral centers. Since there are three chiral centers, we determine that there are eight stereoisomers for this molecule. Keep in mind that this number includes the original molecule.

Next, we need to compare the different stereoisomers to the original molecule. The original molecule will have one enantiomer and six diastereomers. Remember that enantiomers have the same physical properties, so we will not include this isomer in the final answer. Diastereomers, on the other hand, have different physical properties compared to the original molecule. As a result, six stereoisomers will have different boiling points compared to the original molecule.
The first step is to determine how many stereoisomers there are for this molecule. Since the number of stereoisomers is dependent on the number of chiral carbons, we can solve according to the equation 

Next, we need to compare the different stereoisomers to the original molecule. The original molecule will have one enantiomer and six diastereomers. Remember that enantiomers have the same physical properties, so we will not include this isomer in the final answer. Diastereomers, on the other hand, have different physical properties compared to the original molecule. As a result, six stereoisomers will have different boiling points compared to the original molecule.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The correct answer is three. The key to finding chiral carbons is to look for carbons that are attached to four different substituents. We can immediately eliminate any carbons that are involved in double bonds, or that have two hydrogens attached. Given this, we find that there are three chiral carbons. Note that carbon chains of varying content will qualify as different substituents, allowing chiral carbons to bond to two other carbons.
The correct answer is three. The key to finding chiral carbons is to look for carbons that are attached to four different substituents. We can immediately eliminate any carbons that are involved in double bonds, or that have two hydrogens attached. Given this, we find that there are three chiral carbons. Note that carbon chains of varying content will qualify as different substituents, allowing chiral carbons to bond to two other carbons.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Compounds that are mirror images of each other are called __________.
Compounds that are mirror images of each other are called __________.
Stereoisomers are isomers that differ in the orientation of atoms in space, but have the same bonding patterns and structures. Enantiomers are a specific class of stereoisomers that differ in orientation around a chiral center to create mirror image molecules.
Diastereomers are a type of stereoisomer that are not related through a reflection operation, and may differ at more than one chiral center. Conformers have the same structural formula, but different shapes due to bond rotation.
Stereoisomers are isomers that differ in the orientation of atoms in space, but have the same bonding patterns and structures. Enantiomers are a specific class of stereoisomers that differ in orientation around a chiral center to create mirror image molecules.
Diastereomers are a type of stereoisomer that are not related through a reflection operation, and may differ at more than one chiral center. Conformers have the same structural formula, but different shapes due to bond rotation.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

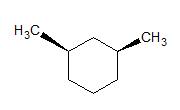
The given molecules are __________.


The given molecules are __________.
Stereoisomers have different orientations around a single stereocenter. The two molecules are stereoisomers. Specifically, these molecules are epimers, meaning that they differ at only one stereocenter.
Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula, but different structures. Conformers have different rotations around a single bond. The molecules are clearly not identical.
Stereoisomers have different orientations around a single stereocenter. The two molecules are stereoisomers. Specifically, these molecules are epimers, meaning that they differ at only one stereocenter.
Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula, but different structures. Conformers have different rotations around a single bond. The molecules are clearly not identical.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following carbons represents the stereogenic center between the given isomers?


Which of the following carbons represents the stereogenic center between the given isomers?


Epimers are isomers that have different configurations at only one carbon atom. This carbon atom is known as the stereogenic center. The given compounds are identical except for the orientation around carbon number 4; thus, carbon 4 is the stereogenic center.
Epimers are isomers that have different configurations at only one carbon atom. This carbon atom is known as the stereogenic center. The given compounds are identical except for the orientation around carbon number 4; thus, carbon 4 is the stereogenic center.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The molecules shown below are best described as __________.

The molecules shown below are best described as __________.
The molecules in this problem are isomers because they each have unique configurations and do not share the same funcitonal groups at the same carbon positions. Enantiomers are reflections of each other. Diastereomers are stereoisomers that differ at one or more stereocenters, while epimers are stereoisomers that differ at only one stereocenter.
The molecules in this problem are isomers because they each have unique configurations and do not share the same funcitonal groups at the same carbon positions. Enantiomers are reflections of each other. Diastereomers are stereoisomers that differ at one or more stereocenters, while epimers are stereoisomers that differ at only one stereocenter.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not a geometric isomer of pentene?
Which of the following is not a geometric isomer of pentene?
Geometric isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but they differ in the way they are arranged spatially. Pentene carries the molecular formula,  . The longest chain of carbon atoms should be five carbons. According to its name, pentene is an alkene due to the -ene form its name, therefore must also contain a
. The longest chain of carbon atoms should be five carbons. According to its name, pentene is an alkene due to the -ene form its name, therefore must also contain a  bond. The only compound without a chain of 5 carbons consecutively is
bond. The only compound without a chain of 5 carbons consecutively is  and this compound is not a geometric isomer of pentene.
and this compound is not a geometric isomer of pentene.
Geometric isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but they differ in the way they are arranged spatially. Pentene carries the molecular formula, 

