Molecules and Compounds - AP Chemistry
Card 0 of 264
How many of the following compounds are ionic?





How many of the following compounds are ionic?
Ionic compounds are chemical compounds made of charged ions held together by forces called ionic bonding. Ionic bonds are formed by transfers of valance electrons, which create charged atoms (ions) which are attracted to each other because they have opposite charges. This is not be confused with covalent bonding, in which atoms form an attraction by sharing electrons.
 contains a positively charged
contains a positively charged  ion and negatively charged
ion and negatively charged 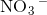 ion which form an ionic bond.
ion which form an ionic bond.  contains two positively charged
contains two positively charged  ions and a negatively charged
ions and a negatively charged  ion which form an ionic bond.
ion which form an ionic bond. 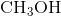 ,
,  , and
, and  are all examples of molecules that contain covalent bonds. None of them contains any charged ions. The answer is therefore "two,"referring to the
are all examples of molecules that contain covalent bonds. None of them contains any charged ions. The answer is therefore "two,"referring to the  and
and  molecules.
molecules.
Ionic compounds are chemical compounds made of charged ions held together by forces called ionic bonding. Ionic bonds are formed by transfers of valance electrons, which create charged atoms (ions) which are attracted to each other because they have opposite charges. This is not be confused with covalent bonding, in which atoms form an attraction by sharing electrons.


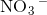



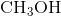




Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is true of Valence Bond theory and Molecular Orbital theory?
Which of the following is true of Valence Bond theory and Molecular Orbital theory?
The Valence Bond theory states that covalent bonds are formed from atomic orbital overlap while the Molecular Orbital theory is the mathematical combination of atomic orbitals to produce anti bonding and bonding orbitals.
Hybridization occurs through combining atomic orbitals, a concept consistent with Valence Bond theory. Common bonds found in Valence Bond hybridization are sigma and pi bonds which overlap end-to-end or side-to-side respectively. Orbitals are combined in Molecular Orbital theory, producing either bonding or anti bonding orbitals. Molecular Orbital theory shows the destructive or constructive interference of sigma and pi bonds (displayed through bonding and anti bonding orbitals).
The Valence Bond theory states that covalent bonds are formed from atomic orbital overlap while the Molecular Orbital theory is the mathematical combination of atomic orbitals to produce anti bonding and bonding orbitals.
Hybridization occurs through combining atomic orbitals, a concept consistent with Valence Bond theory. Common bonds found in Valence Bond hybridization are sigma and pi bonds which overlap end-to-end or side-to-side respectively. Orbitals are combined in Molecular Orbital theory, producing either bonding or anti bonding orbitals. Molecular Orbital theory shows the destructive or constructive interference of sigma and pi bonds (displayed through bonding and anti bonding orbitals).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the orbital hybridization for nitrogen in the molecule  ?
?
What is the orbital hybridization for nitrogen in the molecule 
Start by drawing the Lewis structure of  .
.  has
has  valence electrons.
valence electrons.

Since the nitrogen has  oxygen atoms bonded to it and a lone pair, the steric number must be
oxygen atoms bonded to it and a lone pair, the steric number must be  . From that, we know that it must have sp2 hybridization.
. From that, we know that it must have sp2 hybridization.
Start by drawing the Lewis structure of 



Since the nitrogen has 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following types of hybridization is found in the molecule shown below?

Which of the following types of hybridization is found in the molecule shown below?


Look at each of the carbon atoms in the chain. Each carbon atom has  other atoms bonded to it. This means that the steric number of each carbon is
other atoms bonded to it. This means that the steric number of each carbon is  . Thus, the only type of hybridization found in this molecule is sp2.
. Thus, the only type of hybridization found in this molecule is sp2.

Look at each of the carbon atoms in the chain. Each carbon atom has 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the hybridization for the atom circled in red?

What is the hybridization for the atom circled in red?


Start by counting the number of atoms the nitrogen is bonded to. It has  bonded atoms. The nitrogen also has a lone pair. This means the steric number of the nitrogen is
bonded atoms. The nitrogen also has a lone pair. This means the steric number of the nitrogen is  . Thus, it must have
. Thus, it must have  hybridization.
hybridization.

