Genetics and Evolution
Help Questions
Biology › Genetics and Evolution
How did Darwin's finches help support his theory of evolution?
The size and shape of their beaks varied, allowing them to consume a greater variety of food sources
The finches all lived on different islands in order to survive
Only the largest birds had survived on the island, while the smaller ones went extinct
The birds were different colors, which allowed for camouflage in different habitats
Explanation
Darwin's finches were distinct from one another due to the size and shape of their beaks. Darwin noted that these distinct beaks allowed the different birds to eat specific food groups. The varying food groups allowed the animals to coexist in the same habitat, without resorting to competing for natural food resources. Each species had evolved to occupy a unique ecological niche in order to survive with minimal competition for resources.
The eye color brown is superior to blue. Linda has brown eyes and marries someone with blue eyes. Linda's father has blue eyes and her mother is homozygous dominant. What is the percent chance of Linda's children having blue eyes?
0.50
1.0
0.25
0.75
Explanation
Linda's mother has brown eyes: BB
Linda's father has blue eyes: bb
Using the pedigree (BB x bb), Linda has to be Bb (100%). Linda is marrying someone with blue eyes (bb). Doing the pedigree of Linda (Bb) and her partner (bb) gives you 0.50 Bb (brown eyes) and 0.50 bb (blue eyes).
The eye color brown is superior to blue. Linda has brown eyes and marries someone with blue eyes. Linda's father has blue eyes and her mother is homozygous dominant. What is the percent chance of Linda's children having blue eyes?
0.50
1.0
0.25
0.75
Explanation
Linda's mother has brown eyes: BB
Linda's father has blue eyes: bb
Using the pedigree (BB x bb), Linda has to be Bb (100%). Linda is marrying someone with blue eyes (bb). Doing the pedigree of Linda (Bb) and her partner (bb) gives you 0.50 Bb (brown eyes) and 0.50 bb (blue eyes).
The eye color brown is superior to blue. Linda has brown eyes and marries someone with blue eyes. Linda's father has blue eyes and her mother is homozygous dominant. What is the percent chance of Linda's children having blue eyes?
0.50
1.0
0.25
0.75
Explanation
Linda's mother has brown eyes: BB
Linda's father has blue eyes: bb
Using the pedigree (BB x bb), Linda has to be Bb (100%). Linda is marrying someone with blue eyes (bb). Doing the pedigree of Linda (Bb) and her partner (bb) gives you 0.50 Bb (brown eyes) and 0.50 bb (blue eyes).
Sharon has blonde hair. Her husband is heterozygous for brown hair, with brown being the dominant autosomal trait. What percent chance will their daughter have blonde hair?
50%
100%
25%
75%
0%
Explanation
The genotype for Sharon is rr, because blonde is a recessive trait therefore in order to have blonde hair she must be homozygous recessive. Her husband is Rr, because it states that he has brown hair, which is dominant, in addition to being heterozygous. When drawing out a punnet square, you will find the offspring will be Rr, Rr, rr and rr. Therefore, their daughter has 50% chance of having brown hair and 50% chance of having blonde hair.
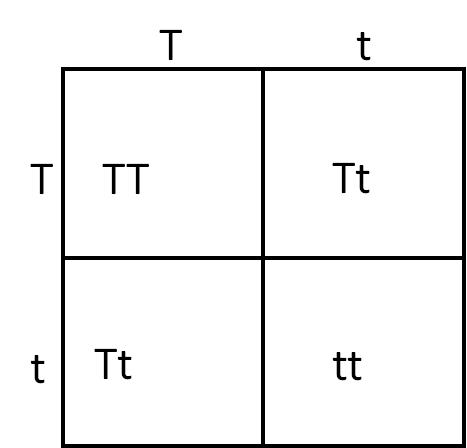
The trait "tall" is dominant (T) while "short" is recessive (t). If two parents are both heterozygous for the trait and have a child, what is the probability that the child would be phenotypically short?
Explanation
The problem can be solved using the following Punnett square. Since short is recessive, the only genotype that will result in a short appearance is tt. tt occurs one time on the Punnett square, out of four possible combinations; therefore, there is a 1-in-4 chance of giving birth to a short child, or 25%.
The central dogma of molecular biology is the method by which cells transfer nucleic acids into functional molecules. Which of the following depicts the central dogma of molecular biology?
Explanation
The central dogma of molecular biology states that DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into protein.
The trait "tall" is dominant (T) while "short" is recessive (t). If two parents are both heterozygous for the trait and have a child, what is the probability that the child would be phenotypically short?
Explanation
The problem can be solved using the following Punnett square. Since short is recessive, the only genotype that will result in a short appearance is tt. tt occurs one time on the Punnett square, out of four possible combinations; therefore, there is a 1-in-4 chance of giving birth to a short child, or 25%.
Sharon has blonde hair. Her husband is heterozygous for brown hair, with brown being the dominant autosomal trait. What percent chance will their daughter have blonde hair?
50%
100%
25%
75%
0%
Explanation
The genotype for Sharon is rr, because blonde is a recessive trait therefore in order to have blonde hair she must be homozygous recessive. Her husband is Rr, because it states that he has brown hair, which is dominant, in addition to being heterozygous. When drawing out a punnet square, you will find the offspring will be Rr, Rr, rr and rr. Therefore, their daughter has 50% chance of having brown hair and 50% chance of having blonde hair.
The central dogma of molecular biology is the method by which cells transfer nucleic acids into functional molecules. Which of the following depicts the central dogma of molecular biology?
Explanation
The central dogma of molecular biology states that DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into protein.