 and this compound is not a geometric isomer of pentene.
and this compound is not a geometric isomer of pentene.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which type of bond is created between carbohydrates and the sidechain amine of select asparagine residues in proteins?
Which type of bond is created between carbohydrates and the sidechain amine of select asparagine residues in proteins?
A glycosidic bond covalently joins a carbohydrate molecule to another molecule. An O-glycosidic bond is a covalent linkage between a carbohydrate and a protein, joining a serine or threonine hydroxyl side chain and a sugar (oxygen in the bond yields "O"). An N-glycosidic linkage involves bonding of a carbohydrate and a protein, joining an asparagine side chain amide and a sugar (nitrogen in the bond yields "N"). Thus, N-glycosidic is the correct answer.
A glycosidic bond covalently joins a carbohydrate molecule to another molecule. An O-glycosidic bond is a covalent linkage between a carbohydrate and a protein, joining a serine or threonine hydroxyl side chain and a sugar (oxygen in the bond yields "O"). An N-glycosidic linkage involves bonding of a carbohydrate and a protein, joining an asparagine side chain amide and a sugar (nitrogen in the bond yields "N"). Thus, N-glycosidic is the correct answer.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following molecules is amphipathic?
Which of the following molecules is amphipathic?
Amphipathic molecules contain both polar and nonpolar regions, making them an extremely diverse class with an array of functions. For example, bile is an amphipathic molecule whose nonpolar region interacts with fats and whose polar region interacts with the aqueous environment of the small intestine.
Most lipids are entirely nonpolar and hydrophobic. Phospholipids, however, are formed from a glycerol molecule bound to two hydrophobic fatty acid tails and a hydrophilic phosphate head. This structure allows phospholipids amphipathic properties. Most notably, phospholipids are able to interact with the aqueous environments in the cell cytosol and extracellular environment, while maintaining the hydrophobic region of the cell membrane that acts as a semipermeable barrier.
Triglycerides are considered nonpolar. Glutamate is an acidic amino acid with highly polar properties. Maltose is a six-carbon sugar (carbohydrate) and is highly polar.
Amphipathic molecules contain both polar and nonpolar regions, making them an extremely diverse class with an array of functions. For example, bile is an amphipathic molecule whose nonpolar region interacts with fats and whose polar region interacts with the aqueous environment of the small intestine.
Most lipids are entirely nonpolar and hydrophobic. Phospholipids, however, are formed from a glycerol molecule bound to two hydrophobic fatty acid tails and a hydrophilic phosphate head. This structure allows phospholipids amphipathic properties. Most notably, phospholipids are able to interact with the aqueous environments in the cell cytosol and extracellular environment, while maintaining the hydrophobic region of the cell membrane that acts as a semipermeable barrier.
Triglycerides are considered nonpolar. Glutamate is an acidic amino acid with highly polar properties. Maltose is a six-carbon sugar (carbohydrate) and is highly polar.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following will you most likely find in a steroid molecule?
Which of the following will you most likely find in a steroid molecule?
Steroids are a type of lipid that are characterized by their four-ring molecular structure. The four rings consist of three six-membered rings and one five-membered ring. Recall that six-membered rings are called cyclohexanes and five-membered rings are called cyclopentanes; therefore, you will most likely find a cyclohexane in a steroid.
Phosphate groups, pentose sugars, and nitrogenous bases are found in nucleotides, which are monomers that make up nucleic acids. Steroids are a type of lipid; therefore, you will most likely not find these substances in a steroid.
Steroids are a type of lipid that are characterized by their four-ring molecular structure. The four rings consist of three six-membered rings and one five-membered ring. Recall that six-membered rings are called cyclohexanes and five-membered rings are called cyclopentanes; therefore, you will most likely find a cyclohexane in a steroid.
Phosphate groups, pentose sugars, and nitrogenous bases are found in nucleotides, which are monomers that make up nucleic acids. Steroids are a type of lipid; therefore, you will most likely not find these substances in a steroid.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Of the following groups of nitrogenous bases, which does not contain a purine?
Of the following groups of nitrogenous bases, which does not contain a purine?
We can use the mnemonic "PurAG" to remember that the purines are adenine and guanine. The only choice that does not contain a purine, therefore, is "cytosine, thymine, and uracil." Remember, pyrimidines contain a single ring, while purines have two.