Start by counting the number of atoms the nitrogen is bonded to. It has 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
The compound hydrazine is given by the molecular formula  . What type of intermolecular forces will govern the behavior of neighboring hydrazine molecules?
. What type of intermolecular forces will govern the behavior of neighboring hydrazine molecules?
The compound hydrazine is given by the molecular formula 
Hydrazine is a polar compound that possesses the requirements for hydrogen bonding: an "acidic hydrogen" (a hydrogen bonded to a highly electronegative atom such as oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine) and the presence of a lone pair. Both Nitrogen atoms in hydrazine have lone (unshared) electron pairs, and all four hydrogen atoms are "acidic," making hydrazine a candidate for intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Hydrazine is a polar compound that possesses the requirements for hydrogen bonding: an "acidic hydrogen" (a hydrogen bonded to a highly electronegative atom such as oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine) and the presence of a lone pair. Both Nitrogen atoms in hydrazine have lone (unshared) electron pairs, and all four hydrogen atoms are "acidic," making hydrazine a candidate for intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The unique properties of water, namely its incredibly high heat capacity and surface tension, can be attributed to which of the following kinds of intermolecular/intramolecular forces?
The unique properties of water, namely its incredibly high heat capacity and surface tension, can be attributed to which of the following kinds of intermolecular/intramolecular forces?
The partial negative and positive charges on a water molecule allow it to be attracted to other polar water molecules, which creates the cohesive nature of water and contributes to its high surface tension and heat capacity. London dispersion and Van der Waals forces are significantly weaker than hydrogen bonding. Additionally, ionic bonding only occurs intramolecularly, so it has little effect on the intermolecular properties of water.
The partial negative and positive charges on a water molecule allow it to be attracted to other polar water molecules, which creates the cohesive nature of water and contributes to its high surface tension and heat capacity. London dispersion and Van der Waals forces are significantly weaker than hydrogen bonding. Additionally, ionic bonding only occurs intramolecularly, so it has little effect on the intermolecular properties of water.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is a characteristic of covalent bonds?
Which of the following is a characteristic of covalent bonds?
A covalent bond is one between two nonmetals, while an ionic bond is formed between a metal and a nonmetal. Covalent bonds also do not dissociate in aqueous solution to form cations and anions; this is a characteristic of ionic bonds. For example,  represents a bond between a metal (
represents a bond between a metal ( ) and a nonmetal (
) and a nonmetal ( ), and it dissociates in aqueous solution to form a cation (
), and it dissociates in aqueous solution to form a cation ( ) and an anion (
) and an anion ( ). In contrast,
). In contrast,  represents a bond between two nonmetals, and it does not dissociate in aqueous solution. Ionic compounds are also good conductors of electricity, while covalent compounds are not. This is because moving electrons are required in order to conduct electricity. When dissolved in aqueous solution, ions are free to move and thus conduct electricity. Covalent bonds have localized electrons, which cannot move and thus cannot conduct electricity well.
represents a bond between two nonmetals, and it does not dissociate in aqueous solution. Ionic compounds are also good conductors of electricity, while covalent compounds are not. This is because moving electrons are required in order to conduct electricity. When dissolved in aqueous solution, ions are free to move and thus conduct electricity. Covalent bonds have localized electrons, which cannot move and thus cannot conduct electricity well.
A covalent bond is one between two nonmetals, while an ionic bond is formed between a metal and a nonmetal. Covalent bonds also do not dissociate in aqueous solution to form cations and anions; this is a characteristic of ionic bonds. For example, 





Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is an example of a nonpolar covalent bond?
Which of the following is an example of a nonpolar covalent bond?
A covalent bond is a bond between two nonmetals, in which electrons are shared. This means that  cannot be the correct answer, as sodium is a metal. In fact,
cannot be the correct answer, as sodium is a metal. In fact,  is a classic example of an ionic compound.
is a classic example of an ionic compound.
A polar covalent bond is a bond between two nonmetals in which one nonmetal is more electronegative than the other, pulling the shared electrons toward itself. This occurs in  ; chlorine is much more electronegative than hydrogen and pulls the shared electrons toward itself. This gives chlorine a partial negative charge and hydrogen a partial positive charge.
; chlorine is much more electronegative than hydrogen and pulls the shared electrons toward itself. This gives chlorine a partial negative charge and hydrogen a partial positive charge.  is also an example of a polar covalent bond; oxygen is much more electronegative than hydrogen, and each oxygen in a water molecule pulls the shared electrons toward itself. This gives oxygen a partial negative charge and hydrogen a partial positive charge.
is also an example of a polar covalent bond; oxygen is much more electronegative than hydrogen, and each oxygen in a water molecule pulls the shared electrons toward itself. This gives oxygen a partial negative charge and hydrogen a partial positive charge.
A nonpolar covalent bond is a bond between two nonmetals in which electrons are shared equally between the nonmetals. This occurs when the two nonmetals are of equal electronegativity. As the atoms of  have the same identity (chlorine), they have the same electronegativity. Thus, electrons are shared equally between the two chlorine atoms--in a nonpolar covalent bond.
have the same identity (chlorine), they have the same electronegativity. Thus, electrons are shared equally between the two chlorine atoms--in a nonpolar covalent bond.
A covalent bond is a bond between two nonmetals, in which electrons are shared. This means that 

A polar covalent bond is a bond between two nonmetals in which one nonmetal is more electronegative than the other, pulling the shared electrons toward itself. This occurs in 

