How to find the length of the side of a right triangle
Help Questions
SSAT Upper Level Quantitative › How to find the length of the side of a right triangle
A right triangle has a hypotenuse of 

Explanation
When calculating the lengths of sides of a right triangle, we can use the Pythagorean Theorem as follows:




Plugging in our given values:
Subtracting 
Taking the square root of each side of the equation:
Simplifying the square root:
A right triangle has a leg of length 

Explanation
When calculating the lengths of sides of a right triangle, we can use the Pythagorean Theorem as follows:




Plugging in our given values:
Subtracting 
Find the length of the missing side.

Explanation
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the missing side.
A right triangle has two legs of length 

Explanation
When calculating the lengths of sides of a right triangle, we can use the Pythagorean Theorem as follows:




Plugging in our given values:
Find the length of the missing side.

Explanation
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the missing side.
Find the length of the missing side.

Explanation
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the missing side.
Find the length of the missing side.

Explanation
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the missing side.
Find the length of the missing side.

Explanation
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the missing side.
Find the length of the missing side.
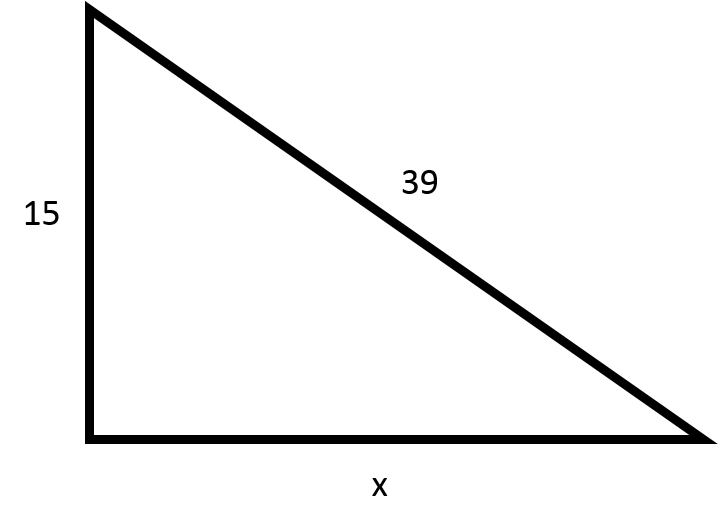
Explanation
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the missing side.
Find the length of the missing side.

Explanation
Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the missing side.



























































































