pH
Help Questions
AP Chemistry › pH
Determine the pH of a solution that is 
Explanation
Since 

Thus, ![[H_3O^+]=0.40M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668813/gif.latex)
Recall how to find the pH of a solution:
Plug in the given hydronium ion concentration to find the pH of the given solution.
Remember to maintain the correct number of significant figures.
What is the pH of a solution with \[OH-\] = 4 X 10-6
8.6
6
4
2.2
12.1
Explanation
\[OH-\] = 4 X 10-6
pOH = 5.4 — use –log \[OH–\] to find pOH
pH = 14– pOH = 8.6
Find the pH of a 0.1M solution of hydrogen cyanide.
Explanation
Hydrogen cyanide will dissociate according to the following reaction.
Hydrogen cyanide is a weak acid, meaning that it will not dissociate completely in solution. We need to use the acid dissociation constant in order to determine the concentration of protons in solution at equilibrium. We can solve for this value using an ICE table.
I. The initial concentration for the acid of 0.1M. There are no protons or cyanide ions in the solution initially, so they both have concentrations of 0.0M.
C. The concentration of both ions will increase by an unknown amount, 

E. Write the equilibrium expression and compare it to the dissociation constant.
The value of 
From our set up, we know that the value of 
Find the pH of a solution that is 

Explanation
Start by assuming that there is 
Next, find the mass of 
Now, find the number of moles of 
Since we initially assumed that we had 

Since 

Recall how to find the pH of a solution.
What is the pH of a soution containing .0001 M HCl?
4
5
6
3
7
Explanation
The pH of a solution is determined by taking the negative log of the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. HCl is strong acid so it completely dissociates in solution. So adding .0001 M HCl is the same as saying that 1 *10-4 moles of H+ ions have been added to solution. The -log\[.0001\] =4, so the pH of the solution =4.
Which of the following solutions contains the greatest number of H+ ions?
0.010 mL of HCl in excess water
0.010 mL of CH3OH in excess water
0.010 mL of KOH in excess water
1.0 mL of NaCl in excess water
5 mL of NaOH
Explanation
This question asks for the solution with the greatest number H+ ions, we can also approach this problem as if we are looking for the solution with the lowest pH. HCl is strong acid, therefore it will dissociate completely in solution. So the solution containing 0.010 mL of HCL contains 0.010 mL of H+ ions in solution, in addition to the H+ ions that are already in solution due to the auto-ionization of water. The only other solution that could have a pH less than 7 would be the one with 0.010 mL of CH3OH in excess water, becasue CH3OH is very slightly acidic. But since it is compared with an equal volume of HCl which is strong acid, it can be said that the most H+ ions will be found in the solution containing a small amount of strong acid, HCl.
What is the range of possible hydrogen ion concentrations in acidic solution?
1 to 7
10–1 to 10–6.999
10–13 to 10–7.001
13 to 14
7
Explanation
For a solution to be acidic, it must have a pH between 1 and 6.99, since 7 is neutral; pH is –log(hydrogen ion concentration), the range of possible values is between 10–1 and 10–6.999.
A chemist adds 

13.18
0.8248
14.0
0
7.00
Explanation
First, we will calculate ![[KOH]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/21614/gif.latex)
Now we will calculate the pOH:
In solution 
![[KOH]=[OH^-]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/21618/gif.latex)
Sodium hydroxide is a strong base. What is the pH of a 0.02M sodium hydroxide solution?
Explanation
Since sodium hydroxide is a strong base, it will dissociate completely in water. This means that the concentration of the base will be equal to the concentration of hydroxide ions after the reaction runs to completion.
We can find the concentration of hydroxide ions via stoichiometry. One hydroxide ion is created from each molecule of sodium hydroxide that dissociates.
Since we have the concentration of hydroxide ions, we can solve for the pOH of the solution.
The question asks us to find the pH of the solution, so we will need to convert pOH to pH. To do so, we simply subtract the pOH from 14.
The pH of the solution is 12.3. Because sodium hydroxide is a strong base, it makes sense that the pH is above 7.
Which two solutions, when combined in equal amounts, will produce the lowest pH?
1.0M HCl and 1.0M NaCl
2.0M HCl and 2.0M KOH
0.5M acetic acid and 1.0M NaCl
2.5M NH3 and 2.5M NH4+
Explanation
HCl is a strong acid, while NaCl is a salt. Mixing these two will result in a pH < 1.
As for the other choices, mixing 2.0M HCl and 2.0M KOH will result in the formation of KCl and H2O, resulting in a neutral pH. Acetic acid (pKa= 4.76) is a weak acid, so it will have a pH less than 7 but greater than 1. Finally, NH3 and NH4+ is a buffer system between a weak base and weak acid, and if equal amounts are present, the pH will be the same as the pKa of NH4+, which is around 9.
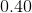



![\text{pH}=-\log([H_3O^+])](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668814/gif.latex)







![\small K_{a} = \frac{[H^{+}][CN^{-}]}{[HCN]} = 6.2*10^{-10}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/94683/gif.latex)
![\small \frac{[x][x]}{[0.1-x]} = 6.2*10^{-10}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/118062/gif.latex)
![\frac{[x][x]}{0.1}=6.2*10^{-10}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/110653/gif.latex)


![pH=-\log{[H^+]}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/118064/gif.latex)









![[\text{HI}]=0.3995M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668687/gif.latex)
![[\text{HI}]=[H_3O^+]=0.3995M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668690/gif.latex)
![\text{pH}=-\log([H_3O^+])](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668691/gif.latex)


![pOH=-log[OH^-]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/21616/gif.latex)
![pOH=-log[1.497\times 10^{-1}]=8.248\times 10^{-1}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/21619/gif.latex)







![\small pOH = -\log[OH^{-}]=-\log(0.02)](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/94697/gif.latex)