A nonpolar covalent bond is a bond between two nonmetals in which electrons are shared equally between the nonmetals. This occurs when the two nonmetals are of equal electronegativity. As the atoms of 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of these following diatomic molecules is joined by a double covalent bond?
Which of these following diatomic molecules is joined by a double covalent bond?
Oxygen has a valence of 6, meaning it is looking to form two covalent bonds to complete its octet. Thus,  exists as a diatomic molecule joined by a double covalent bond.
exists as a diatomic molecule joined by a double covalent bond.  and
and  are held together by single covalent bonds, and
are held together by single covalent bonds, and  is held together by a triple covalent bond.
is held together by a triple covalent bond.
Oxygen has a valence of 6, meaning it is looking to form two covalent bonds to complete its octet. Thus, 



Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following lists bond strength in order of weakest to strongest?
Which of the following lists bond strength in order of weakest to strongest?
Dipole-dipole interactions are the weakest because they are the result of attractions between weak partial charges
Hydrogen bonds are a special type of dipole-dipole interaction, but they are much stronger.
An ionic bond is the result of the complete transfer of electrons from on atom to another. This results in a positive charge on one atom and a negative charge on the other. The charges on these ions are much stronger than in dipoles. The two oppositely charged atoms are held together by electrostatic attraction.
Atoms that are part of a covalent bond share electrons. This makes the atoms harder to separate and, therefore, the bond is very strong.
Dipole-dipole interactions are the weakest because they are the result of attractions between weak partial charges
Hydrogen bonds are a special type of dipole-dipole interaction, but they are much stronger.
An ionic bond is the result of the complete transfer of electrons from on atom to another. This results in a positive charge on one atom and a negative charge on the other. The charges on these ions are much stronger than in dipoles. The two oppositely charged atoms are held together by electrostatic attraction.
Atoms that are part of a covalent bond share electrons. This makes the atoms harder to separate and, therefore, the bond is very strong.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following compounds contains  covalent bonds?
covalent bonds?
Which of the following compounds contains 
For this question, we're asked to determine which answer choice represents a compound with a total of six covalent bonds.
To answer this, we'll need to know the structure of each of the compounds. Moreover, it's important to remember that double bonds count as two covalent bonds.
Both sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid have a total of eight covalent bonds, while nitric acid has five. Carbonic acid is the only one shown that contains six covalent bonds, making it the correct answer.
For this question, we're asked to determine which answer choice represents a compound with a total of six covalent bonds.
To answer this, we'll need to know the structure of each of the compounds. Moreover, it's important to remember that double bonds count as two covalent bonds.
Both sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid have a total of eight covalent bonds, while nitric acid has five. Carbonic acid is the only one shown that contains six covalent bonds, making it the correct answer.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following best explains the main difference between strong and weak acids or bases?
Which of the following best explains the main difference between strong and weak acids or bases?
Molarity has no determination in whether an acid or base is strong or weak. Rather, molarity specifies the concentration of hydroxide or hydrogen ions in a solution. Weak Acids do not completely dissociate in water, while strong acids do. Polyprotic acids, those with more than one proton to donate, do not necessarily determine if an acid is strong (e.g. hydrochloric acid is an example of a strong, monoprotic acid).
Molarity has no determination in whether an acid or base is strong or weak. Rather, molarity specifies the concentration of hydroxide or hydrogen ions in a solution. Weak Acids do not completely dissociate in water, while strong acids do. Polyprotic acids, those with more than one proton to donate, do not necessarily determine if an acid is strong (e.g. hydrochloric acid is an example of a strong, monoprotic acid).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Is  an atomic element, molecular element, molecular compound, or ionic compound?
an atomic element, molecular element, molecular compound, or ionic compound?
Is 
 is an ionic compound because it is composed of a metal and a nonmetal.
is an ionic compound because it is composed of a metal and a nonmetal.

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Is  an atomic element, molecular element, molecular compound, or ionic compound?
an atomic element, molecular element, molecular compound, or ionic compound?
Is 
 is a molecular compound because it consists of a nonmetal connected to another nonmetal.
is a molecular compound because it consists of a nonmetal connected to another nonmetal.