We can use the mnemonic "PurAG" to remember that the purines are adenine and guanine. The only choice that does not contain a purine, therefore, is "cytosine, thymine, and uracil." Remember, pyrimidines contain a single ring, while purines have two.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Cellulose is a polymer that is composed of what monomer?
Cellulose is a polymer that is composed of what monomer?
Cellulose is a polysaccharide (a sugar). Glucose is the monosaccharide used to generate the structure of cellulose via  linkages. Cellulose is composed of several hundred glucose molecules bound in this chain. Due to the nature of the beta linkage, humans cannot digest cellulose.
linkages. Cellulose is composed of several hundred glucose molecules bound in this chain. Due to the nature of the beta linkage, humans cannot digest cellulose.
Cellulose is a polysaccharide (a sugar). Glucose is the monosaccharide used to generate the structure of cellulose via 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
An enzyme that cleaves disulfide bridges would most disrupt a protein containing which amino acid sequence?
An enzyme that cleaves disulfide bridges would most disrupt a protein containing which amino acid sequence?
Disulfide bridges are made between two cysteine amino acids. An enzyme that cleaves disulfide bonds would disrupt a protein containing the most cysteine residues; therefore, Tyr–Cys–Cys–Thr–Val–Leu is the correct answer.
Disulfide bridges are made between two cysteine amino acids. An enzyme that cleaves disulfide bonds would disrupt a protein containing the most cysteine residues; therefore, Tyr–Cys–Cys–Thr–Val–Leu is the correct answer.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
How many water molecules are lost from the condensation of 100 amino acids into a polypeptide?
How many water molecules are lost from the condensation of 100 amino acids into a polypeptide?
A peptide bond is formed via the condensation of one amino acid's alpha-carboxy group with the alpha-amino group of another amino acid. Thus, the joining together of two amino acids results in the loss of one water molecule. Likewise, joining three amino acids together results in the loss of two water molecules. Following this pattern, we can conclude that the number of water molecules lost is equal to the number of amino acids joined together, minus 1. Therefore, the joining together of 100 amino acids results in the loss of 99 water molecules.
A peptide bond is formed via the condensation of one amino acid's alpha-carboxy group with the alpha-amino group of another amino acid. Thus, the joining together of two amino acids results in the loss of one water molecule. Likewise, joining three amino acids together results in the loss of two water molecules. Following this pattern, we can conclude that the number of water molecules lost is equal to the number of amino acids joined together, minus 1. Therefore, the joining together of 100 amino acids results in the loss of 99 water molecules.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following can reduce an alkene to an alkane?
Which of the following can reduce an alkene to an alkane?
Neither lithium aluminum hydride, nor sodium borohydride will reduce C–C double bonds.
H2/Raney nickel and H2/Pd can each (individually) reduce an alkene to an alkane. Since both H2/Raney nickel and H2/Pd can reduce the alkene, the answer is both of those reagents. This is a catalytic hydrogenation reaction, and H2/Raney nickel not only reduces C–C double bonds, but also carbonyl compounds.
Neither lithium aluminum hydride, nor sodium borohydride will reduce C–C double bonds.
H2/Raney nickel and H2/Pd can each (individually) reduce an alkene to an alkane. Since both H2/Raney nickel and H2/Pd can reduce the alkene, the answer is both of those reagents. This is a catalytic hydrogenation reaction, and H2/Raney nickel not only reduces C–C double bonds, but also carbonyl compounds.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Identify the major organic product expected from the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-2-pentanol.
Identify the major organic product expected from the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-2-pentanol.
The initial compound is a five-carbon alkane chain with methyl and hydroxy groups on the second carbon. Dehydration involves the hydrogenation of the hydroxy group. That group then leaves, and a double bond is formed. Zaitsev's rule states that double bonds are more stable on more highly substituted carbons. The double bond forms across carbons two and three.
The initial compound is a five-carbon alkane chain with methyl and hydroxy groups on the second carbon. Dehydration involves the hydrogenation of the hydroxy group. That group then leaves, and a double bond is formed. Zaitsev's rule states that double bonds are more stable on more highly substituted carbons. The double bond forms across carbons two and three.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
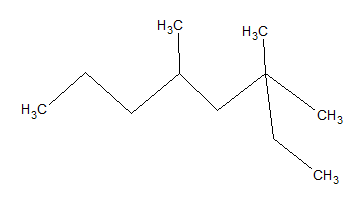
What is the IUPAC name of the given molecule?

