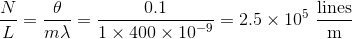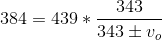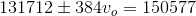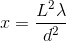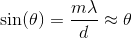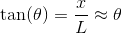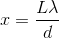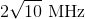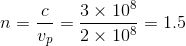Waves
Help Questions
GRE Subject Test: Physics › Waves
A beam of light, with wavelength 

Explanation
The equation describing maxima of a diffraction grating is:
Where d is the separation of slits, which can also be expressed as:
Substituting d into the first equation and making the small angle approximation, one can solve for 
Note that the angle had to be converted from degrees to radians. Finally, the question asks for lines per centimeter, not meter, so the answer becomes 
A beam of light, with wavelength 

Explanation
The equation describing maxima of a diffraction grating is:
Where d is the separation of slits, which can also be expressed as:
Substituting d into the first equation and making the small angle approximation, one can solve for 
Note that the angle had to be converted from degrees to radians. Finally, the question asks for lines per centimeter, not meter, so the answer becomes 
A car's horn has a frequency of 

Explanation
The equation for the Doppler effect with frequency for a moving source is given by:
Where 



A double slit experiment is set up with the following parameters: two slits are a separated by a distance 




Explanation
The condition for constructive interference with double slit diffraction is given by:
Where 
Solving for the angle and using the small angle approximation, we get;
The distance 
Again, with the help of the small angle approximation. Setting the two thetas equal to each other and solving for 
For the central band, 


A double slit experiment is set up with the following parameters: two slits are a separated by a distance 




Explanation
The condition for constructive interference with double slit diffraction is given by:
Where 
Solving for the angle and using the small angle approximation, we get;
The distance 
Again, with the help of the small angle approximation. Setting the two thetas equal to each other and solving for 
For the central band, 


A car's horn has a frequency of 

Explanation
The equation for the Doppler effect with frequency for a moving source is given by:
Where 



Two waves with frequencies: 
Explanation
The beat from two combined sound waves is:
A monochromatic beam of 

Explanation
The phase velocity of light through a medium with refractive index 
Solving this for 

Two waves with frequencies: 
Explanation
The beat from two combined sound waves is:
A monochromatic beam of 

Explanation
The phase velocity of light through a medium with refractive index 
Solving this for