Inheritance Patterns
Help Questions
Biology › Inheritance Patterns
The eye color brown is superior to blue. Linda has brown eyes and marries someone with blue eyes. Linda's father has blue eyes and her mother is homozygous dominant. What is the percent chance of Linda's children having blue eyes?
0.50
1.0
0.25
0.75
Explanation
Linda's mother has brown eyes: BB
Linda's father has blue eyes: bb
Using the pedigree (BB x bb), Linda has to be Bb (100%). Linda is marrying someone with blue eyes (bb). Doing the pedigree of Linda (Bb) and her partner (bb) gives you 0.50 Bb (brown eyes) and 0.50 bb (blue eyes).
The eye color brown is superior to blue. Linda has brown eyes and marries someone with blue eyes. Linda's father has blue eyes and her mother is homozygous dominant. What is the percent chance of Linda's children having blue eyes?
0.50
1.0
0.25
0.75
Explanation
Linda's mother has brown eyes: BB
Linda's father has blue eyes: bb
Using the pedigree (BB x bb), Linda has to be Bb (100%). Linda is marrying someone with blue eyes (bb). Doing the pedigree of Linda (Bb) and her partner (bb) gives you 0.50 Bb (brown eyes) and 0.50 bb (blue eyes).
Sharon has blonde hair. Her husband is heterozygous for brown hair, with brown being the dominant autosomal trait. What percent chance will their daughter have blonde hair?
50%
100%
25%
75%
0%
Explanation
The genotype for Sharon is rr, because blonde is a recessive trait therefore in order to have blonde hair she must be homozygous recessive. Her husband is Rr, because it states that he has brown hair, which is dominant, in addition to being heterozygous. When drawing out a punnet square, you will find the offspring will be Rr, Rr, rr and rr. Therefore, their daughter has 50% chance of having brown hair and 50% chance of having blonde hair.
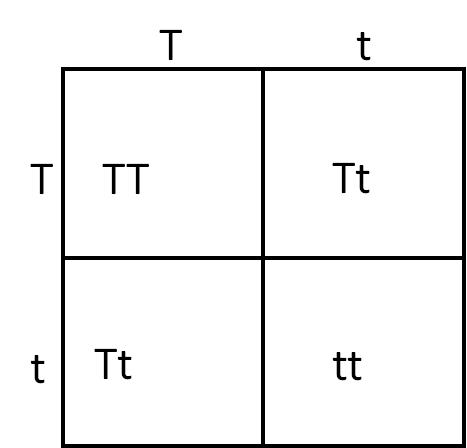
The trait "tall" is dominant (T) while "short" is recessive (t). If two parents are both heterozygous for the trait and have a child, what is the probability that the child would be phenotypically short?
Explanation
The problem can be solved using the following Punnett square. Since short is recessive, the only genotype that will result in a short appearance is tt. tt occurs one time on the Punnett square, out of four possible combinations; therefore, there is a 1-in-4 chance of giving birth to a short child, or 25%.
The trait "tall" is dominant (T) while "short" is recessive (t). If two parents are both heterozygous for the trait and have a child, what is the probability that the child would be phenotypically short?
Explanation
The problem can be solved using the following Punnett square. Since short is recessive, the only genotype that will result in a short appearance is tt. tt occurs one time on the Punnett square, out of four possible combinations; therefore, there is a 1-in-4 chance of giving birth to a short child, or 25%.
Sharon has blonde hair. Her husband is heterozygous for brown hair, with brown being the dominant autosomal trait. What percent chance will their daughter have blonde hair?
50%
100%
25%
75%
0%
Explanation
The genotype for Sharon is rr, because blonde is a recessive trait therefore in order to have blonde hair she must be homozygous recessive. Her husband is Rr, because it states that he has brown hair, which is dominant, in addition to being heterozygous. When drawing out a punnet square, you will find the offspring will be Rr, Rr, rr and rr. Therefore, their daughter has 50% chance of having brown hair and 50% chance of having blonde hair.
A collection of an individual’s genes—inherited alleles—is defined as which of the following?
Genotype
Phenotype
Locus of alleles
Morphology
Explanation
Genotype is defined as the sequence of genetic makeup that determines specific characteristics and traits—phenotypes—of an individual. The genome is defined as the collection of an individual’s genes and consists of DNA. A genotype is expressed when information in DNA makes RNA and protein molecules, which determine the structure and function of cells; however, a genotype can also refer to genes carried by an individual, which includes mutations. Last, phenotype refers to observable physical characteristics within an individual. Some phenotypical traits are determined by the genotype, while others are shaped by environmental factors.
A collection of an individual’s genes—inherited alleles—is defined as which of the following?
Genotype
Phenotype
Locus of alleles
Morphology
Explanation
Genotype is defined as the sequence of genetic makeup that determines specific characteristics and traits—phenotypes—of an individual. The genome is defined as the collection of an individual’s genes and consists of DNA. A genotype is expressed when information in DNA makes RNA and protein molecules, which determine the structure and function of cells; however, a genotype can also refer to genes carried by an individual, which includes mutations. Last, phenotype refers to observable physical characteristics within an individual. Some phenotypical traits are determined by the genotype, while others are shaped by environmental factors.
Consider a rare plant that exhibits the phenotype of dark blue leaves (BB) as its dominant trait and and light blue leaves (bb) as its recessive trait. It flowers a bright yellow flower (YY) when dominant, and an orange flower (yy) when recessive.
When two dihybrid plants of the same species are crossed, what will be the expected phenotypic ratio of offspring that exhibit light blue leaves and yellow flowers?
3:16
1:2
1:4
5:16
1:8
Explanation

Once you properly set up your punnet square of a dihybrid cross, you should obtain a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1. There will be 9 plants with dark blue leaves/yellow flowers, 3 plants with light blue leaves/yellow flowers, 3 plants with dark blue leaves/orange flowers, and 1 plant with light blue leaves/orange flowers.
Consider a rare plant that exhibits the phenotype of dark blue leaves (BB) as its dominant trait and and light blue leaves (bb) as its recessive trait. It flowers a bright yellow flower (YY) when dominant, and an orange flower (yy) when recessive.
When two dihybrid plants of the same species are crossed, what will be the expected phenotypic ratio of offspring that exhibit light blue leaves and yellow flowers?
3:16
1:2
1:4
5:16
1:8
Explanation

Once you properly set up your punnet square of a dihybrid cross, you should obtain a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1. There will be 9 plants with dark blue leaves/yellow flowers, 3 plants with light blue leaves/yellow flowers, 3 plants with dark blue leaves/orange flowers, and 1 plant with light blue leaves/orange flowers.