What is the IUPAC name of the given molecule?
The longest carbon chain that can be formed is eight carbons. The base molecule is octane.
Using IUPAC rules, substituents should have the lowest possible numbers; thus, we start counting carbons from the right side rather than the left. If you count from the correct side, there are two methyl groups on carbon 3 and one on carbon 5. Thus, the name of the moleculue is 3,3,5-trimethyloctane.
The longest carbon chain that can be formed is eight carbons. The base molecule is octane.
Using IUPAC rules, substituents should have the lowest possible numbers; thus, we start counting carbons from the right side rather than the left. If you count from the correct side, there are two methyl groups on carbon 3 and one on carbon 5. Thus, the name of the moleculue is 3,3,5-trimethyloctane.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

How could you brominate the compound?

How could you brominate the compound?
The given molecule is an alkane. The only way to brominate an alkane is with bromine gas and UV light. The energy from the light serves to creat two radical bromines. These radicals are capable of bonding with alkanes. If the given compound were an alkene, either hydrobromic acid or bromine and peroxides would work.
The given molecule is an alkane. The only way to brominate an alkane is with bromine gas and UV light. The energy from the light serves to creat two radical bromines. These radicals are capable of bonding with alkanes. If the given compound were an alkene, either hydrobromic acid or bromine and peroxides would work.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The stereochemical pathway for the hydrogenation of an alkene with a metal catalyst, such as platinum, occurs via __________.
The stereochemical pathway for the hydrogenation of an alkene with a metal catalyst, such as platinum, occurs via __________.
Hydrogenation of an alkene with a metal catalyst, such as platinum, occurs via syn addition.
It is important to note the three main types of reactions for alkenes. The first type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism in which the electrophile attacks the carbocation nucleophile. This can yield syn or anti products. The second type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism that forms a bridged carbocation as the intermediate. This can yield only anti products. The third and last type of reaction is a 1-step addition. This can only yield syn products.
An example of the third type of reaction is the addition of a hydrogen with palladium, platinum, or nickel as demonstrated in the picture.

Hydrogenation of an alkene with a metal catalyst, such as platinum, occurs via syn addition.
It is important to note the three main types of reactions for alkenes. The first type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism in which the electrophile attacks the carbocation nucleophile. This can yield syn or anti products. The second type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism that forms a bridged carbocation as the intermediate. This can yield only anti products. The third and last type of reaction is a 1-step addition. This can only yield syn products.
An example of the third type of reaction is the addition of a hydrogen with palladium, platinum, or nickel as demonstrated in the picture.

Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is(are) the product(s) in the Pd-catalyzed hydrogenation if 1,2-dimethylcyclopentene?
What is(are) the product(s) in the Pd-catalyzed hydrogenation if 1,2-dimethylcyclopentene?
The product for this hydrogenation is _cis-_1,2-dimethylcyclopentane.
It is important to note the three main types of reactions for alkenes. The first type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism in which the electrophile attacks the carbocation nucleophile. This can yield syn or anti products. The second type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism that forms a bridged carbocation as the intermediate. This can yield only anti products. The third and last type of reaction is a 1-step addition. This can only yield syn products.
The cis product alone forms because the reagents used were hydrogen and a metal catalyst palladium (other common metal catalysts are platinum and nickel). This type of reagent with an alkene will always be a 1-step addition that yields solely syn products. Cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane is the only answer that solely indicates syn products.
The product for this hydrogenation is _cis-_1,2-dimethylcyclopentane.
It is important to note the three main types of reactions for alkenes. The first type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism in which the electrophile attacks the carbocation nucleophile. This can yield syn or anti products. The second type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism that forms a bridged carbocation as the intermediate. This can yield only anti products. The third and last type of reaction is a 1-step addition. This can only yield syn products.
The cis product alone forms because the reagents used were hydrogen and a metal catalyst palladium (other common metal catalysts are platinum and nickel). This type of reagent with an alkene will always be a 1-step addition that yields solely syn products. Cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane is the only answer that solely indicates syn products.
Compare your answer with the correct one above