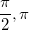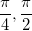Angles in the Unit Circle
Help Questions
Trigonometry › Angles in the Unit Circle
Give the exact value.
Consider the unit circle. What is the value of the given trigonometric function?
Explanation
Use the unit circle to locate the following:
Recall that the 
Since the tangent is equal to the sine divided by the cosine, we need to find the following:
Now, we will use this information to solve the problem.
Substitute the calculated values:
Solve. Remember that dividing by a fraction is the same as multiplying by its reciprocal.
What are the ways to write 360o and 720o in radians?
Explanation


Which of the following is not an angle in the unit circle?
Explanation
The unit circle is in two increments: 






What is the equivalent of 
Explanation
To convert from degrees to radians, use the equality


From here we use 
What is the value of 
Explanation
To help with this one, draw a 45-45-90 triangle. With legs equal to 1 and a hypotenuse of 
Then, use the definition of tangent as opposite over adjacent to find the value.
Since the legs are congruent, we get that the ratio is 1.
What is 
Explanation
Recall that on the unit circle, sine represents the y coordinate of the unit circle.
Then, since we are at 90˚, we are at the positive y axis, the point (0,1).
At this point on the unit circle, the y value is 1.
Thus 
Which of the following is NOT a special angle on the unit circle?
Explanation
For an angle to be considered a special angle, the angle must be able to produce a 

The only angle that is not capable of the special angles formation is 
If 


The solution does not lie in the given interval.
Explanation
We first make the substitution 
In the interval 


Solving for 

What is the value of 
Explanation
From the unit circle, the value of

This can be found using the coordinate pair associated with the angle 

Recall that the 

What is

using the unit circle?
Explanation
Recall that the unit circle can be broken down into four quadrants. Each quadrant has similar coordinate pairs basic on the angle. The only difference between the actual coordinate pairs is the sign on them. In quadrant I all signs are positive. In quadrant II only sine and cosecant are positive. In quadrant III tangent and cotangent are positive and quadrant IV only cosine and secant are positive.



From the unit circle, the coordinate point of