Compare your answer with the correct one above
classifying compounds/elements
Is xenon an atomic element, molecular element, molecular compound, or ionic compound?
classifying compounds/elements
Is xenon an atomic element, molecular element, molecular compound, or ionic compound?
Xenon is an atomic element because its elemental form consists of one atom.
Xenon is an atomic element because its elemental form consists of one atom.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following molecules would you expect to have the highest boiling point?
Which of the following molecules would you expect to have the highest boiling point?
In order to answer this question correctly, you must remember the different types of intermolecular forces and their effects.
 only contains London dispersion forces. Since it is a smaller molecule compared to the others, it cannot have the highest boiling point.
only contains London dispersion forces. Since it is a smaller molecule compared to the others, it cannot have the highest boiling point.
 also only contains London dispersion forces. However, since it is a bigger molecule, it will have a higher boiling point than
also only contains London dispersion forces. However, since it is a bigger molecule, it will have a higher boiling point than  .
.
While  contains both London dispersion forces and dipole-dipole interactions, it lacks hydrogen boding as the fluorine atom is attached directly to the second carbon.
contains both London dispersion forces and dipole-dipole interactions, it lacks hydrogen boding as the fluorine atom is attached directly to the second carbon.
 has the highest boiling point because it contains London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole interactions, and hydrogen bonding.
has the highest boiling point because it contains London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole interactions, and hydrogen bonding.
In order to answer this question correctly, you must remember the different types of intermolecular forces and their effects.



While 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which molecule will not form hydrogen bonds?
Which molecule will not form hydrogen bonds?
A hydrogen bond refers to the attraction between a hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of another molecule. The atoms which commonly form hydrogen bonds are oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine, which are very electronegative. When a hydrogen bond forms between hydrogen and one of these three atoms, hydrogen gains a partial positive charge while the electronegative atom gains a partial negative charge. Carbon is not a very electronegative atom and thus cannot form a hydrogen bond.
A hydrogen bond refers to the attraction between a hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of another molecule. The atoms which commonly form hydrogen bonds are oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine, which are very electronegative. When a hydrogen bond forms between hydrogen and one of these three atoms, hydrogen gains a partial positive charge while the electronegative atom gains a partial negative charge. Carbon is not a very electronegative atom and thus cannot form a hydrogen bond.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Three types of intermolecular forces include: hydrogen bonding, London dispersion forces, and dipole-dipole interactions. Which of these is the strongest intermolecular force?
Three types of intermolecular forces include: hydrogen bonding, London dispersion forces, and dipole-dipole interactions. Which of these is the strongest intermolecular force?
London dispersion forces are the weakest of the three. Every molecule is composed of electrons, which are free to move around. This can create a temporary charge, on any molecule, at any time. When two molecules come close together, their varying charges can orient such that one end of a molecule may be slightly positive, while the end of a nearby molecule may be slightly negative. This leads to a slight attraction between the two molecules, called London dispersion forces until they move around again. This is a weak, temporary force.
Dipole-dipole interactions develop when polar compounds line up and are attracted to each other. These forces are stronger than London dispersion forces due to the permanency of the dipoles, but weaker than hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen bonds are the strongest force of the three. The name refers to the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to one electronegative atom (usually oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) and an electronegative atom of a different molecule. The electronegative atom gains a partial negative charge, while the hydrogen gains a partial positive charge. These forces are responsible for many of the qualities of water.
London dispersion forces are the weakest of the three. Every molecule is composed of electrons, which are free to move around. This can create a temporary charge, on any molecule, at any time. When two molecules come close together, their varying charges can orient such that one end of a molecule may be slightly positive, while the end of a nearby molecule may be slightly negative. This leads to a slight attraction between the two molecules, called London dispersion forces until they move around again. This is a weak, temporary force.
Dipole-dipole interactions develop when polar compounds line up and are attracted to each other. These forces are stronger than London dispersion forces due to the permanency of the dipoles, but weaker than hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen bonds are the strongest force of the three. The name refers to the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to one electronegative atom (usually oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) and an electronegative atom of a different molecule. The electronegative atom gains a partial negative charge, while the hydrogen gains a partial positive charge. These forces are responsible for many of the qualities of water.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following C-N bonds is the shortest?
Which of the following C-N bonds is the shortest?
Drawing the Lewis Diagrams for these molecules reveals that the C-N bond in  is a triple covalent bond, whereas the C-N bonds in
is a triple covalent bond, whereas the C-N bonds in  and
and  are double covalent bonds and the C-N bond in
are double covalent bonds and the C-N bond in  is a single covalent bond. Triple covalent bonds between two given atoms are always stronger than double bonds between these same two atoms, and similarly double bonds are even stronger than single bonds. Bond length is inversely related to bond strength; therefore a shorter bond is a stronger bond, and triple covalent bonds are shorter than either double or single covalent bonds. Thus, the C-N bond in
is a single covalent bond. Triple covalent bonds between two given atoms are always stronger than double bonds between these same two atoms, and similarly double bonds are even stronger than single bonds. Bond length is inversely related to bond strength; therefore a shorter bond is a stronger bond, and triple covalent bonds are shorter than either double or single covalent bonds. Thus, the C-N bond in  is the shortest in length.
is the shortest in length.
Drawing the Lewis Diagrams for these molecules reveals that the C-N bond in 




Compare your answer with the correct one above




