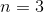Reactions by Product
Help Questions
Organic Chemistry › Reactions by Product

What is the value of 
Explanation
Huckel's rule states that an aromatic compound must have 
If 4n+2=18, then n=4.

What is the value of 
Explanation
Huckel's rule states that an aromatic compound must have 
If 4n+2=18, then n=4.

What is the value of 
Explanation
Huckel's rule states that an aromatic compound must have 
If 4n+2=18, then n=4.

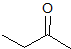
What is the product of the given reaction?




Explanation
The hydrolyzation of a nitrile with hydronium leads to a carboxylic acid. Only one choice is a carboxylic acid.

What is the product of the given reaction?





Explanation
The hydrolyzation of a nitrile with hydronium leads to a carboxylic acid. Only one choice is a carboxylic acid.

What is the product of the given reaction?





Explanation
The hydrolyzation of a nitrile with hydronium leads to a carboxylic acid. Only one choice is a carboxylic acid.

What is the product of the given reaction?





Explanation
This question tests knowledge on carboxylic acid derivatives and the formation of the carboxylic acid derivatives. 




What is the product of the given reaction?





Explanation
This question tests knowledge on carboxylic acid derivatives and the formation of the carboxylic acid derivatives. 




What is the product of the given reaction?





Explanation
This question tests knowledge on carboxylic acid derivatives and the formation of the carboxylic acid derivatives. 



What is the product of a hydroboration–oxidation reaction with 1-hexylcyclohexene?
2-hexylcyclohexanol
1-hexylcyclohexanol
3-hexylcyclohexanol
Hexylcyclohexane
Cyclohexane
Explanation
This reaction is an electrophilic addition reaction with an alkene. This is one of many alkene addition reactions that can add an -OH group onto your starting material. The key aspect of an hydroboration-oxidation reaction is the anti-Markovinikov addition to the double bond. The -OH group should be on the least substituted of the two carbons that originate from the double bond. In light of this information, the answer is 2-cyclohexanol.