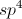Reactions by Reactant
Help Questions
Organic Chemistry › Reactions by Reactant

What is the product of the given reaction?




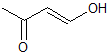
Explanation
This is a basic Claisen condensation reaction in which the 
 .
.
The attack at the ester carbonyl leads to the leaving of 

What is the product of the given reaction?





Explanation
This is a basic Claisen condensation reaction in which the 
 .
.
The attack at the ester carbonyl leads to the leaving of 

What is the product of the given reaction?





Explanation
This is a basic Claisen condensation reaction in which the 
 .
.
The attack at the ester carbonyl leads to the leaving of 
What is the product of the following reaction?


II and III
II only
I and II
IV only
Explanation
Treatment of ethyl acetate with methoxide will yield the enolate ion (II). However, side trans-esterification reactions will also result in formation of product III.
What is the product of the following reaction?


II and III
II only
I and II
IV only
Explanation
Treatment of ethyl acetate with methoxide will yield the enolate ion (II). However, side trans-esterification reactions will also result in formation of product III.
Predict the major product of the following reaction.

I
II
III
IV
Explanation
Alkenes are saturated by hydrogen gas in the presence of a palladium catalyst. This type of reaction is termed catalytic hydrogenation and results in syn addition of hydrogen across a double bond. Molecules II, III, and IV have all undergone oxidation-reduction reactions and do not result from the given conditions. Molecule I is altered only by hydrogenation of the 2-3 double bond and is the correct answer.
What is the product of the following reaction?


II and III
II only
I and II
IV only
Explanation
Treatment of ethyl acetate with methoxide will yield the enolate ion (II). However, side trans-esterification reactions will also result in formation of product III.
Predict the major product of the following reaction.

I
II
III
IV
Explanation
Alkenes are saturated by hydrogen gas in the presence of a palladium catalyst. This type of reaction is termed catalytic hydrogenation and results in syn addition of hydrogen across a double bond. Molecules II, III, and IV have all undergone oxidation-reduction reactions and do not result from the given conditions. Molecule I is altered only by hydrogenation of the 2-3 double bond and is the correct answer.
Predict the major product of the following reaction.

I
II
III
IV
Explanation
Alkenes are saturated by hydrogen gas in the presence of a palladium catalyst. This type of reaction is termed catalytic hydrogenation and results in syn addition of hydrogen across a double bond. Molecules II, III, and IV have all undergone oxidation-reduction reactions and do not result from the given conditions. Molecule I is altered only by hydrogenation of the 2-3 double bond and is the correct answer.
The compound below is reacted with 

Explanation
The initially chiral carbon has an